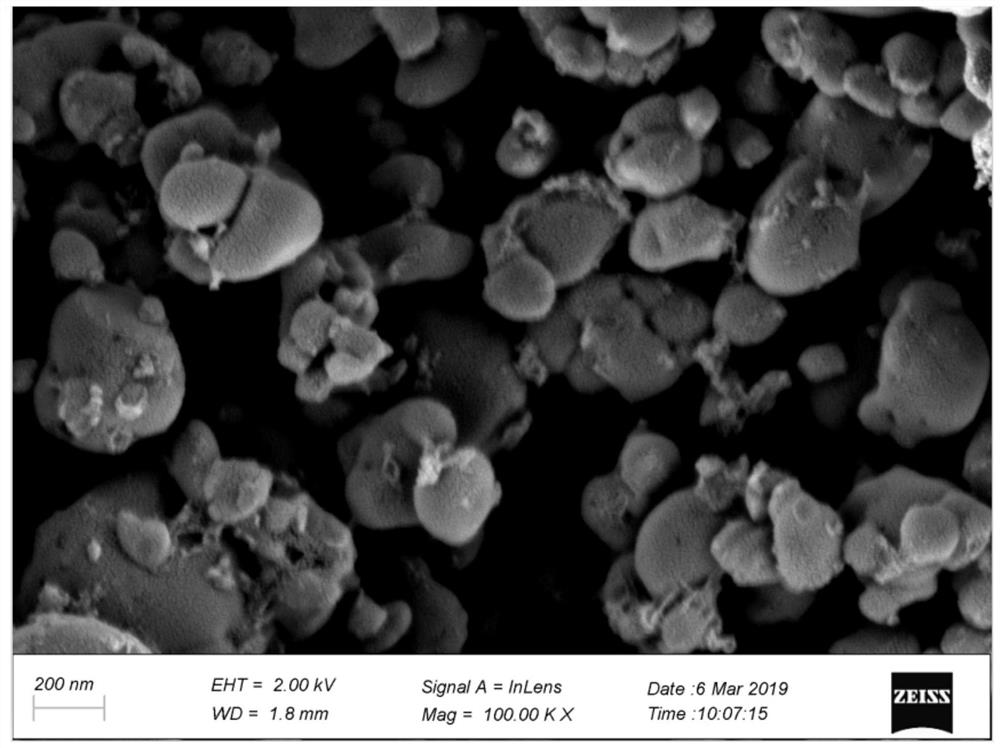
A kind of processing method of waste lithium iron phosphate
A technology for lithium iron phosphate and treatment methods, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, recycling by waste collectors, etc. It can solve the problems of low added value of products, impact on the service life of lithium iron phosphate, and reduced safety performance of lithium iron phosphate batteries, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
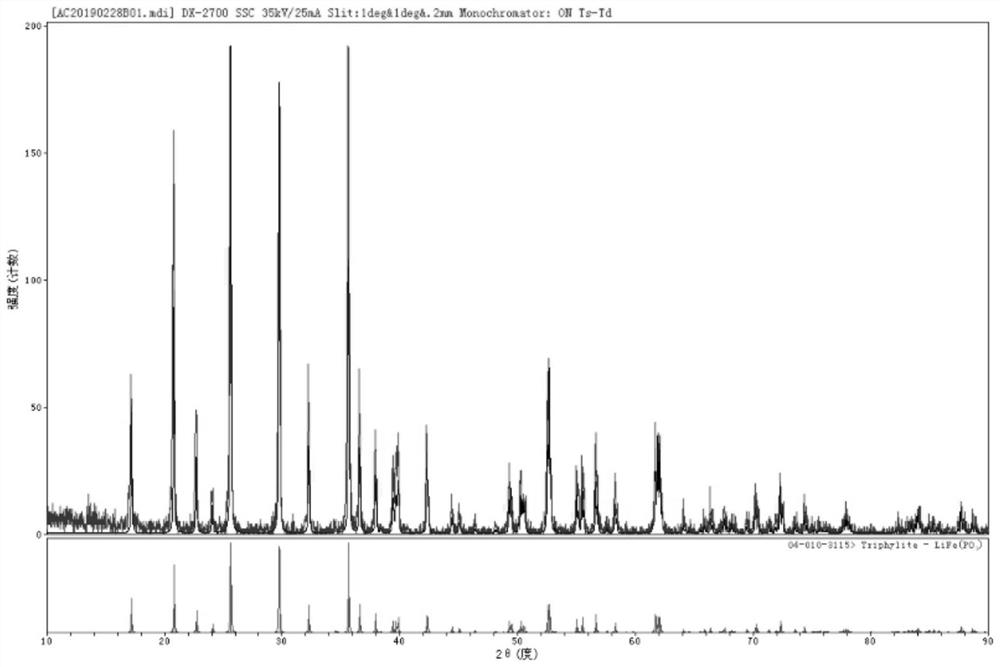
Image
Examples
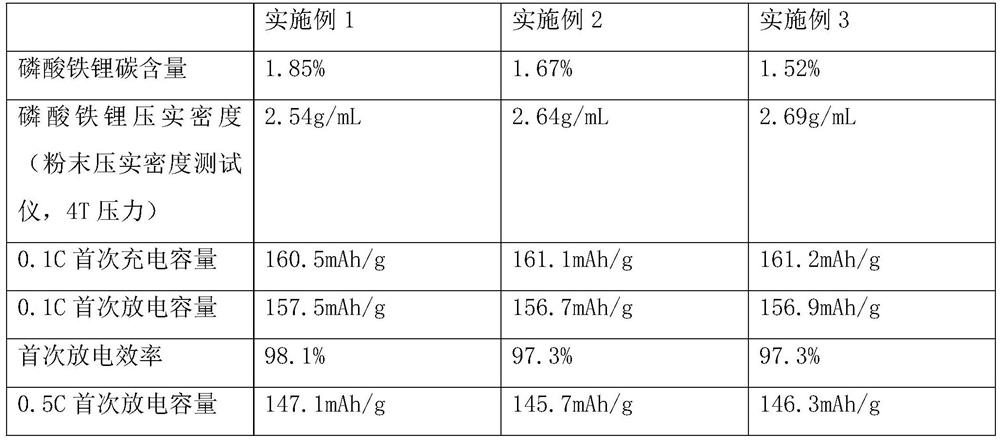
Embodiment 1
[0053] A processing method for waste lithium iron phosphate, which comprises the following steps:
[0054] 1) pretreating the waste lithium iron phosphate material, adding phosphoric acid solution to the pretreated material, stirring and reacting at a temperature of 90°C for 2 hours, and filtering to obtain the first filtrate and the first filter residue;
[0055] 2) adding the first filtrate to the sulfide, stirring and reacting at a temperature of 45°C until the total content of nickel, cobalt, copper, zinc, cadmium and lead in the solution is lower than 50ppm, then stopping the reaction, then filtering to obtain the second filtrate and second filter residue;
[0056] 3) Add iron powder to the second filtrate, then stir and react at a temperature of 65°C for 4 hours, and remove iron from the obtained slurry through a permanent magnetic iron remover and an electromagnetic iron remover, and add battery-grade lithium carbonate to the obtained iron-removed material, and stir Re...
Embodiment 2
[0070] A processing method for waste lithium iron phosphate, which comprises the following steps:
