A method and application of Monascus purple bacterium and its co-fermentation to produce lovastatin
A technology of Monascus purple bacteria and strains, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., can solve problems such as few reports, achieve the effect of improving color, increasing product value, and improving fermentation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
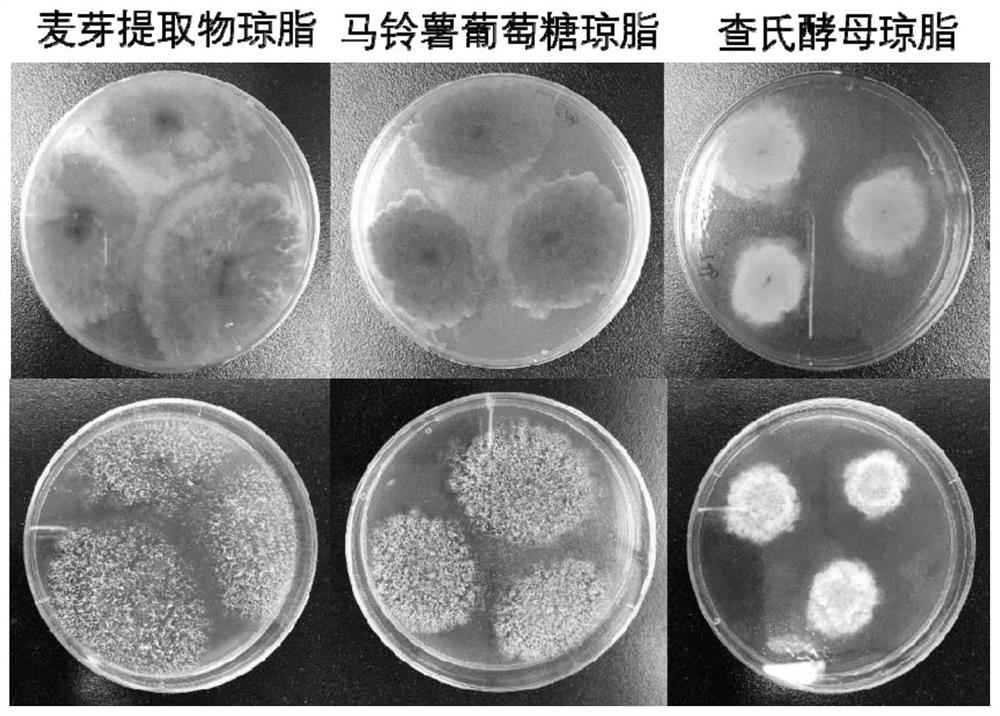
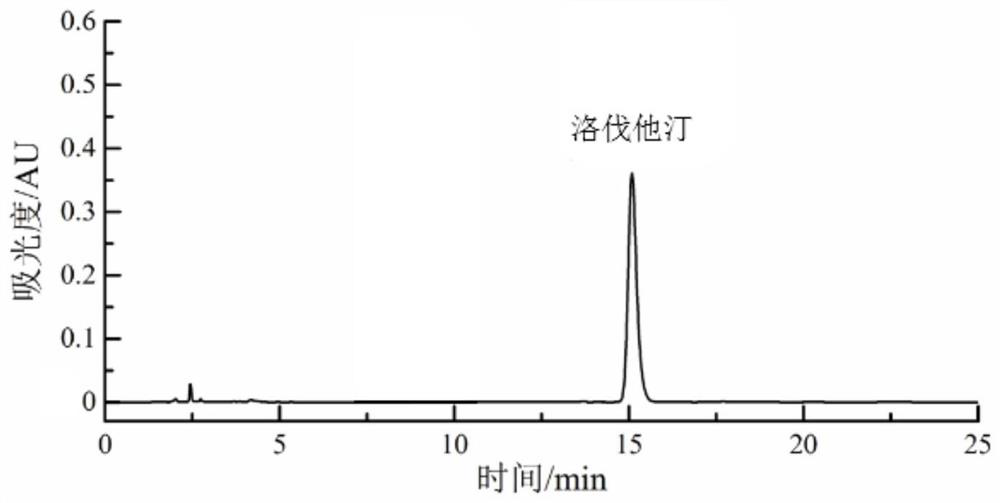
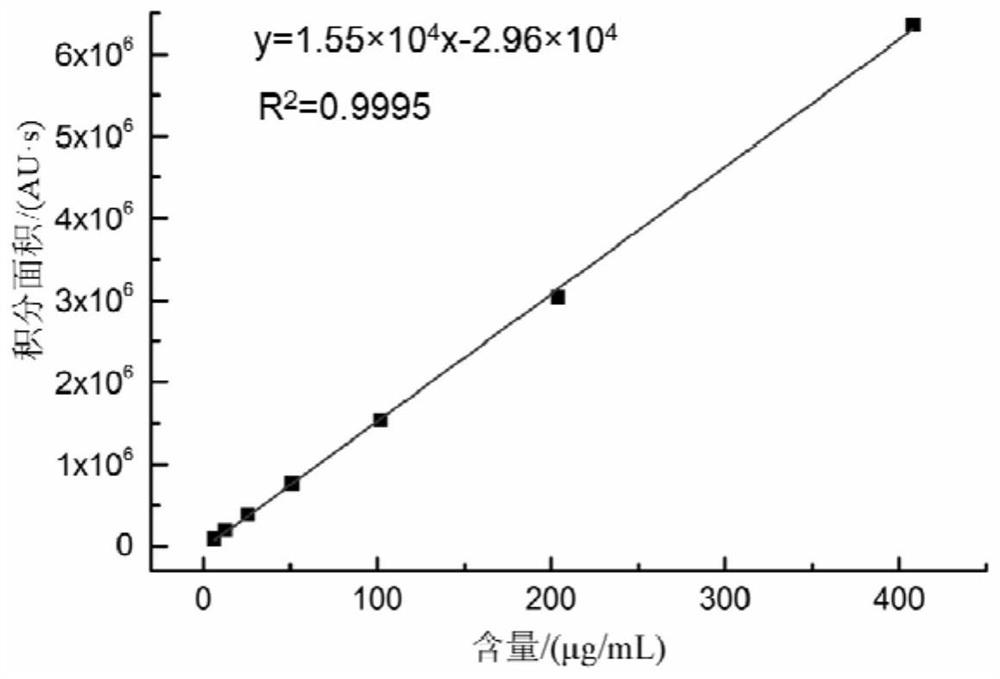
[0033] Example 1: Screening and identification of high-yield lovastatin strains in red yeast rice
[0034] Step 1, sample collection and processing:
[0035] Red yeast rice was collected from Gutian County, Ningde City, Fujian Province, and the collected red yeast rice was stored in sealed sterile plastic bags at 4°C. Weigh 5 g of red yeast rice, grind it into powder in a sterile mortar, place it in a 95 mL Erlenmeyer flask of sterile saline with glass beads, and shake it on a shaker for 30 min. followed by serial dilution.
[0036] PDA medium: 200 grams of potatoes, 20 grams of glucose, 15-20 grams of agar, 1000 ml of distilled water, natural pH, sterilized at 121°C for 15 minutes.
[0037] Step 2, screening of strains:
[0038] Under the aseptic operating environment, shake the Erlenmeyer flask evenly, draw 5mL of bacterial suspension from it and perform serial gradient dilution with sterile water to obtain 10 -2 、10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 、10 -7 times sample dilue...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: co-fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Monascus to prepare Monascus starter
[0050] Preparation of starter cultures containing Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Monascus. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae CCTCC NO:M 2015119 has been disclosed in the patent with publication number CN104911116B.
