Fast-degradation plant fiber material and preparation method thereof
A plant fiber material and plant fiber technology, which is applied in the field of fast-degrading plant fiber materials and its preparation, can solve the problems of not widely used, compressive strength, tensile strength, bending strength, hardness and low impact, and improve the compressive strength Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
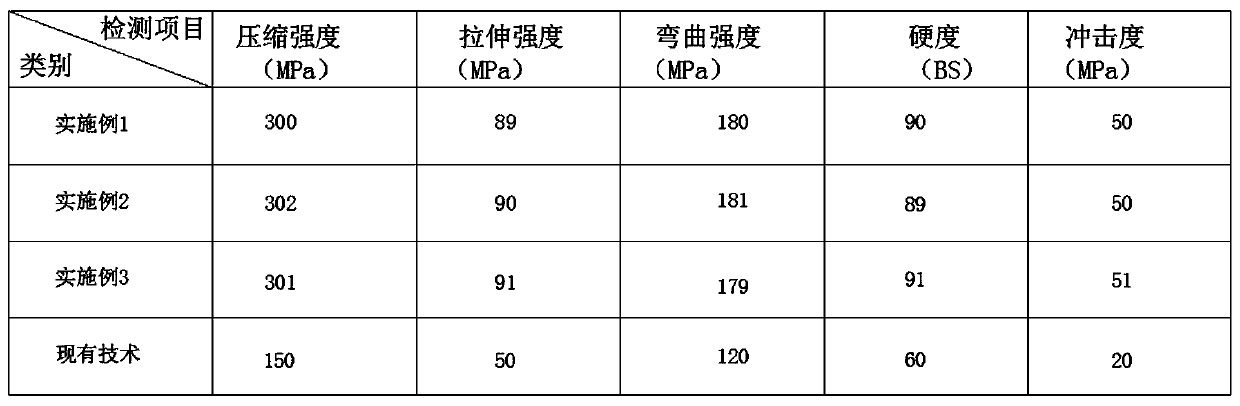
[0025] A plant fiber material that degrades quickly, including components and mass percentages of 60% plant fiber, 30% natural starch, 6% polypropylene, 8% polyvinyl chloride, 10% polyvinyl alcohol, 5% reactive additives, 10% plasticizer, 11% talc, 11% pulp, 6% adhesive, 8% filler and 2% crosslinking agent.
[0026] In this embodiment, the natural starch is one or more mixtures of mung bean starch, tapioca starch, sweet potato starch, sweet potato starch, potato starch, wheat starch, water chestnut starch, lotus root starch, and corn starch.
[0027] In this embodiment, the plant fiber is one or more of wheat straw fiber, bean straw fiber, castor-oil fiber, ramie fiber, hemp fiber, flax fiber, jute fiber, sisal fiber, abaca fiber and bamboo fiber mix.
[0028] In this embodiment, the filler is one or more mixtures of calcium carbonate powder, barium sulfate powder, clay powder, fumed silica powder, calcium oxide powder, aluminum hydroxide powder, and magnesium hydroxide powde...
Embodiment 2
[0032] A plant fiber material that degrades quickly, including components and mass percentages of 80% plant fiber, 60% natural starch, 10% polypropylene, 12% polyvinyl chloride, 14% polyvinyl alcohol, 9% reactive additives, 20% plasticizer, 17% talc, 17% pulp, 12% adhesive, 10% filler and 4% crosslinking agent.
[0033] In this embodiment, the natural starch is one or more mixtures of mung bean starch, tapioca starch, sweet potato starch, sweet potato starch, potato starch, wheat starch, water chestnut starch, lotus root starch, and corn starch.
[0034] In this embodiment, the plant fiber is one or more of wheat straw fiber, bean straw fiber, castor-oil fiber, ramie fiber, hemp fiber, flax fiber, jute fiber, sisal fiber, abaca fiber and bamboo fiber mix.
[0035] In this embodiment, the filler is one or more mixtures of calcium carbonate powder, barium sulfate powder, clay powder, fumed silica powder, calcium oxide powder, aluminum hydroxide powder, and magnesium hydroxide p...
Embodiment 3
[0039] A plant fiber material that degrades quickly, including components and mass percentages of 70% plant fiber, 45% natural starch, 8% polypropylene, 10% polyvinyl chloride, 12% polyvinyl alcohol, 7% reactive additives, 15% plasticizer, 14% talc, 14% pulp, 9% adhesive, 9% filler and 3% crosslinking agent.
[0040] In this embodiment, the natural starch is one or more mixtures of mung bean starch, tapioca starch, sweet potato starch, sweet potato starch, potato starch, wheat starch, water chestnut starch, lotus root starch, and corn starch.
[0041] In this embodiment, the plant fiber is one or more of wheat straw fiber, bean straw fiber, castor-oil fiber, ramie fiber, hemp fiber, flax fiber, jute fiber, sisal fiber, abaca fiber and bamboo fiber mix.
[0042] In this embodiment, the filler is one or more mixtures of calcium carbonate powder, barium sulfate powder, clay powder, fumed silica powder, calcium oxide powder, aluminum hydroxide powder, and magnesium hydroxide powd...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com