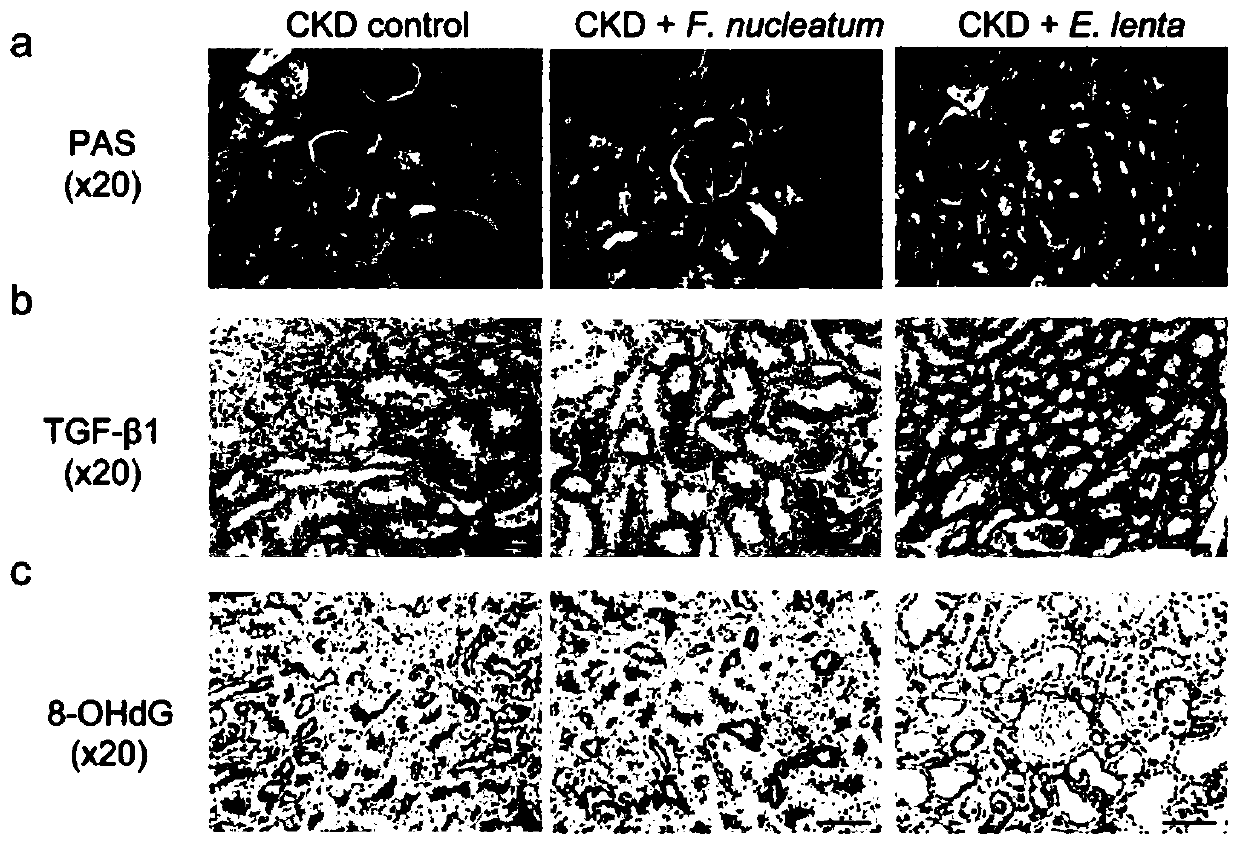
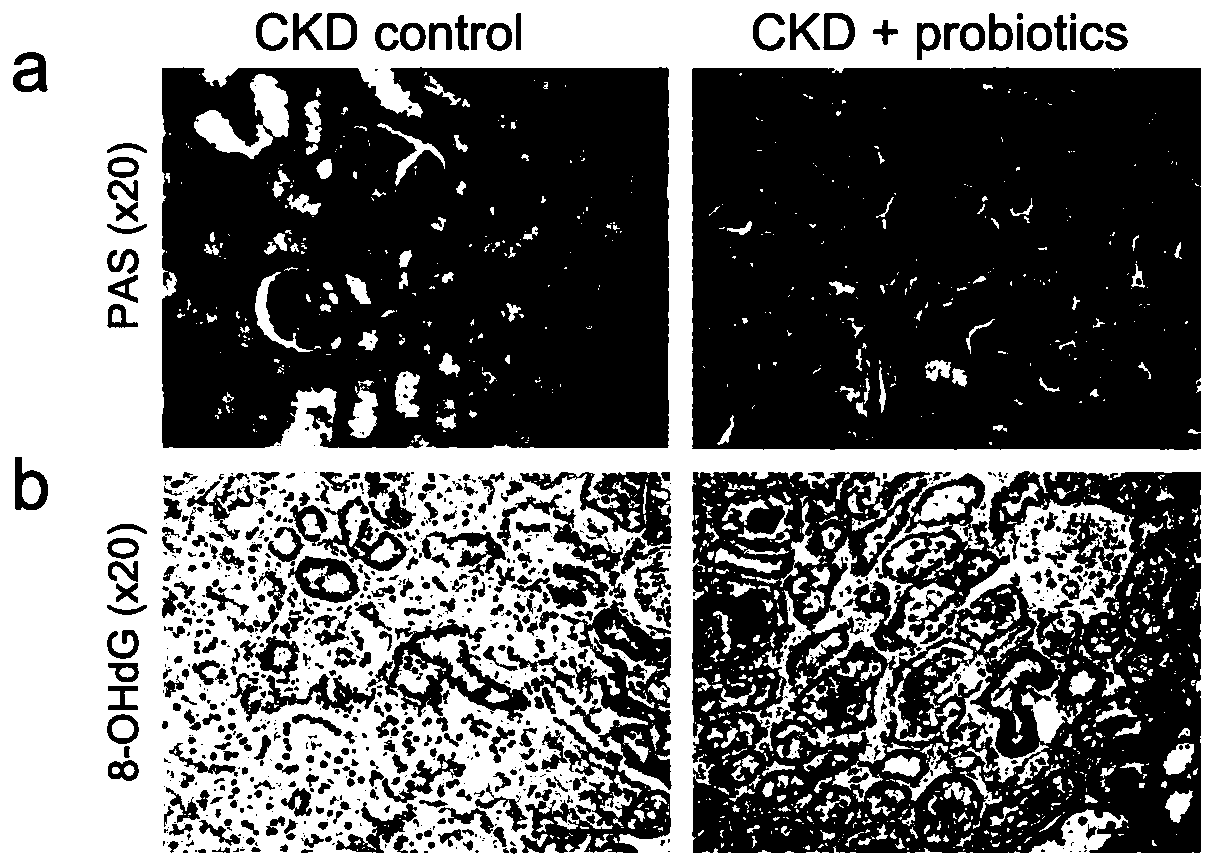
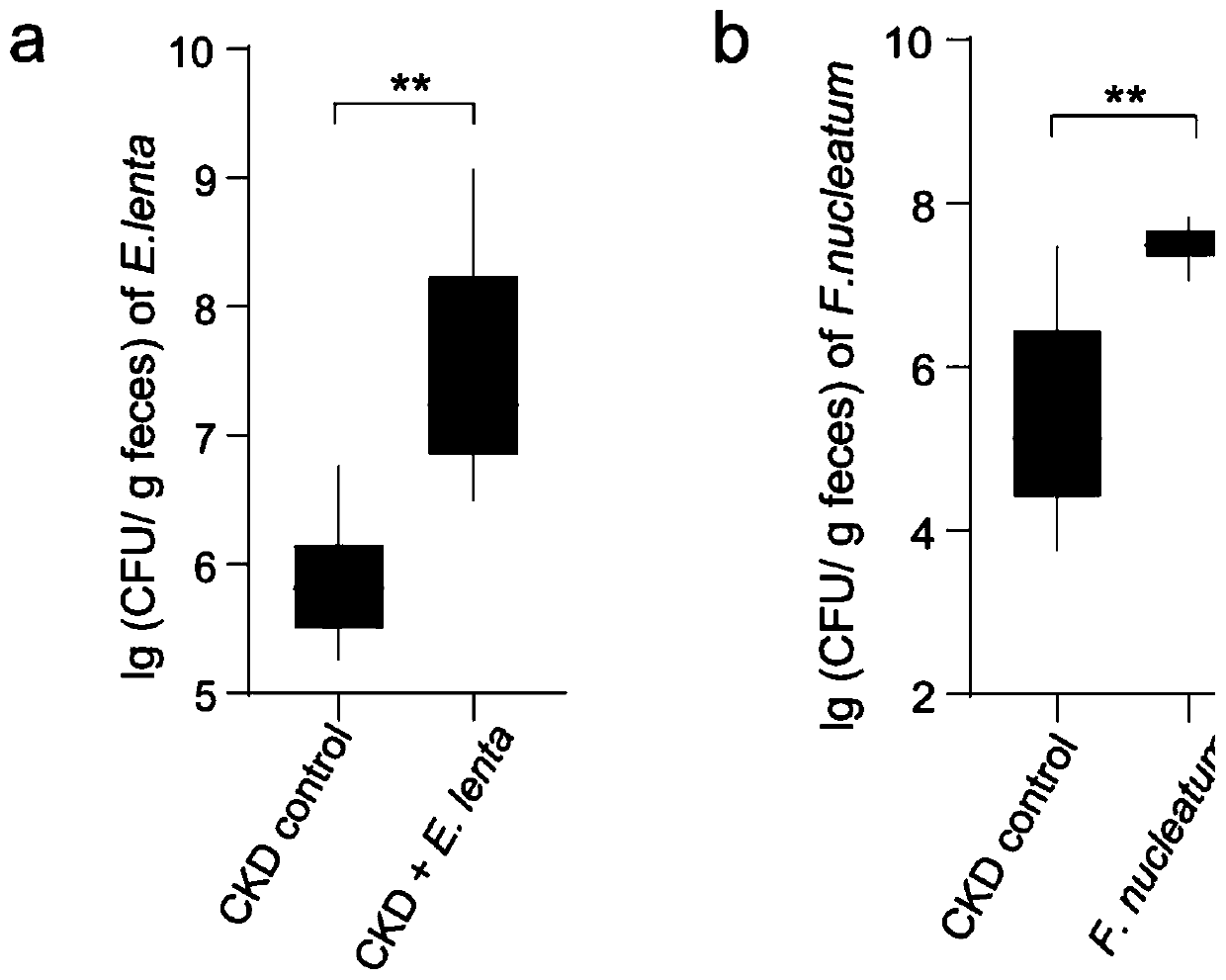
Biomarkers for end-stage renal disease and application thereof
A technology for end-stage renal disease and microorganisms, which can be used in the determination/examination of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., and can solve problems such as end-stage renal disease that needs to be improved.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Sample Collection
[0044] 223 hemodialysis patients (21-72 years old) were recruited from four hemodialysis centers in Beijing, China. All participants were diagnosed with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) according to Improving Kidney Outcomes Global Organization (KDIGO) clinical practice guidelines and on stable hemodialysis (1-3 times per week). Among the 223 patients with ESRD, 77 cases (34.5%) of glomerulonephritis, 73 cases (32.7%) of end-stage renal disease, 32 cases (14.3%) of hypertensive nephrosclerosis, 6 cases (2.7%) of polycystic kidney disease, interim There were 12 cases (5.4%) of qualitative nephritis, 5 cases (2.2%) of kidney transplantation failure, and 19 cases (8.5%) of unexplained renal failure.
