A preparation method and application of stainless steel wet hydrogen for improving thermal radiation coefficient
A heat radiation coefficient, stainless steel technology, applied in hot-dip plating process, coating, melt spraying, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the electric vacuum performance of the ray tube, affecting the service life of the ray tube, and reducing the vacuum degree of the ray tube. Accelerate heat conduction and heat dissipation performance, improve bonding force and wear resistance, and improve the effect of thermal radiation coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A method for preparing stainless steel wet hydrogen with improved thermal radiation coefficient, mainly comprising the following steps:
[0040] S1: Substrate treatment
[0041] Use acetone solution to ultrasonically treat the surface of the stainless steel substrate, then use deionized water to clean and dry the surface of the stainless steel substrate after ultrasonic treatment, and finally, use a suction sandblasting machine to roughen the surface of the stainless steel substrate after cleaning. The sand used is brown corundum, and the brown corundum is used to roughen the surface of the stainless steel substrate to increase the surface roughness of the stainless steel substrate, thereby improving the bonding force between the stainless steel substrate and the coating, thereby increasing the thermal radiation coefficient;
[0042] S2: Spray powder preparation
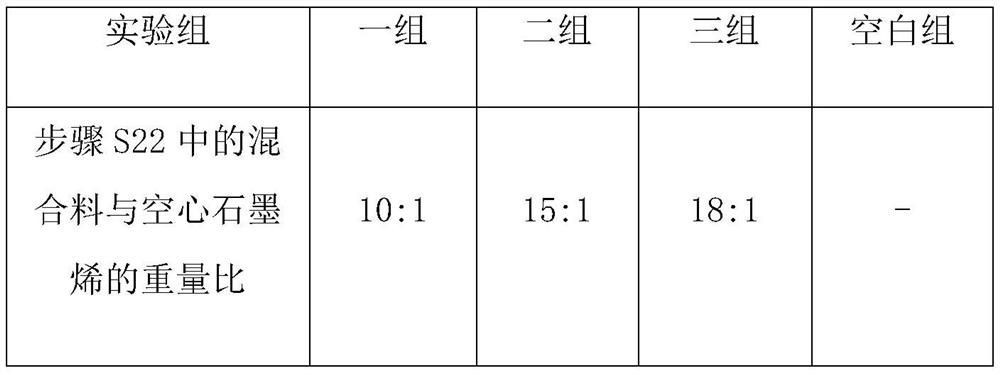
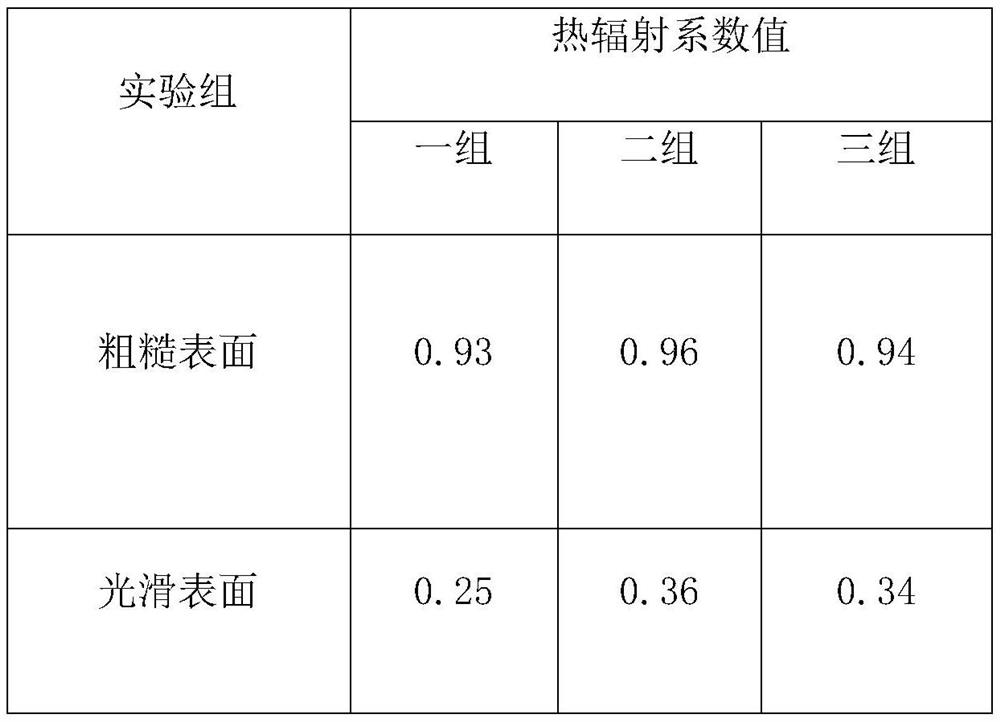
[0043] S21: Wet hydrogen powder making: take 2.3g of nickel sulfate hexahydrate, 20g of potassium sodium t...
Embodiment 2
[0055] A method for preparing stainless steel wet hydrogen with improved thermal radiation coefficient, mainly comprising the following steps:
[0056] S1: Substrate treatment
[0057] Use acetone solution to ultrasonically treat the surface of the stainless steel substrate, then use deionized water to clean and dry the surface of the stainless steel substrate after ultrasonic treatment, and finally, use a suction sandblasting machine to roughen the surface of the stainless steel substrate after cleaning. The sand used is brown corundum, and the brown corundum is used to roughen the surface of the stainless steel substrate to increase the surface roughness of the stainless steel substrate, thereby improving the bonding force between the stainless steel substrate and the coating, thereby increasing the thermal radiation coefficient;
[0058] S2: Spray powder preparation
[0059] S21: Wet hydrogen powder making: take 2.8g of nickel sulfate hexahydrate, 21g of potassium sodium t...
Embodiment 3
[0071] A method for preparing stainless steel wet hydrogen with improved thermal radiation coefficient, mainly comprising the following steps:
[0072] S1: Substrate treatment
[0073] Use acetone solution to ultrasonically treat the surface of the stainless steel substrate, then use deionized water to clean and dry the surface of the stainless steel substrate after ultrasonic treatment, and finally, use a suction sandblasting machine to roughen the surface of the stainless steel substrate after cleaning. The sand used is brown corundum, and the brown corundum is used to roughen the surface of the stainless steel substrate to increase the surface roughness of the stainless steel substrate, thereby improving the bonding force between the stainless steel substrate and the coating, thereby increasing the thermal radiation coefficient;
[0074] S2: Spray powder preparation
[0075] S21: Wet hydrogen powder making: take 3.5g of nickel sulfate hexahydrate, 22g of potassium sodium t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| emissivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com