Method for isolating extracellular vesicle using hydrophobic interaction
A technology for separating cells and vesicles, which can be used in separation methods, cell dissociation methods, general culture methods, etc., and can solve problems such as ineffective removal of lipoproteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
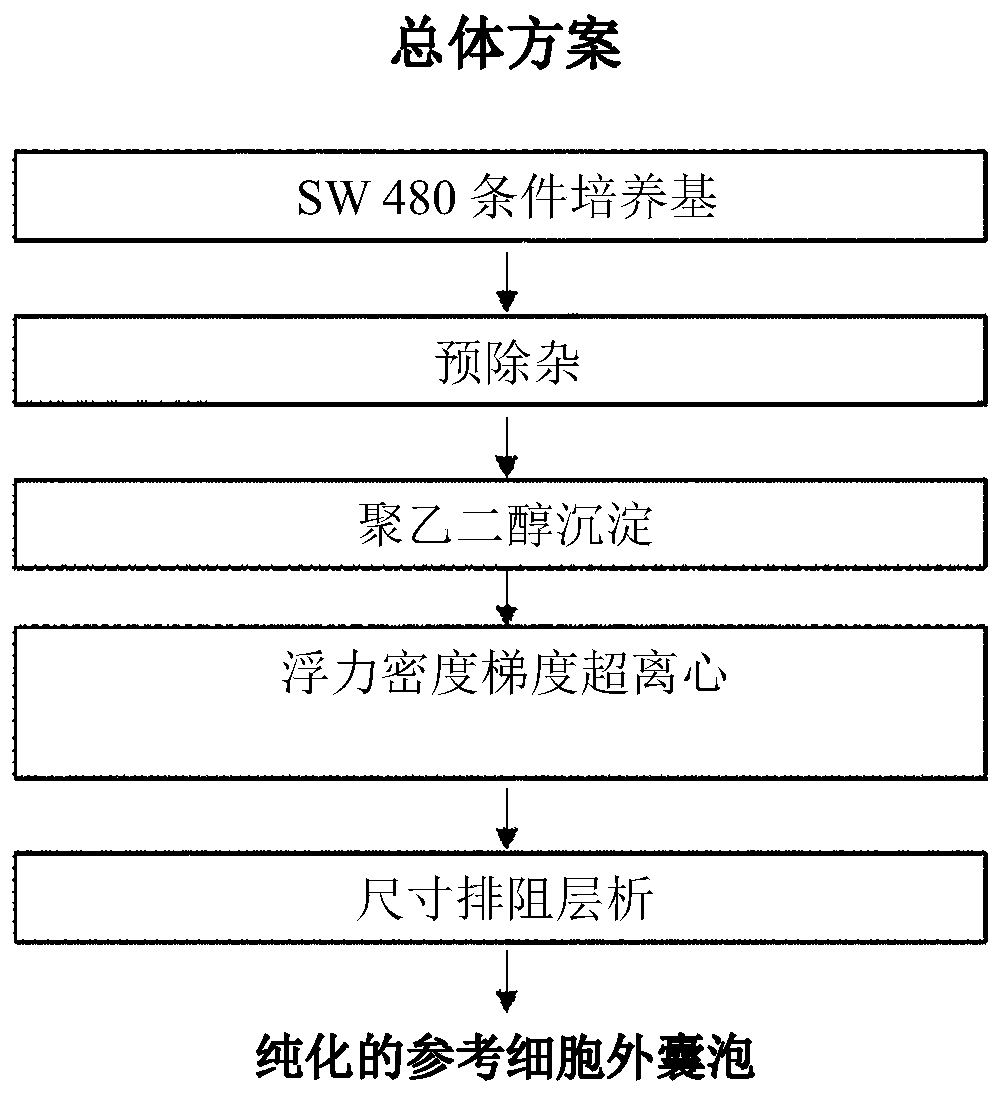
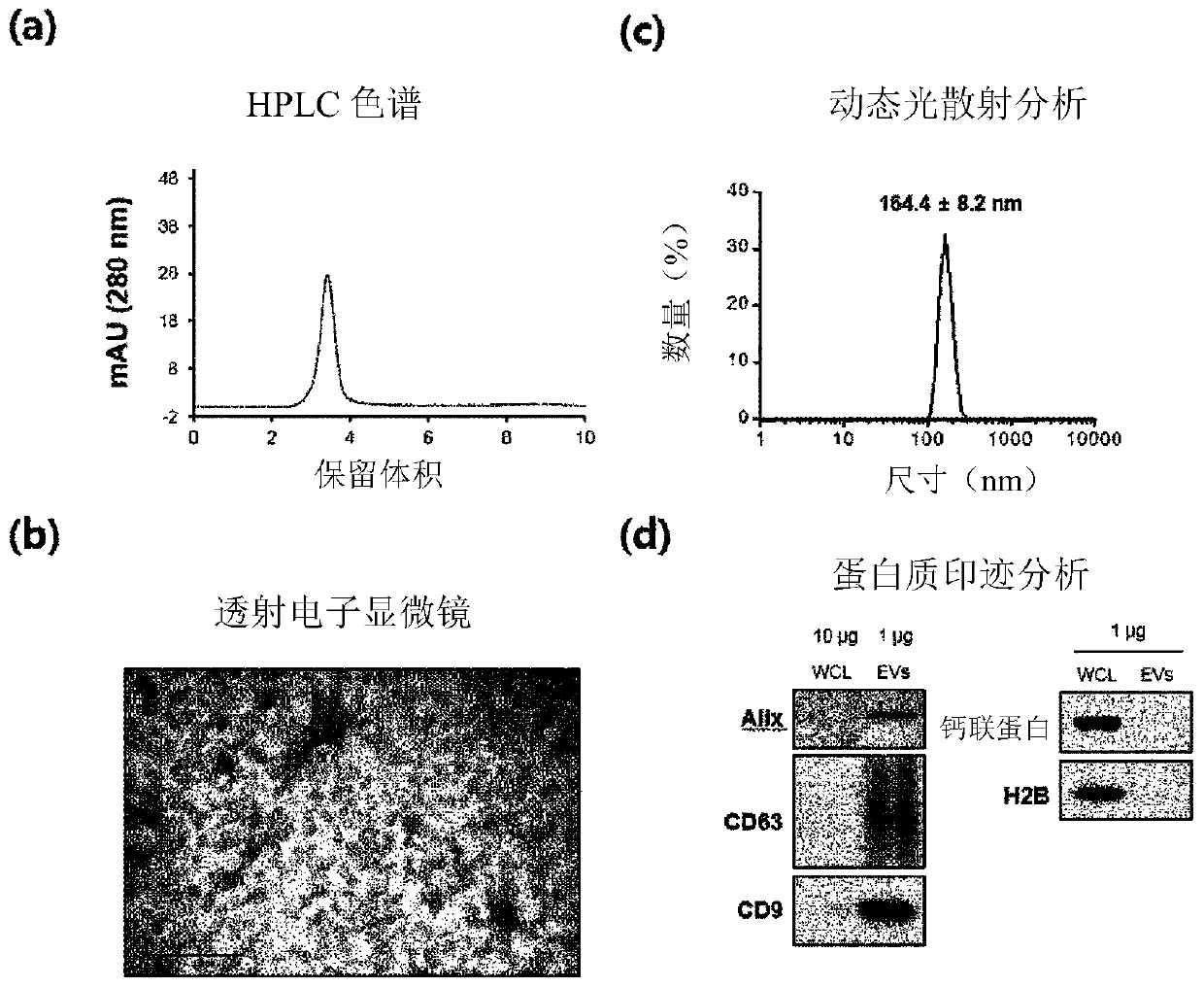
[0076] Example 1: Purification and Analysis of Reference Extracellular Vesicles
[0077] Fresh cultures of the colon cancer cell line SW480 were centrifuged at 500 xg for 10 minutes (totally repeated twice). After removing cell debris and precipitates, the supernatant was centrifuged again at 2,000×g for 20 minutes (repeated twice in total) to remove the precipitates.
[0078] A precipitation inducer (8.4% polyethylene glycol 6000, 250 mM NaCl, 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4) was added to the supernatant to first purify and precipitate the extracellular vesicles present therein. After 16 hours in the refrigerator, the supernatant was centrifuged at 12,000 xg for 30 minutes to obtain extracellular vesicles in pellet form. The precipitate was dissolved in HEPES buffer (HEPES buffered saline, 20 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4).
[0079] For a second purification of extracellular vesicles by density and buoyancy, the samples were mixed with OptiPrep TM (30% final concentration) mix and loa...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Example 2: Binding behavior of reference extracellular vesicles to stationary phases with hydrophobic functional groups
[0084] Assays are performed to see if extracellular vesicles bind hydrophobic functional groups. To achieve the above purpose, the HPLC system was used to detect the binding behavior of the reference extracellular vesicles isolated in Example 1.
