Lipase mutant and application thereof in decontamination
A lipase and mutant technology, applied in the field of enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of poor lipase stability, loss of enzyme activity, loss of activity, etc., and achieve the effect of improving pH stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1: Expression of wild-type lipase
[0083] Specific steps are as follows:
[0084] The gene encoding the lipase whose amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 is amplified from Rhizopus chinonsis; the obtained gene proRCL is connected to the pPIC9K vector by Not I and EcoR I double digestion to obtain the recombinant Plasmid pPIC9K-proRCL; Transform the recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-proRCL into Escherichia coli JM109 to obtain E. L Kanamycin), cultured at 37°C for 10 h, screened positive clones and confirmed by sequencing, obtained the correct recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-proRCL; linearized the recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-proRCL with Sal I, and electrotransformed into Pichia In the yeast GS115, the Pichia GS115 / pPIC9K-proRCL was obtained; the Pichia GS115 / pPIC9K-proRCL was spread on the MD plate (containing 100mg / L kanamycin), and cultured at 37°C for 10h Afterwards, the genome was extracted, and positive clones were identified by PCR to obtain positive transform...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Example 2: Preparation and expression of lipase mutants
[0089] Specific steps are as follows:
[0090] Using the whole plasmid PCR technology, the recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-proRCL obtained in Example 1 was used as a template for site-directed mutation to obtain mutants S151N, S235A, K171R, S343Y, G275A, Q332F, D310V, L180H, F316C\G340C, S178C\Q238C, F316C\G340C\S178C\Q238C、S235A\S343Y\Q332F\D310V、S151N\K171R\G275A\L180H、S235A\S343Y\Q332F\D310V\S151N\K171R\G275A\L180H、S235A\S343Y\Q332F\D310V\S151N\ K171R\G275A\L180H\F316C\G340C\S178C\Q238C, D159R and T319V;
[0091] Wherein, the mutation primer is:
[0092] S151N:
[0093] S151N-Fm: 5'-CTGCTTACTGTCGT AAC GTCGTTCCAGGTACC-3' (SEQ ID NO. 4);
[0094] S151N-Rm: 5'-GGTACCTGGAACGAC GTT ACGACAGTAAGCAG-3' (SEQ ID NO. 5);
[0095] S235A:
[0096] S235A-Fm: 5'-GTTTCCTTTCC GCA TACAACCAAGTTGTCAAAG-3' (SEQ ID NO. 6);
[0097] S235A-Rm: 5'-CTTTGACAACTTGGTTGTA TGC GGAAAGGAAAC-3' (SEQ ID NO. 7);
[0098] K171R:
[00...
Embodiment 3
[0136] Embodiment 3: Research on the enzymatic properties of different lipases
[0137] Specific steps are as follows:
[0138] 1. The optimum temperature (T opt )
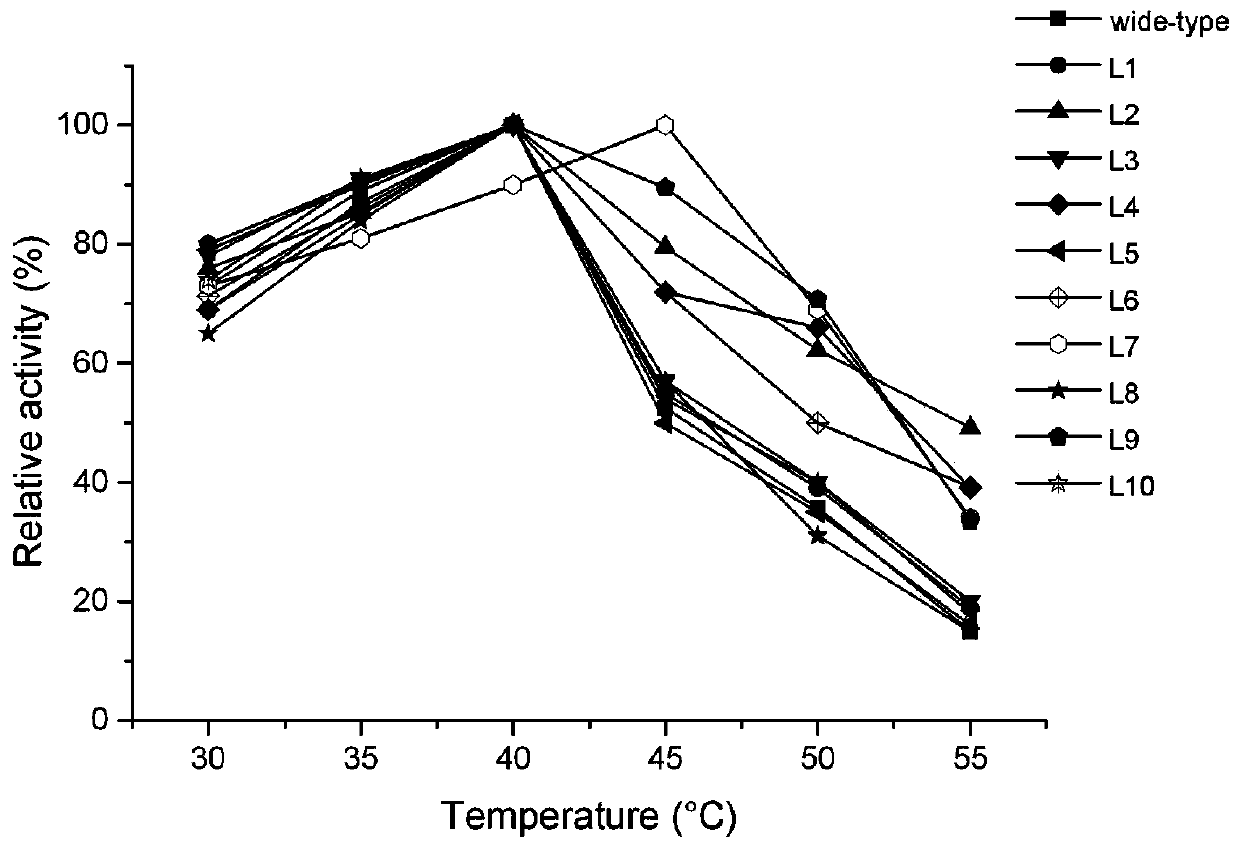
[0139] The wild type obtained in Example 1 and the L1, L2, L3, L4, For the lipase activity of L5, L6, L7, L8, L9, L10, L11, L12, L13, L14, L15, L16 and L17, the highest enzyme activity is 100%, and the other enzyme activities are compared with it to calculate the relative enzyme activity live to investigate the optimum action temperature of the enzyme (see the test results in Figure 3-4 ).
[0140] Depend on Figure 3-4 It can be seen that the optimum temperature of the wild type is 40°C; the optimum temperature of L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, L6, L8, L9, L10, L16 and L17 is also 40°C, which is no different from that of the wild type. The optimum temperature of L7 increased to 45°C; the optimum temperature of L13 increased to 43°C; the optimum temperature of L11 and L12 increased to 45°C; the optimum temperature of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| half-life | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com