A kind of Aureobasidium pullulans using starch to produce polymalic acid and its application
A technology of Aureobasidium pullulans and polymalic acid, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of difficult quality control, high cost of raw materials, and increased operating costs of fermentation equipment, so as to reduce the consumption of cooling water , Strain nutritional requirements are simple, the effect of good industrial production value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
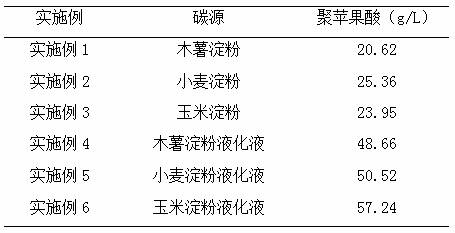
[0029] Aureobasidium pullulans ( Aureobasidium pullulans ) GXL-1 utilizes tapioca starch to produce polymalic acid, including the following steps:
[0030] (1) Strain activation: Aureobasidium pullulans preserved in glycerol ( Aureobasidium pullulans ) GXL-1 was streaked on PDA slant medium and incubated at 30°C for 2 days.
[0031] (2) Seed cultivation: Scrape a ring on the slanted surface of the activated strain, inoculate it into a 500mL shaker flask containing 80mL of liquid seed medium, and cultivate for 36h at a shaker speed of 220rpm and a temperature of 25ºC to obtain seed solution. Described liquid seed medium is glucose 100g / L, ammonium chloride 2g / L, KCl 0.6g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.2g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.3g / L, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g / L, CaCO 3 30g / L.
[0032] (3) Fermentation culture: The seed liquid obtained from the culture was placed in a 250mL conical flask containing 30mL liquid fermentation medium according to the inoculation amount of 8% (v / v), and cultured f...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Aureobasidium pullulans ( Aureobasidium pullulans ) GXL-1 utilizes wheat starch to produce polymalic acid, including the following steps:
[0036] (1) Strain activation: Aureobasidium pullulans preserved in glycerol ( Aureobasidium pullulans ) GXL-1 was streaked on PDA slant medium and incubated at 30°C for 2 days.
[0037] (2) Seed cultivation: Scrape a ring on the slanted surface of the activated strain, inoculate it into a 500mL shaker flask containing 80mL of liquid seed medium, and cultivate for 36h at a shaker speed of 220rpm and a temperature of 25ºC to obtain seed solution. Described liquid seed medium is glucose 100g / L, ammonium chloride 2g / L, KCl 0.6g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.2g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.3g / L, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g / L, CaCO 3 30g / L.
[0038] (3) Fermentation culture: The seed liquid obtained from the culture was placed in a 250mL conical flask containing 30mL liquid fermentation medium according to the inoculation amount of 8% (v / v), and cultured for...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Aureobasidium pullulans ( Aureobasidium pullulans ) GXL-1 utilizes cornstarch to produce polymalic acid, which involves the following steps:
[0042] (1) Strain activation: Aureobasidium pullulans preserved in glycerol ( Aureobasidium pullulans ) GXL-1 was streaked on PDA slant medium and incubated at 30°C for 2 days.
[0043] (2) Seed cultivation: Scrape a ring on the slanted surface of the activated strain, inoculate it into a 500mL shaker flask containing 80mL of liquid seed medium, and cultivate for 36h at a shaker speed of 220rpm and a temperature of 25ºC to obtain seed solution. Described liquid seed medium is glucose 100g / L, ammonium chloride 2g / L, KCl 0.6g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.2g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.3g / L, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g / L, CaCO 3 30g / L.
[0044] (3) Fermentation culture: The seed liquid obtained from the culture was placed in a 250mL conical flask containing 30mL liquid fermentation medium according to the inoculation amount of 8% (v / v), and cultured ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com