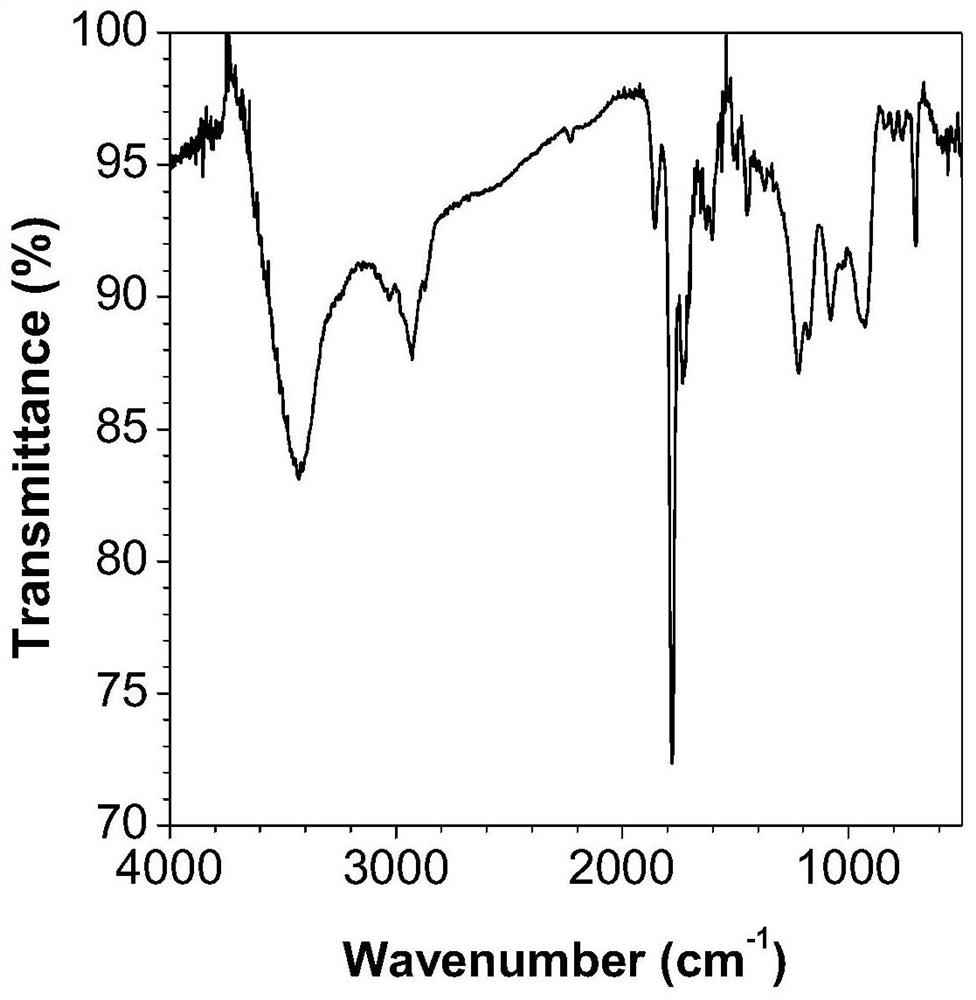
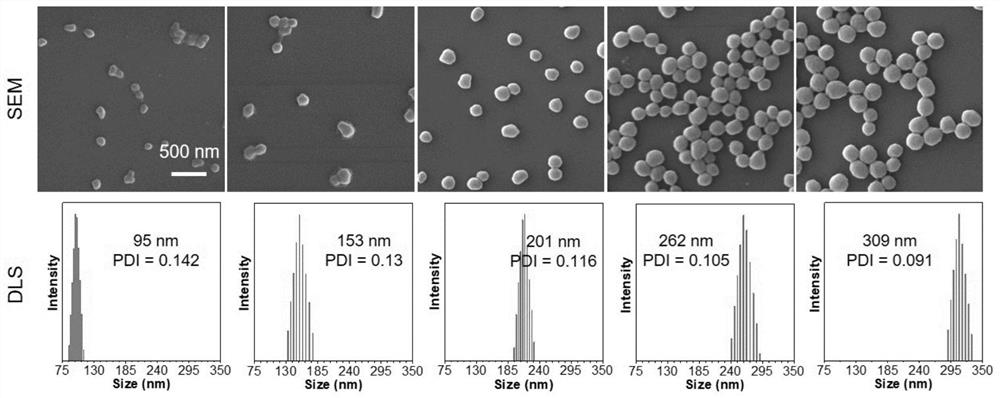
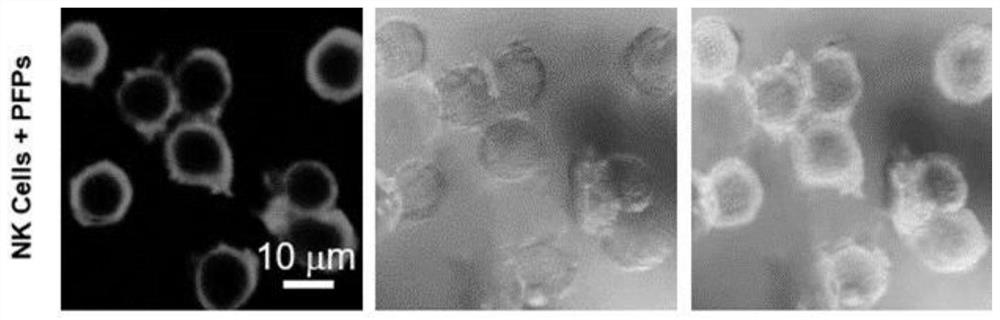
Fluorescent polymer based on aggregation-induced emission effect as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of aggregation-induced luminescence and fluorescent polymers, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, applications, luminescent materials, etc., can solve the problems of poor particle uniformity, low content of fluorescent molecules, and limited wide application, and achieve the effect of surface cleanliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Preparation of polymer particles containing AIE properties with controllable particle size: five sets of polymerization reaction solutions were respectively prepared, and the composition of each reaction solution was consistent. Among them, 0.05g of maleic anhydride, 0.04g of styrene, 0.005g of divinylbenzene, 0.01g of TPE-VBC, and 0.001g of azobisisobutyronitrile were added to a 50mL single-necked flask, and then 10mL of butyl acetate was added to The complete dissolution of the above reagents constitutes a set of polymerization reaction solutions. After the above five groups were passed through nitrogen and deoxygenated for 10 minutes, they were placed in a water bath at 50°C for polymerization. Take out a group of polymerization reaction solution at intervals of 10 minutes, centrifuge and wash three times with a mixed solution of ethyl acetate and petroleum ether, then place the product in a vacuum oven at 50°C, and vacuum-dry to obtain fluorescent polymer particles ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Preparation of polymer fluorescent nanoparticles with a particle size of 500 nm: Take 0.05 g of maleic anhydride, 0.04 g of styrene, 0.005 g of divinylbenzene, 0.01 g of TPE-VBC, and 0.001 g of azobisisobutyronitrile, and