Genetically engineered bacteria for producing lincomycin as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacteria
A genetically engineered bacterium and a technology for producing lincomycin, applied in the field of genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0126] Example 1 Construction of slinc566, slinc4481, slinc6027, slinc6156, slinc348, slinc4742 knockout vectors
[0127] The gene knockout scheme in this example is based on CRISPR / Cas9 technology.
[0128] The PCR reaction conditions of this embodiment are: 98°C, 10 minutes; (98°C, 40 seconds; 64°C, 30 seconds; 72°C, 80 seconds) × 30 cycles; 72°C, 10 minutes; 25°C, 2 minutes .
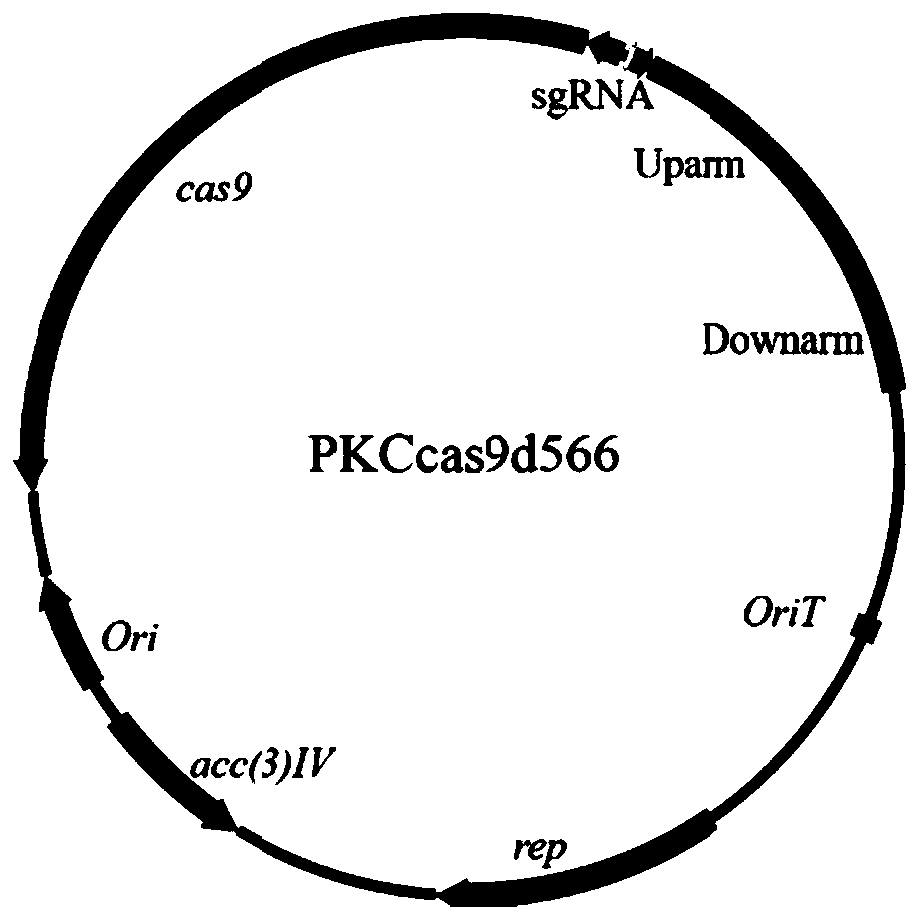
[0129] 1. Construction of slinc566 knockout vector
[0130] Step 1: Using u566-F / R and d566-F / R as primers and Streptomyces lincolnensis NRRL 2936 genome as a template, PCR amplifies the upstream and downstream homology arms of slinc566. After detection by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, the target band at 1.1 kb was cut and purified.
[0131] Step 2: Use the upstream and downstream homology arm fragments obtained in the previous PCR reaction as templates, and use sg566 / u566-R as primers to amplify by PCR to add the sgRNA sequence that specifically recognizes the sequence within the slinc566 gene....
