Preparation method of litsea cubeba mesophyll cell protoplast
A technology of protoplasts and litsea cubeba leaves, which is applied in the field of plant cell protoplast preparation, can solve the problems of litsea cubeba protoplast separation failure and poisoning of protoplasts, shorten the time required for enzymatic hydrolysis, promote development, and maintain normal morphology Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The preparation of embodiment 1 litsea cubeba mesophyll cell protoplast
[0028] The preparation method of litsea cubeba mesophyll cell protoplast comprises the following steps:
[0029] Step 1. Material selection: In mid-May 2019, mature leaves of litsea cubeba with good growth and no pests and diseases were collected in Shending Mountain, Miluo City, Hunan Province, and the collected leaves were sterilized with 0.1% mercury chloride solution for 3 minutes to obtain no Litsea cubeba leaves, set aside;
[0030] Step 2. Leaf enzymatic hydrolysis
[0031] Use a sterile scalpel to cut the sterilized litsea cubeba leaves into strips with a width of 1mm, take 0.1g of the pieces and place them in 3ml of enzymatic hydrolysis solution, and let them stand in the dark Enzymolysis for 6 hours; the enzymolysis solution contains the following final concentrations of each component: 10g / l cellulase R-10, 10g / l isolated enzyme R-10, 91g / l mannitol, 0.1g / l sodium dihydrogen phosphate...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The preparation of embodiment 2 litsea cubeba mesophyll cell protoplast
[0045] The preparation method of litsea cubeba mesophyll cell protoplast comprises the following steps:
[0046] Step 1, material selection: tissue culture test-tube plantlets have the advantage of being sterile and can be obtained throughout the year. Therefore, the present embodiment uses the young leaves of litsea cubeba aseptic test-tube plantlets with a seedling height of about 3cm as material to obtain aseptic litsea cubeba. Cotyledons, to be used;
