Advanced treatment process for thallium-containing wastewater
A technology for advanced treatment of waste water, which is applied in the advanced treatment of thallium-containing waste water, metallurgical industrial waste water and metal recovery process waste water, and can solve the problems of reducing agent residue, high treatment cost, and smelly adsorbent, etc. Achieve the effect of reducing the amount of hazardous waste generated, realizing closed loop and reducing treatment costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
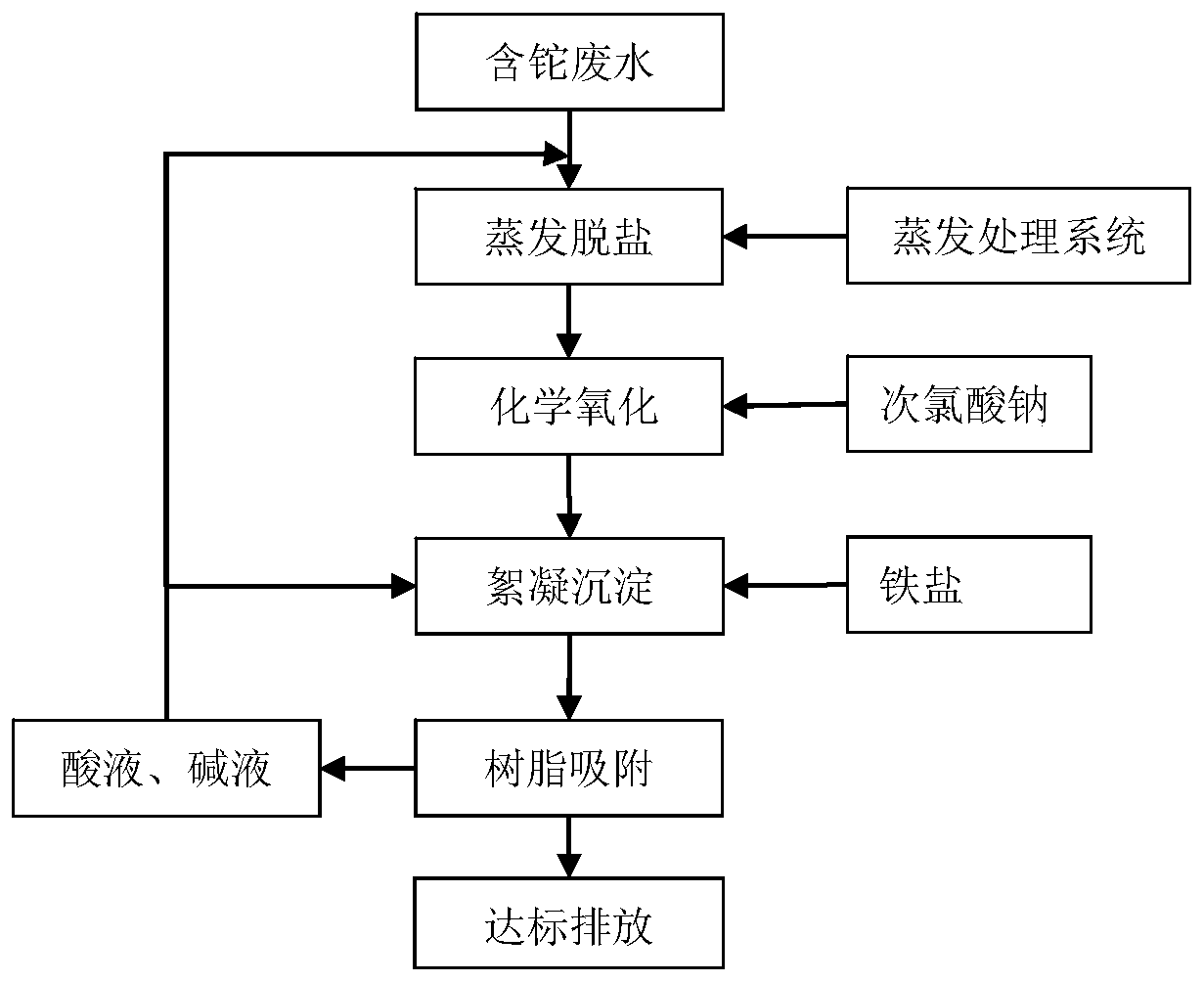
[0046] An embodiment of the advanced treatment method of thallium-containing wastewater according to the present invention. The wastewater treated in this embodiment is the thallium-containing wastewater produced during the recovery process of valuable metals in a metallurgical company. ICP-OES and ICP-MS are used to analyze and detect the thallium-containing wastewater. Heavy metal concentration, the result is that the thallium content is 5mg / L, and the soluble salt content is 7.3%. The advanced processing method includes the following steps:
[0047] (1) Evaporation desalination: 30m 3 The pH value of the above wastewater is adjusted to about 7-8, and after filtration, evaporation and desalination treatment is performed to obtain wastewater with a salt content of less than 0.005 wt%.
[0048] (2) Chemical oxidation: adding a sodium hypochlorite solution with a sodium hypochlorite concentration of 10 wt% (the sodium hypochlorite used is industrial grade) in an amount of 1.5 ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] An embodiment of the advanced treatment method of thallium-containing wastewater according to the present invention. The wastewater treated in this embodiment is the thallium-containing wastewater produced during the recovery process of valuable metals in a metallurgical company. ICP-OES and ICP-MS are used to analyze and detect the thallium-containing wastewater. Heavy metal concentration, the result is that the thallium content is 8mg / L, and the soluble salt content is 11.2%. The advanced processing method includes the following steps:
[0053] (1) Evaporation desalination: 30m 3 The pH value of the above wastewater is adjusted to about 8-9, and after filtration, evaporation and desalination treatment is performed to obtain wastewater with a salt content of less than 0.008wt%.
[0054] (2) Chemical oxidation: adding a sodium hypochlorite solution with a sodium hypochlorite concentration of 10 wt% (the sodium hypochlorite used is industrial grade) in an amount of 2 mL...
Embodiment 3
[0058] An embodiment of the advanced treatment method of thallium-containing wastewater according to the present invention. The wastewater treated in this embodiment is the thallium-containing wastewater produced during the recovery process of valuable metals in a metallurgical company. ICP-OES and ICP-MS are used to analyze and detect the thallium-containing wastewater. Heavy metal concentration, the result is that the thallium content is 10mg / L, and the soluble salt content is 5.6%. The advanced processing method includes the following steps:
[0059] (1) Evaporation desalination: 30m 3 The pH value of the above wastewater is adjusted to about 8-9, and after filtration, evaporation and desalination treatment is performed to obtain wastewater with a salt content of less than 0.003 wt%.
[0060] (2) Chemical oxidation: adding a sodium hypochlorite solution with a sodium hypochlorite concentration of 10 wt% (the sodium hypochlorite used is industrial grade) to the above-mentio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com