[0045] The control group (26-71 years old, 18.5<BMI<29.9kg / m2) included 69 healthy volunteers who went to Beijing Aerospace Center Hospital for physical examination every year. Exclusion criteria for the control group included hypertension, end-...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: DNA extraction and sequencing
[0047] 2.1 Collection and storage of fecal samples
[0048] Collect fresh stool at home or in the hospital. All participants were asked to defecate on a special collection paper (developed by Aiken Chemical Co., Ltd., Japan) and separate the feces in sterile test tubes. Put the fresh feces in the test tube into the ice pack, and send it to the laboratory within 2 hours after putting in the ice pack. Soak a stool sample in sterile DNA protection solution (pH 5.2, 0.01mol / L EDTA, 0.025mol / L Na 3 C 6 H 5 O 7 and 5.3mol / L Na 2 SO 4 ) tubes at 4°C until DNA extraction and metagenomic analysis. Other stool samples were immediately frozen and stored at −80°C until use.
[0049] 2.2 DNA extraction
[0050] Total DNA was extracted from approximately 180-200 mg of feces using standard methods. Fresh genomic DNA samples were mechanically fragmented to ~400 bp with Bio.orPico (Dia.de, Belgium). DNA fragments were selected using...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: Identification of biomarkers
[0054] 3.1 Basic processing of sequencing data
[0055] Under the sequencing platform, the basic processing of WMS data is performed based on the default parameters of the system. Low-quality reads were defined as containing: 1) reads with an estimated error rate >1% for more than 30% of bases; or 2) ambiguous "N" >15 bp. These reads are deleted in pairs. Human genomic DNA reads were identified by SOAP2 and removed if they shared >95% of their sequence with the human genome reference sequence (hg19).
[0056] 3.2 Update gene catalog
[0057] A new gene catalog was established based on the WMS data of all samples. High-quality WMS data were assembled and gene prediction was performed using IDBA-UD (version 1.1.2). If any two genes from different samples have a similarity of 95% or more in 90% of the regions, the shorter gene will be listed as a redundant gene. After removing all redundant genes, we obtained a non-redundant ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com