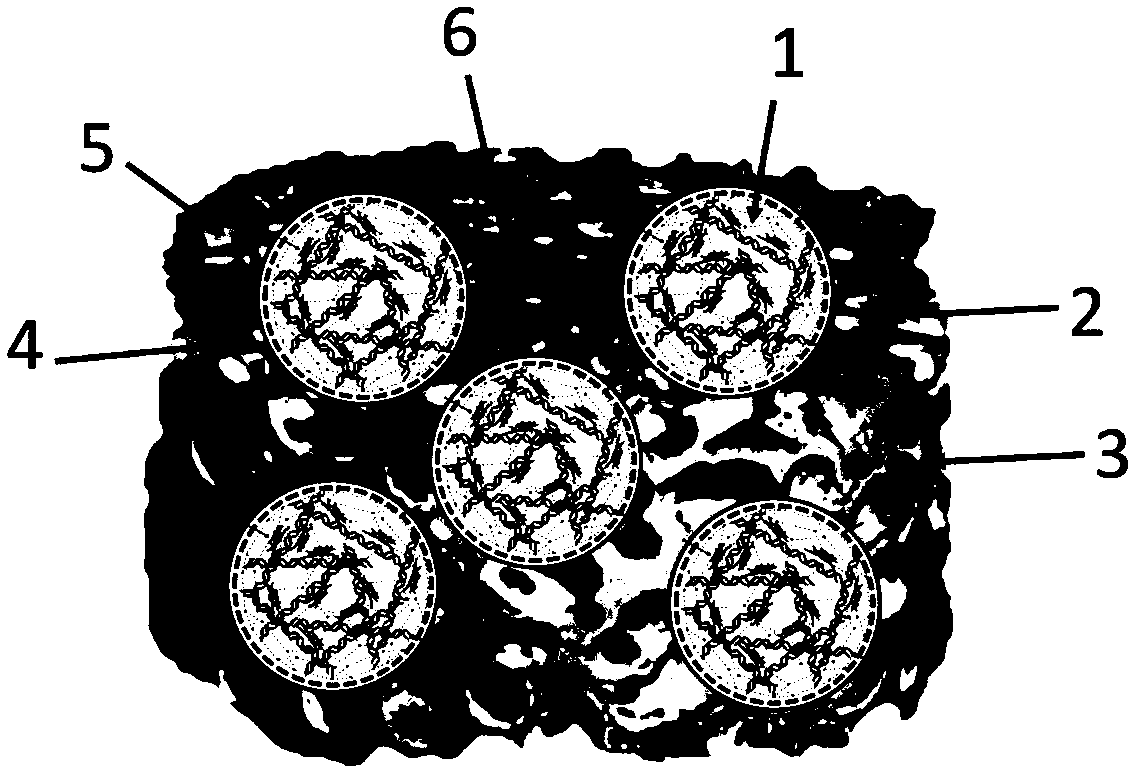
Artificial structure for rapidly regenerating vascularized tissue as well as construction method and application of artificial structure
A construction method and vascularization technology, applied in the field of artificial structures and their construction, can solve the problems of insufficient nutrient supply, cell necrosis, slow growth of blood vessels into implants, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0143] Example 1 Preparation of islet cells / hydrogel microspheres
[0144] Take conventionally cultured human pancreatic cells, use a sodium alginate / collagen mixture as a carrier material, and use a high-voltage electrostatic spray preparation device to make pancreatic cell / hydrogel microspheres:
[0145] 1. A solution of sodium alginate (Sigma-Aldrich, A0682) and a collagen solution (Sigma, C7661) were mixed to form carrier material solutions with final concentrations of 2% (w / w) and 1 mg / mL (w / v), respectively.
[0146] 2. Human pancreatic cells (PriCells, HUM-CELL-0058) were mixed with 10 6 The density per ml is uniformly mixed with the carrier material solution and filled into a disposable syringe with a volume of 5 ml.
[0147] 3. Connect the high-voltage electrostatic spraying cell microsphere preparation device. The high-voltage electrostatic generating device adopts SA167-Y (Tianjin) high-voltage electric field generator with an output voltage of 10kV; clamp the syri...
Embodiment 2
[0154] Example 2 Preparation of hepatic parenchymal cells / hydrogel microspheres
[0155] Take conventionally cultured human hepatic parenchymal cells and use sodium alginate / gelatin system as the carrier material, and use a high-voltage electrostatic spraying cell microsphere preparation device to make hepatocyte / hydrogel microspheres:
[0156] 1. Mix a solution of sodium alginate (Sigma-Aldrich, A0682) and a solution of gelatin (Sigma-Aldrich, G1890) (solvent PBS buffer solution or saline) to a final concentration of 2% (w / w) and 3% respectively (w / w) carrier material solution.
[0157] 2. Hepatocytes (PriCells, HUM-CELL-0036) were mixed with 10 6 The density per ml is uniformly mixed with the carrier material solution and filled into a disposable syringe with a volume of 10 ml.
[0158] 3. Connect the high-voltage electrostatic spraying cell microsphere preparation device. The high-voltage electrostatic generating device adopts SA167-Y (Tianjin) high-voltage electric field...
Embodiment 3
[0167] Example 3 Preparation of cervical cancer tumor cells / hydrogel microspheres
[0168] Take conventionally cultured cervical cancer tumors, prepare human cervical cancer tumor cell / hydrogel microspheres, and use sodium alginate / vitronectin system as the microsphere material:
[0169] 1. Sodium alginate solution and vitronectin solution were mixed to obtain solutions with final concentrations of 2% and 1 mg / ml, respectively, as the microsphere material precursor solution.
[0170] 2. Cervical cancer cells (ATCC, H1HeLa) were treated with 10 7 The density of each / ml is uniformly mixed with the carrier material precursor solution and filled into a disposable syringe with a volume of 10ml.
[0171] 3. Referring to step 3 in Example 2, cervical cancer tumor cell / sodium alginate / vitronectin microspheres were prepared.
[0172] 4. Collect the cell microspheres within 5 minutes, wash twice with normal saline and observe and record. The shape of the cell microspheres is round and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com