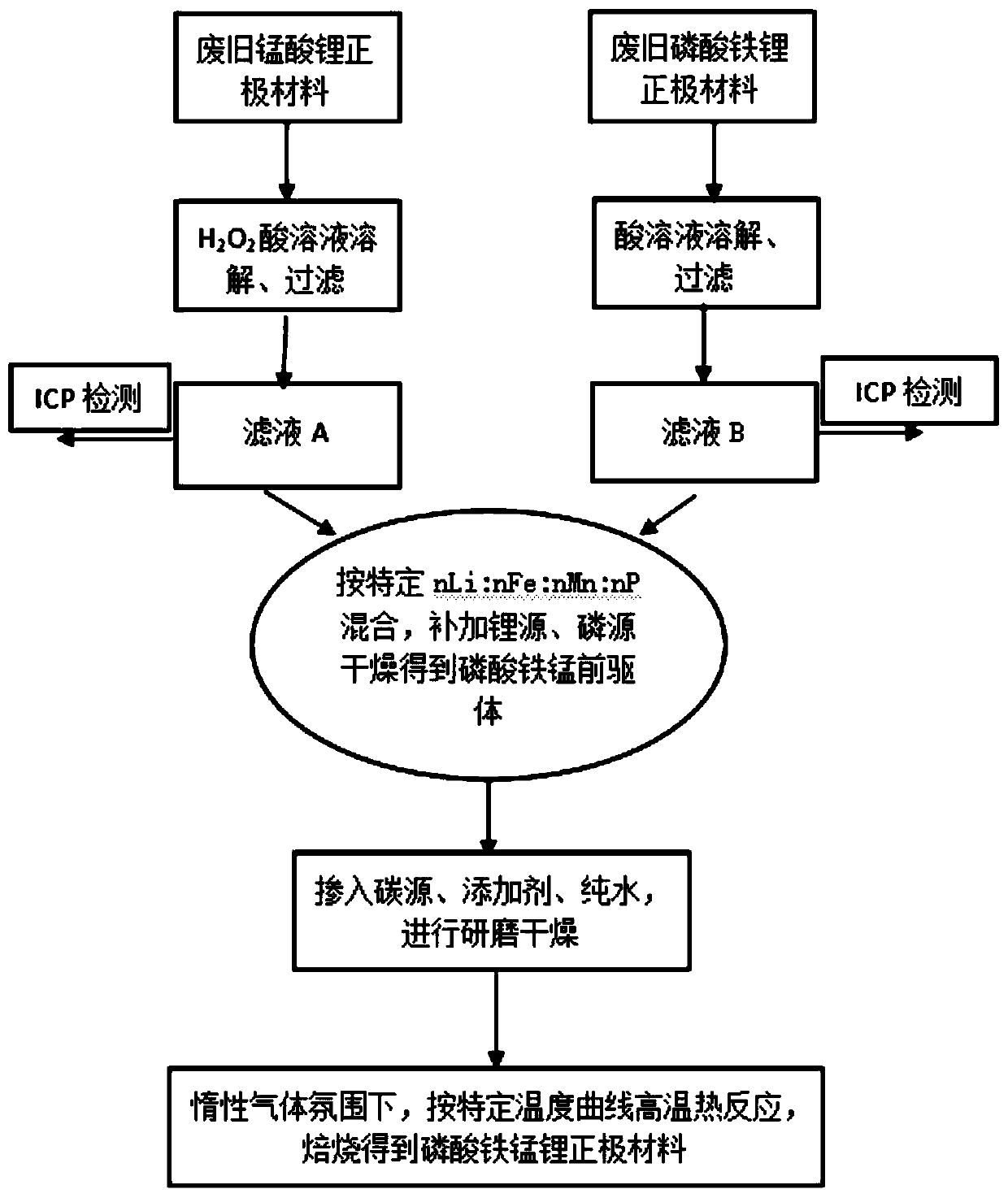
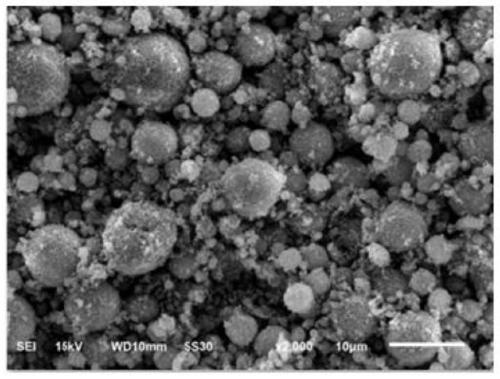
Method for preparing lithium iron manganese phosphate by using waste lithium iron phosphate and lithium manganate materials
A technology of lithium iron manganese phosphate and lithium iron phosphate, which is applied in the field of battery material recycling, can solve the problems of inability to recycle the positive electrode material of lithium batteries, inability to promote the development of the field of battery material recycling, and inability to form economic benefits, etc., to achieve good development Foreground, satisfactory energy density, high voltage platform effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] (1) Take the filtrate A and filtrate B obtained after the treatment in (1) above, mix according to filtrate A: filtrate B=0.69L: 3L, and set n according to the element molar ratio Li :n Fe :n Mn :n P =1.04:0.8:0.2:1, add 35.23g of lithium carbonate, 117.68g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, slowly add ammonia water dropwise under stirring at 85°C to adjust pH=9~10, after stirring for 8 hours, suction filter, wash and dry Dry to give a solid.
[0087] (2) Take the dried solids, glucose (carbon source), titanium oxide (additive), and pure water in step (1), and carry out batching according to the formula whose mass ratio of each substance is 200:20.8:0.87:300, and grind , Control the particle size of the slurry to 450-550nm, preferably 500nm.
[0088] (3) The slurry obtained after grinding in step (2) is spray-dried, the air inlet temperature is 260° C., and the air outlet temperature is 105° C. to obtain lithium iron manganese phosphate precursor powder.
[0089] (4...
Embodiment 2
