Tamarix hispida PHD3 transcription factor encoding gene and application thereof
A technology of tamarisk bristles and transcription factors, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to use PHD transcription factor coding genes to cultivate excellent salt-tolerant plants, and achieve the effect of obvious salt tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: Cloning of Tamarix bristles ThPHD3 gene
[0038] The seeds of Tamarix bristles were sown in the artificial soil prepared with peat soil and sand at a mass ratio of 2:1, placed at a relative humidity of 65-75% and a light intensity of 400 μmol m -2 ·s -1 , Grow in a greenhouse with an average temperature of 22±2°C. After 2 months of growth, use 0.3mol·L -1 NaHCO 3 The roots were irrigated with the solution for stress treatment, and the leaves and roots were taken at 0h, 12h, 24h and 48h respectively and put into liquid nitrogen for quick freezing for RNA extraction.
[0039] The CTAB method was used to extract the RNA of Tamarix seedlings in each stress treatment period, and the extracted RNA samples were sent to Shenzhen Huada Gene Technology Co., Ltd. for the construction and sequencing of the transcriptome library. The RNA sequencing results obtained in each processing period were compared and spliced, and the results after sequencing comparison and sp...
Embodiment 2
[0043]Example 2: Using bioinformatics software and online network resources to perform sequence analysis on the gene encoding the DHP3 transcription factor of Tamarix brix
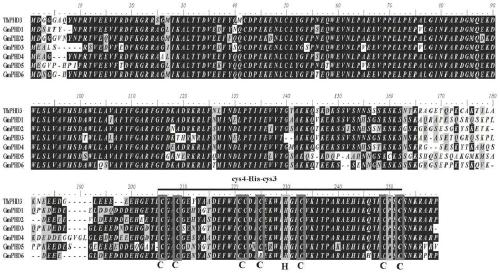
[0044] As shown in SEQ ID No: 1, the coding region of the gene coding for the DHP3 transcription factor of Tamarix biribilis cloned in Example 1 is 759 bp long, encoding 252 amino acids shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. Through BLASTx similarity analysis, it was found that there was a typical PHD domain (595-744bp) at the C-terminal of the gene. Combining ExPASy-PROSITE analysis and figure 1 It was shown that the C-terminus of the ThPHD3 protein sequence contains a conserved PHD domain, which is a typical ZF-PHD (Zinc finger PHD-type profile) protein.
[0045] For the obtained ThPHD3 gene, use ProtParam( http: / / au.expasy.org / tools / protparam.html ) software to calculate and deduce protein molecular weight and theoretical isoelectric point. Select soybean PHD family protein and Tamarix bristles ThPHD3 protein fo...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Analysis of the expression pattern of ThPHD3 gene under different abiotic stresses and hormone treatments
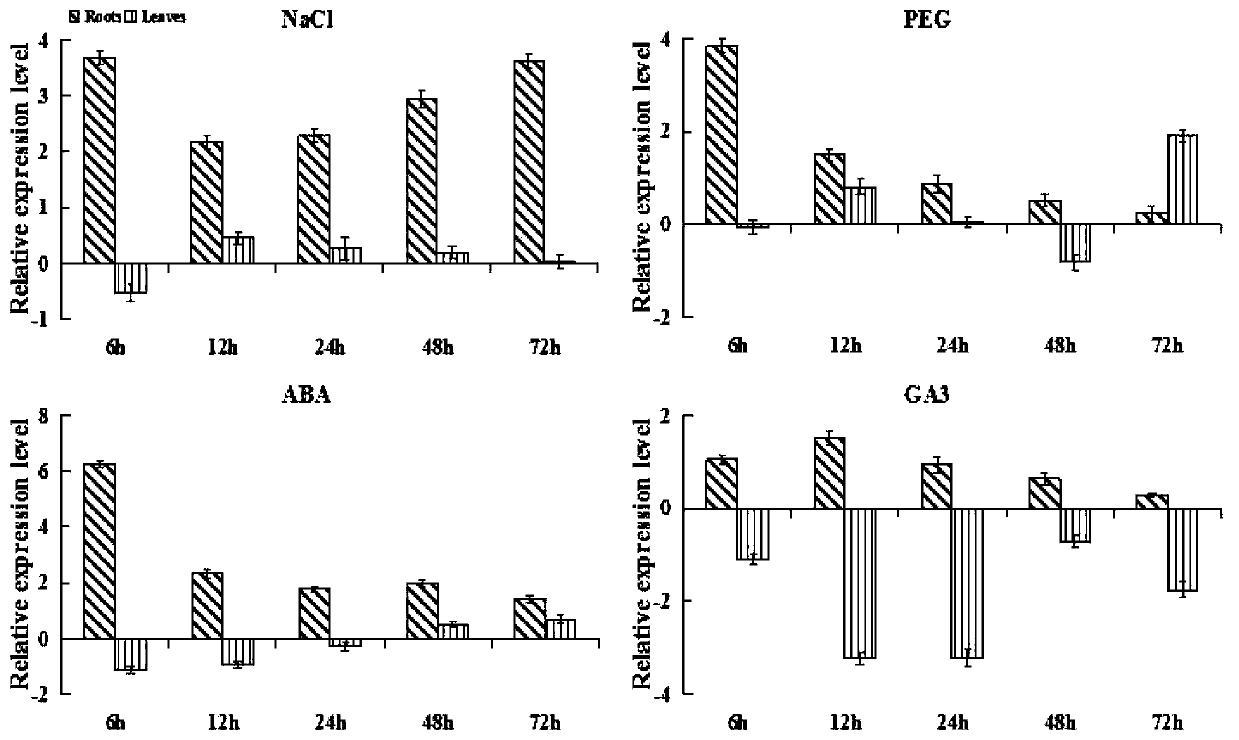
[0048] ThPHD3 transcription factor plays an important role in the regulation of plant stress resistance. A single Tamarix ThPHD3 gene with complete open reading frame was cloned and its sequence was analyzed. In order to study the function of Tamarix ThPHD3 gene, real-time fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR was further used to analyze its different abiotic stresses: high salt-400mmol NaCl, drought-20% PEG and hormone stress: ABA-100μmol, GA 3 Expression patterns under -50 μmol treatment condition. Using the same amount of control (0h), the cDNA of the roots and leaf tissues of Tamarix bristles at 6h, 12h, 24h, 48h and 72h of each treatment as templates, real-time quantitative RT-PCR amplification was carried out to detect the ThPHD3 gene of Tamarix bristles under different stresses. The expression situation under treatment, and β-actin, α-tubulin and β-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com