add 50 mL of single port In the flask, 10 mL of butyl acetate was then added to completely dissolve the above reagents. After passing nitrogen to remove oxygen for 10 minutes, place it in a 60°C water bath for polymerization. Polymer particles with a particle diameter of about 500 nm were obtained after polymerization for 120 minutes.
[0058] 0.1 g of the obtained fluorescent polymer particles were re-dispersed into 10 mL of 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.4) by ultrasound, and then left for 3 hours to completely disperse the polymer particles in the buffer solution. Subsequently, 0.05 g of powdered lipase was added to the mixed solution, placed in a shaker at 37° C. for 60 minutes to react, and then the polymer parti...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Preparation of polymer fluorescent nanoparticles with a particle size of 200 nm: Take 0.05 g of maleic anhydride, 0.04 g of styrene, 0.005 g of divinylbenzene, 0.087 g of TPE-V, and 0.001 g of azobisisoheptanonitrile, and add 50 mL of single-port In the flask, 10 mL of amyl acetate was then added to completely dissolve the above reagents. After passing nitrogen to remove oxygen for 10 minutes, place it in a 60°C water bath for polymerization. After 20 minutes of polymerization, polymer particles with a particle diameter of about 200 nm were obtained.
[0061] Cell labeling experiments
[0062] Take 0.1 g of the resulting fluorescent polymer particles and re-disperse them into 10 mL of 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.4) by ultrasound, and then leave it for 3 hours to completely disperse the polymer particles into the buffer solution, and then use PBS to buffer The solution was diluted to obtain a 10 g / mL dispersion of polymeric particles. Place natural killer ce...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com