Method for regulating proportion of S/G type lignin and improving degradation and conversion efficiency of cell walls by using laccase PtoLAC14
A lignin and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of improving lignin, and achieve the effect of reducing the content of G-type lignin, improving the degradability and reducing the total content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] 1. Example 1: PtoLAC14 gene cloning
[0022] Design specific primers, use Populus tomentosa cDNA as a template, perform PCR amplification, recover the product, and sequence to obtain the CDS sequence of PtoLAC14 with a length of 1677bp. The CDS sequence of PtoLAC14 is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The primers are as follows,
[0023] Forward primer: ATGGAGTACGCTTGCTGGCTCC (SEQ ID No. 2); reverse primer: TCAACATTTTGGAAGGTCGCTT (SEQ ID No. 3).
Embodiment 2
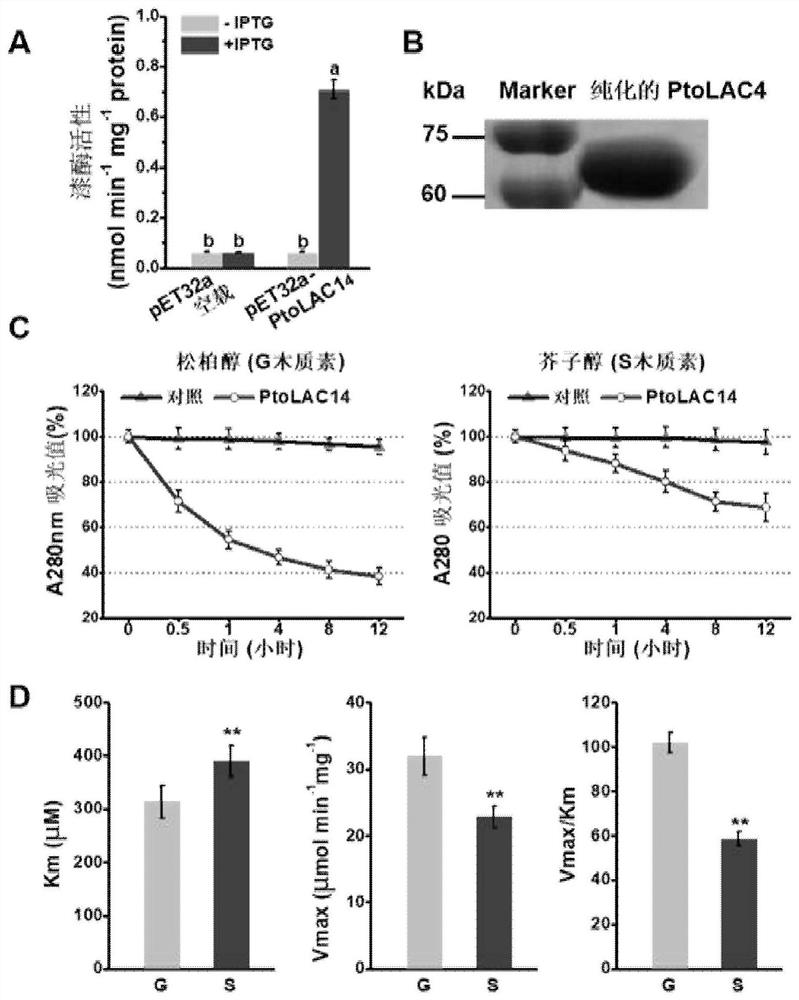
[0024] 2. Example 2: PtoLAC14 protein induction purification and enzyme activity assay
[0025] 1. Construct the prokaryotic expression vector of PtoLAC14 protein. The prokaryotic expression vector used in the present invention is pET32a + , the Escherichia coli strain for prokaryotic induced expression is BL21.
[0026] 2. Determination of laccase activity of PtoLAC14 fusion protein. The invention uses ABTS as a substrate to measure the laccase activity of PtoLAC14 fusion protein.
[0027] ABTS (2,2'-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzodihydrothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt) is a synthetic compound specially used for the determination of laccase activity. Enzymatic oxidation produces dark green cationic free radical ABTS + , ABTS at 420nm + The absorption coefficient of free radicals is much larger than that of the substrate ABTS. With ABTS + As the concentration of free radicals increases, the absorbance value becomes larger. The time elapsed when the absorbance value...
Embodiment 3
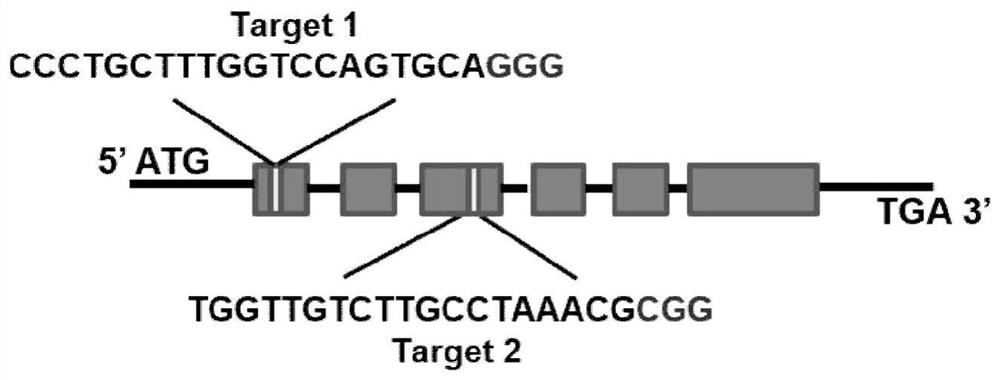
[0066] Three. Example 3: Construction of CRISPR / Cas9 editing vector
[0067] According to the CDS sequence of PtoLAC14, design the target sites at the 1st and 3rd exons respectively, connect to the U3b and U3d promoters, and connect to the pYLCRISPR / Cas9-DH / B vector backbone in sequence. The primers are as follows, Vector construction as attached figure 2 shown.
[0068] Target 1, forward primer: GTCACCCTGCTTTGGTCCAGTGCA (SEQ ID No.4), reverse primer: AAACTGCACTGGACCAAAGCAGGG (SEQ ID No.5);
[0069] Target 2, forward primer: GTCAGCGTTTAGGCAAGACAACCA (SEQ ID No.6), reverse primer: AAACTGGTTGTCTTGCCTAAACGC (SEQ ID No.7);
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com