[0047] Step 2. Leaf enzymatic hydrolysis
[0048] Use a sterile scalpel to cut the sterilized leaves of Litsea Cubeba into strips with a width of 2 mm, take 0.3 g of the leaves and place them in 5 ml of enzymatic hydrolysis solution, and let them stand in the dark Enzymolysis for 12 hours; the enzymolysis solution contains the following final concentrations of each component: 20g / l cellulase R-10, 20g / l isolated enzyme R-10, 128g / l mannitol, 0...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Influence of different enzymatic hydrolysis solutions on the separation effect of protoplasts when preparing litsea cubeba mesophyll cell protoplasts in embodiment 3
[0057] 1. Effects of different concentrations of vitamin C, Tween 80 and PEG 4000 on the separation of protoplasts from litsea cubeba mesophyll cells
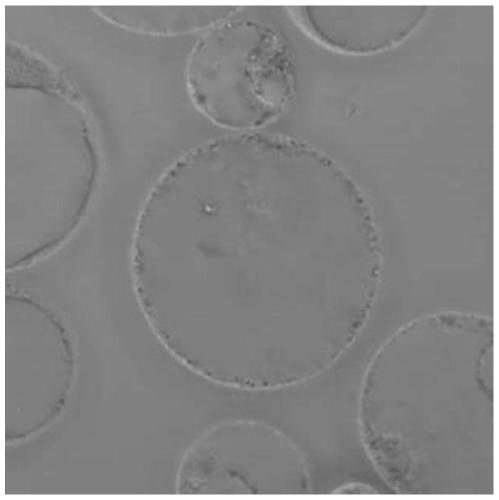
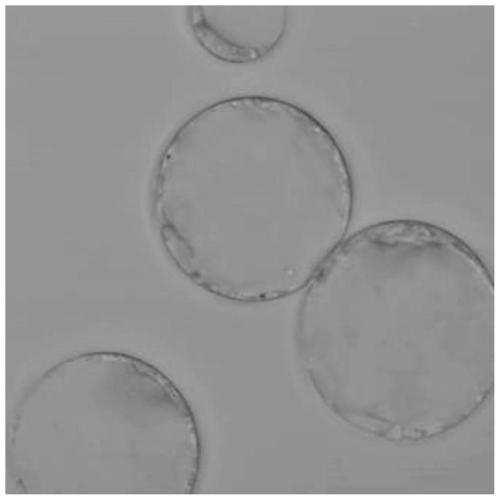
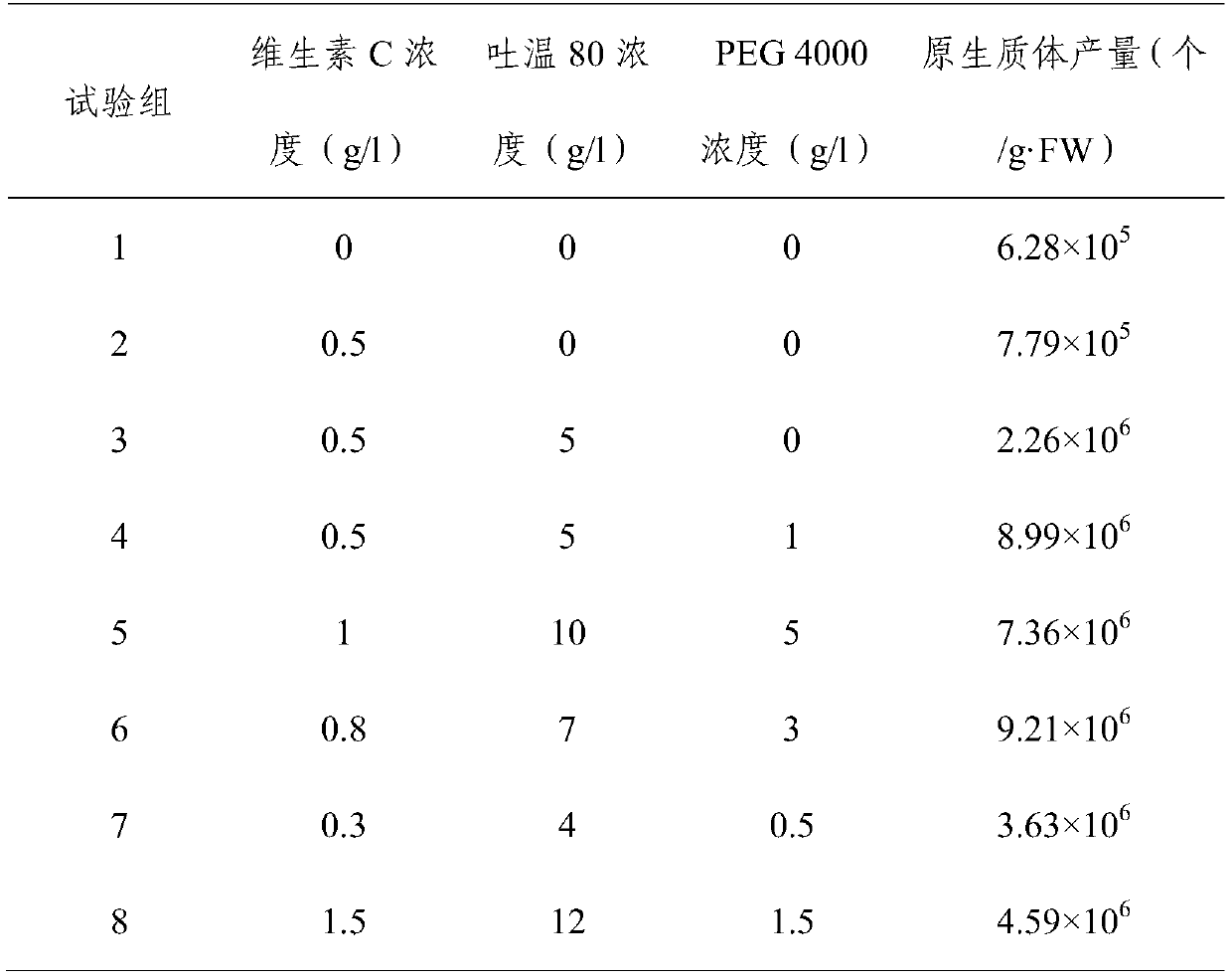
[0058] In step 2 of Example 1, vitamin C, Tween 80 and PEG 4000 were adjusted in different concentrations to obtain protoplast cells. The morphology of protoplast cells was observed and counted under a microscope. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0059] Table 1 Effects of different concentrations of vitamin C, Tween 80 and PEG 4000 on protoplast production of litsea cubeba mesophyll cells
[0060]
[0061] As can be seen from the above table 1, the number of protoplasts prepared from test group 1 to test group 3 was significantly lower than that of test group 4 to test group 8, which indicated that a certain proportion of vitamin C and PEG 4000 were ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com