[0051] Saccharomyces cerevisiae CCTCC NO:M 2015119 was inoculated into potato dextrose water liquid medium, and cultured at 28±2°C for 24-32 hours to obtain the fermentation broth.
[0052] Use the sterile inoculation loop to scrape the Monascus strains in the preservation tube and streak them on the wort slope. Cultivate at 30°C for 7 days until Monascus grows spores.
[0053] Wash the spores on the slope with 0.1% sterile Tween water, soak 30g of indica rice for 2 hours, transfer to a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, seal and sterilize at 121°C, 0.08MPa for 20 minutes, beat the rice grains while hot, and inoculate for 10 6 spores / g (dry weight of rice) were inoculated ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3: Lactic acid bacteria and Monascus co-fermentation prepare Monascus starter
[0055] Taking Lactobacillus plantarum as an example, a starter containing Lactobacillus plantarum and Monascus was prepared. The Lactobacillus plantarum is Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC No.8097, which has been disclosed in a patent with publication number CN103421723B.
[0056] Inoculate lactic acid bacteria into potato dextrose water liquid culture medium and culture at 28±2°C for 24-32 hours to obtain the fermentation broth.
[0057] Use the sterile inoculation loop to scrape the Monascus strains in the preservation tube and streak them on the wort slope. Cultivate at 30°C for 7 days until Monascus grows spores.
[0058] Wash the spores on the slope with 0.1% sterile Tween water, soak 30g of indica rice for 2 hours, transfer to a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, seal and sterilize at 121°C, 0.08MPa for 20 minutes, beat the rice grains while hot, and inoculate for 10 6 spores / g (dry we...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com