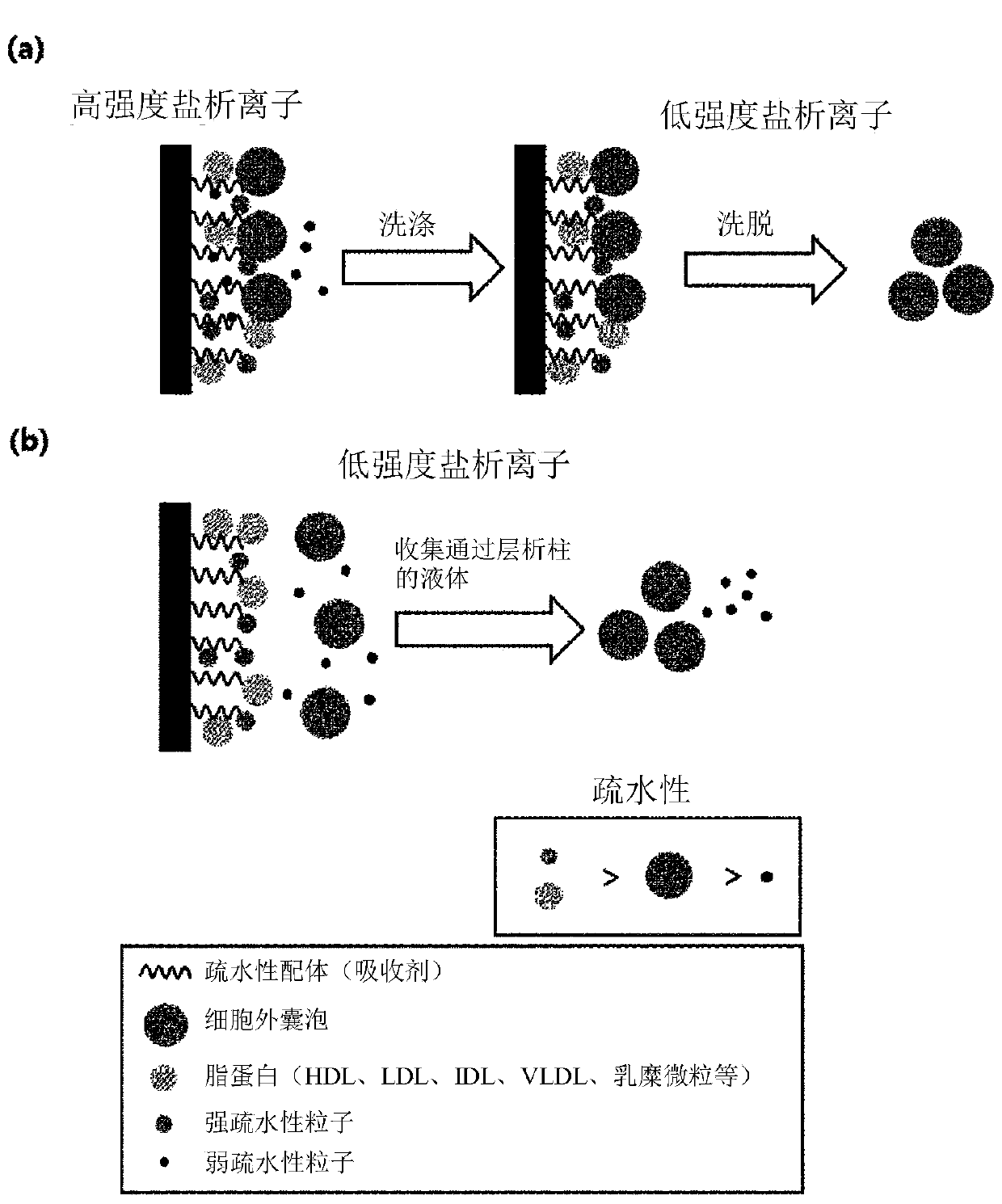
[0085] First, a column (1 ml) packed with a hydrophobic functional group stationary phase (Phenyl-Sepharose) was washed with 20 column volumes of binding buffer (1M NaCl, 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.2) at a pressure of 1 ml / min. The reference extracellular vesicles isolated in Example 1, according to 4x10 10 Individual amounts were dissolved in the same binding buffer.
[0086] Using the same binding buffer, the reference EV solution was loaded for 5 min onto the washed stationary phase with hydrophobic functional groups, followed by a 5 min wash with the same buffer to remove unbound residues. Then, 20 column vol...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3: Binding behavior of reference extracellular vesicles to stationary phases with hydrophobic functional groups depending on salt concentration
[0090] To examine the binding behavior of reference EVs to stationary phases with hydrophobic functional groups depending on the NaCl concentration, the following experiments were performed.
[0091] Reference extracellular vesicles were purified by polyethylene glycol precipitation. Precipitated reference extracellular vesicles were added to buffers of various NaCl concentrations (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.2 and 0 M, 50 mM, 150 mM, 500 mM NaCl, respectively).
[0092]The empty column was filled with 0.4 ml of a stationary phase (Phenyl-Sepharose) having a hydrophobic functional group, and then washed 3 times with 0.5 ml of water by centrifugation (700×g, 1 minute) to prepare a hydrophobic interaction chromatography column. Each time 0.5ml of the corresponding buffer solution (20mM HEPES, pH7.2 and respectively 0M, 50mM, 150m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com