[0071] 1) pretreating the waste lithium iron phosphate material, adding phosphoric acid solution to the pretreated material, stirring and reacting at a temperature of 85° C. for 2 hours, and filtering to obtain the first filtrate and the first filter residue;
[0072] 2) adding the first filtrate to the sulfide, stirring and reacting at a temperature of 50°C until the total content of nickel, cobalt, copper, zinc, cadmium and lead in the solution is lower than 50ppm, then stopping the reaction, then filtering to obtain the second filtrate and second filter residue;
[0073] 3) Add iron powder to the second filtrate, then stir and react at a temperature of 65°C for 4.5 hours, and remove iron from the obtained slurry through a permanent magnetic iron remover and an electromagnetic iron remover, and add battery-grade lithium carbonate to the obtained iron removal material, Stir th...
Embodiment 3
[0085] A processing method for waste lithium iron phosphate, which comprises the following steps:
[0086] 1) pretreating the waste lithium iron phosphate material, adding phosphoric acid solution to the pretreated material, stirring and reacting at a temperature of 88° C. for 2 hours, and filtering to obtain the first filtrate and the first filter residue;
[0087] 2) adding the first filtrate to the sulfide, stirring and reacting at a temperature of 45°C until the total content of nickel, cobalt, copper, zinc, cadmium and lead in the solution is lower than 50ppm, then stopping the reaction, then filtering to obtain the second filtrate and second filter residue;
[0088] 3) Add iron powder to the second filtrate, then stir and react at a temperature of 60°C for 4 hours, and remove iron from the obtained slurry through a permanent magnetic iron remover and an electromagnetic iron remover, and add battery-grade lithium carbonate to the obtained iron-removed material, and stir ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com