Embodiment 2
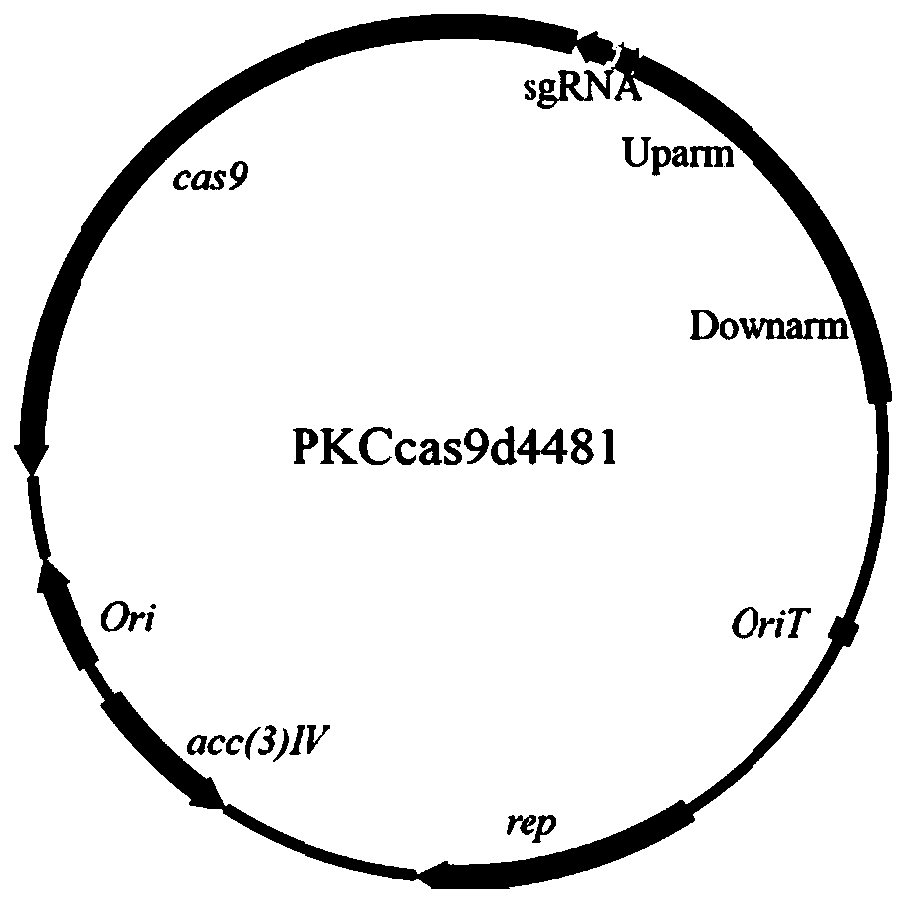
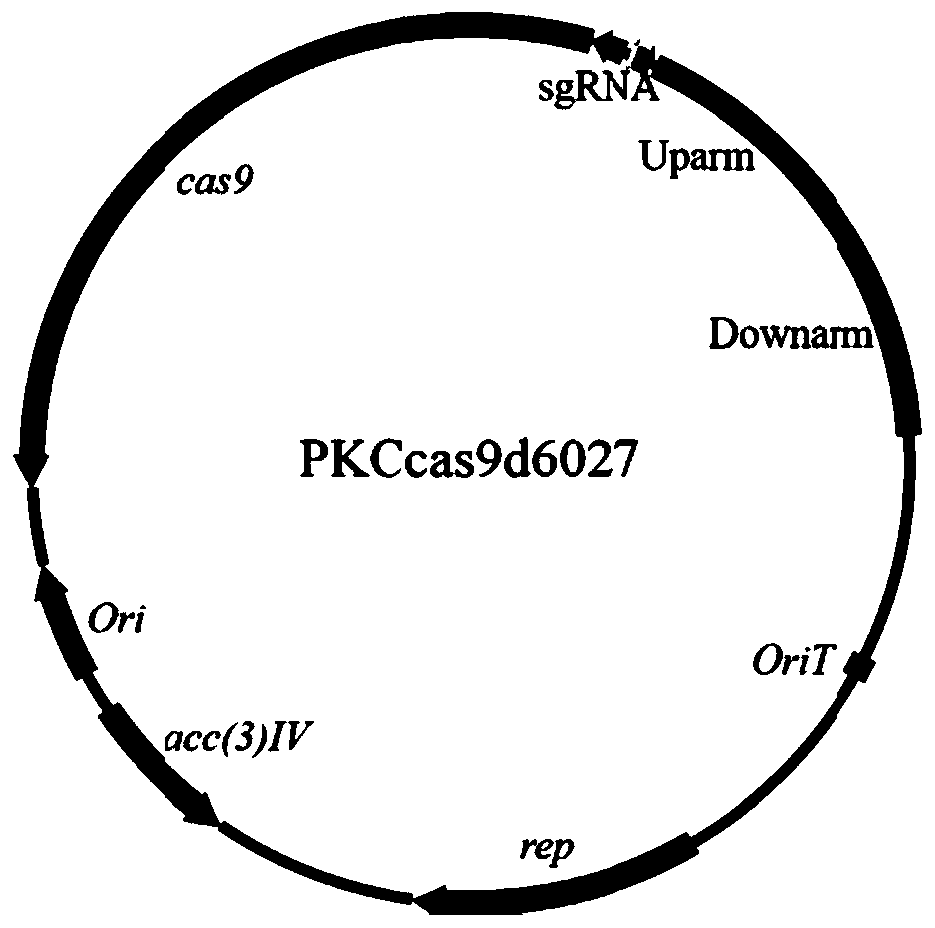
[0143] Example 2 Gene knockout of slinc566, slinc4481, slinc6027, slinc6156, slinc348, and slinc4742.
[0144] The PCR reaction conditions of this embodiment are: 98°C, 10 minutes; (98°C, 40 seconds; 64°C, 30 seconds; 72°C, 80 seconds) × 30 cycles; 72°C, 10 minutes; 25°C, 2 minutes .
[0145] 1. The principle of slinc566 gene knockout of the present invention is as follows: Figure 7 shown.
[0146] Step 1, transforming the pKCcas9d566 plasmid into Escherichia coli S17-1. Cultured in LB medium to OD 600 =0.4 pKCcas9d566 / S17-1 and Streptomyces lincolnensis NRRL2936 cultured in YEME medium until the hyphae were uniform and dense, collected by centrifugation and washed, resuspended in 2×YT medium, and spread on ISP4 medium together, at 28°C Cultured for conjugative transfer. After 18 hours of plate coating, 1 mL of sterile aqueous solution containing apramycin (Apramycin, 20 μg / mL) and nalidixic acid (Nalidixic acid, 25 μg / mL) was covered for screening. After continuing to ...
Embodiment 3
[0163] Example 3 Construction of genetically engineered bacteria Δ4481Δ6156
[0164] The PCR reaction conditions of this embodiment are the same as that of embodiment 2.
[0165] Step 1: The pKCcas9d6156 plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli S17-1. Cultured in LB medium to OD 600 =0.4 pKCcas9d6156 / S17-1 and the genetically engineered strain Δ4481 that was cultured in YEME medium until the hyphae were uniform and dense, collected by centrifugation and washed, resuspended in 2×YT medium, and spread on ISP4 medium together, at 28°C Cultured for conjugative transfer. After 18 hours of plate coating, 1 mL of sterile aqueous solution containing apramycin (Apramycin, 20 μg / mL) and nalidixic acid (Nalidixic acid, 25 μg / mL) was covered for screening. After continuing to culture at 28°C for 4-7 days, colonies of transformants can grow. Pick 10 transformant mycelia and transfer them to MS medium containing 20 μg / μL apramycin, continue culturing at 28°C for 3-5 days, then inoc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com