Protein N-terminal peptide fragment reverse enrichment method based on guanidination labeling
A guanidine and protein technology, which is applied in the field of reverse enrichment of protein N-terminal peptides based on guanidine labeling, can solve the problems of complex secondary fragment information, unfavorable peptide ionization, and interference with peptide identification, etc. Achieve the effect of improving secondary ion fragment information, improving ionization efficiency, and efficient enzyme cleavage rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
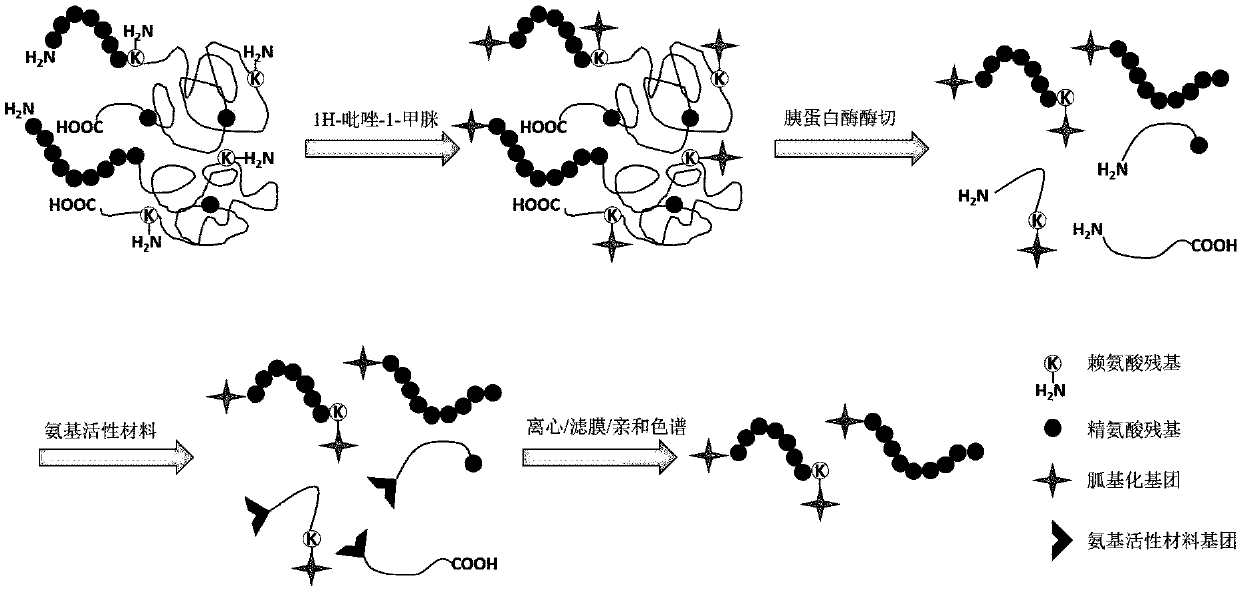
[0026] like figure 1 As shown, after reductive alkylation of the protein, the N-terminal amino group of the protein and the ε-amino group of lysine were guanylated using 1H-pyrazole-1-carboxamidine, and the guanidinylated Enzymatic digestion of protein to obtain peptides, use HPG-ALD or sixteen circles to label the enzyme-digested peptides, and use filter membrane or C18 reverse chromatography to remove non-protein N-terminal peptides, so as to realize the identification of protein N-terminal peptides Inverse enrichment.
[0027] Taking yeast as a sample, the yeast was first ground by liquid nitrogen grinding method, and the protein was extracted by using 6M guanidine hydrochloride. Take 200 μl of yeast protein with a concentration of 1 μg / μl for enrichment of N-terminal peptides. Add 2 μl of 1M dithiothreitol, denature at 56°C for 30 minutes, add 6 μl of 1M iodoacetamide and react in the dark for 30 minutes at room temperature, then add 6 μl of 1M dithiothreitol to the reac...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Taking yeast as a sample, the yeast was first ground by liquid nitrogen grinding method, and the protein was extracted by using 6M guanidine hydrochloride. Take 200 μl of yeast protein with a concentration of 1 μg / μl for enrichment of N-terminal peptides. Add 2 μl of dithiothreitol with a concentration of 1M, denature and reduce at 56°C for 30 minutes, add 6 μl of iodoacetamide with a concentration of 1M and react in the dark for 30 minutes at room temperature, and then add 6 μl of 100 with a concentration of 1M dithiothreitol to the reaction system, Incubate at room temperature for 30 min to terminate excess iodoacetamide, add 1H-pyrazole-1-carboxamidine and 500 mM triethylamine at a final concentration of 500 mM to the solution, and label at 95° C. for 15 min. Use formic acid to adjust the pH of the reaction system to 7-8, use a 10kDa filter to remove unreacted guanidinylation reagents, dissolve the protein in 200 μl of 50 mM HEPES, adjust the pH to 8.0, and add 4 μg ...
Embodiment 3
[0031]Taking yeast as a sample, the yeast was first ground by liquid nitrogen grinding method, and the protein was extracted by using 6M guanidine hydrochloride. After the protein was reductively alkylated, 1H-pyrazole-1-carboxamidine and 500 mM triethylamine were added to the solution at a final concentration of 500 mM, and labeled at 95° C. for 30 min. Add acetone with a final concentration of 80 to the reaction system, and place it at -20°C for more than 2 hours. Centrifuge to get the protein pellet, and wash three times with acetone at -20°C. Finally, the protein was dissolved in 50 mM TEAB solution, the amount of trypsin used was 1 / 50 of the protein mass, and digested at 37 degrees overnight. Add N-hydroxysuccinimide ester active agarose to the peptide generated after enzymatic hydrolysis, react at 25°C for 1 hour, then use 100mM Tris-Cl to terminate the active group on the amino active material, react at 37°C for 1 hour, Centrifuge at 2000rcf for 10min to separate the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com