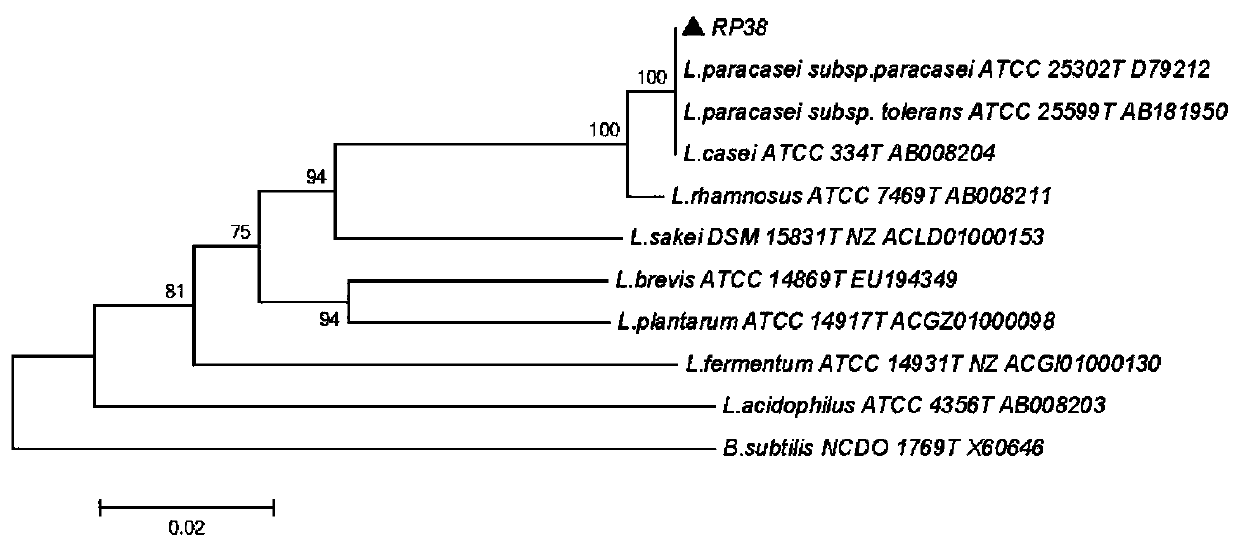
Lactobacillus paracasei subsp.paracasei RP38
A technology of paracheese and Lactobacillus, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of poor physical deodorization effect, safety and pollution, and insufficient fruit aroma of loquat products.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] The separation and breeding of embodiment 1 bacterial strain RP38
[0030]Use naturally fermented grape juice with strong fermentation aroma and good flavor as the bacterial source, carry out gradient dilution with sterile water, spread it on the improved TJA medium with 1.5% CaCO3, cultivate it at 30°C for 72 hours, and select the ones with obvious calcium-dissolving circles The dominant colony continued to be streaked and purified, and a single colony that was positive for Gram staining, negative for catalase, and non-spore in line with the characteristics of lactic acid bacteria was selected, checked with an oil microscope, and preserved for screening and identification. The 10 strains of suspected lactic acid bacteria purified and selected were expanded and cultured to the logarithmic stable phase, respectively inserted into sterilized grape juice, and fermented at 25°C for 2 days, and the best fermented flavor and taste were screened out through sensory evaluation. ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Identification of embodiment 2 bacterial strain RP38
[0032] 1. Morphological, physiological and biochemical characteristics of lactic acid bacteria RP38
[0033] It can be seen from Table 1 that the cells of lactic acid bacteria RP38 are rod-shaped, the cell size is 0.5 μm × 1.0-1.67 μm (length × width), and the cells are arranged in single, paired or short chains without spores; the colony diameter is 0.7-1.3 mm , round, wet, smooth surface, convex, milky white, opaque, with neat edges; liquid culture solution is turbid, sterile film, no bubbles, obvious layers, white precipitate at the bottom, see Figure 2-3 .
[0034] Table 1 Morphological and physiological characteristics of strain RP38
[0035]
[0036] Note: "+", positive; "-", negative; "+w", weakly positive; ND, not tested.
[0037] As can be seen from Table 1 and Table 2, lactic acid bacteria RP38 has the following physiological and biochemical characteristics: the bacterial strain can grow at 10°C and...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: Research on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of lactic acid bacteria RP38
[0045] 1. High acid resistance test
[0046] Using the standard lactic acid bacteria strain ATCC14917 as the control bacteria, inoculate the target strains into the MRS liquid medium with a pH value of 2.0 at a 5% (v / v) inoculation amount, and culture them at 37°C for 18 hours to detect the OD 600 value, see Figure 5 . Except for RHJ24 and RP38, other strains could not proliferate, and RP38 had obvious high tolerance to acid stress.
[0047] In order to eliminate the influence of the oxidative browning of the medium itself on the OD 600 Taking the culture medium without strains as the control, the proliferation ability is expressed as (ΔOD600 (18h with bacteria)-ΔOD600 (18h with sterile medium))-(ΔOD600(0h with bacteria)-ΔOD600(0h with sterile medium ))express.
[0048] 2. Osmotic pressure resistance test
[0049] The activated strains were inoculated into t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com