[0091] (1) Take the filtrate A and filtrate B obtained after the treatment in (1) above, mix according to filtrate A: filtrate B=1.55L: 1.7L, according to the element molar ratio is n Li :n Fe :n Mn :n P =1.04:0.5:0.5:1, add 58.18g of lithium carbonate, 293.33g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, slowly add ammonia water dropwise under stirring at 85°C to adjust the pH=9~10, after stirring for 8 hours, suction filter, wash and dry Dry to give a solid.
[0092] (2) Take the dried solids, glucose (carbon source), titanium oxide (additive), and pure water in step (1), and carry out batching according to the formula whose mass ratio of each substance is 200:20.8:0.87:300, and grind , Control the particle size of the slurry to 450-550nm, preferably 500nm.
[0093] (3) The slurry obtained after grinding in step (2) is spray-dried, the air inlet temperature is 260° C., and the air outlet temperature is 105° C. to obtain lithium iron manganese phosphate precursor powder.
[0094] (...
Embodiment 3
[0096] (1) Take the filtrate A and filtrate B obtained after the treatment in (1) above, after mixing according to filtrate A: filtrate B=2L: 1.46L, according to the element molar ratio is n Li :n Fe :n Mn :n P =1.04:0.4:0.6:1, add 72.02g of lithium carbonate and 382.70g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, slowly add ammonia water dropwise under stirring at 85°C to adjust the pH=9~10, after stirring for 8 hours, suction filter, wash and dry A solid was obtained.
[0097] (2) Take the dried solids, glucose (carbon source), titanium oxide (additive), and pure water in step (1), and carry out batching according to the formula whose mass ratio of each substance is 200:20.8:0.87:300, and grind , Control the particle size of the slurry to 450-550nm, preferably 500nm.
[0098] (3) The slurry obtained after grinding in step (2) is spray-dried, the air inlet temperature is 260° C., and the air outlet temperature is 105° C. to obtain lithium iron manganese phosphate precursor powder. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com