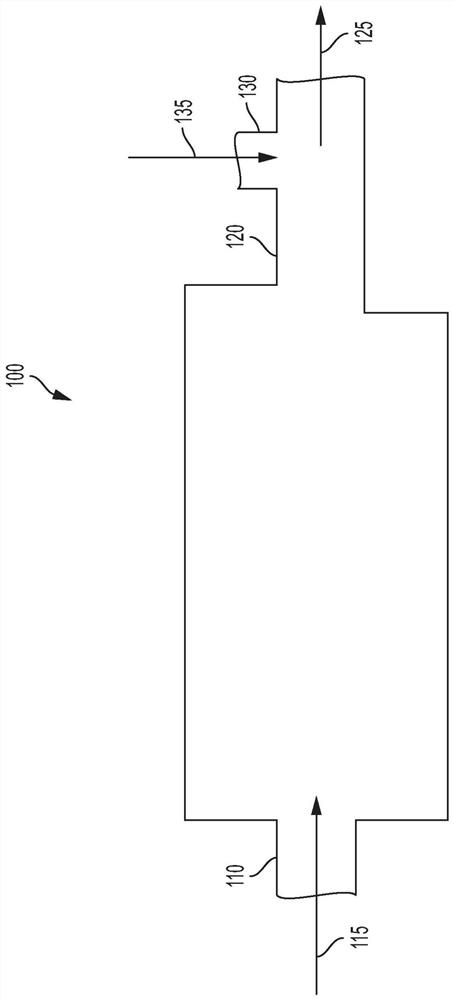
Ziegler-natta catalyst deactivation and neutralization
A Natta catalyst, catalyst technology, applied in the field of deactivation and neutralization, solution polymerization for the production of ethylene polymers, Ziegler-Natta catalyst deactivation and neutralization methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1 and comparative example 1
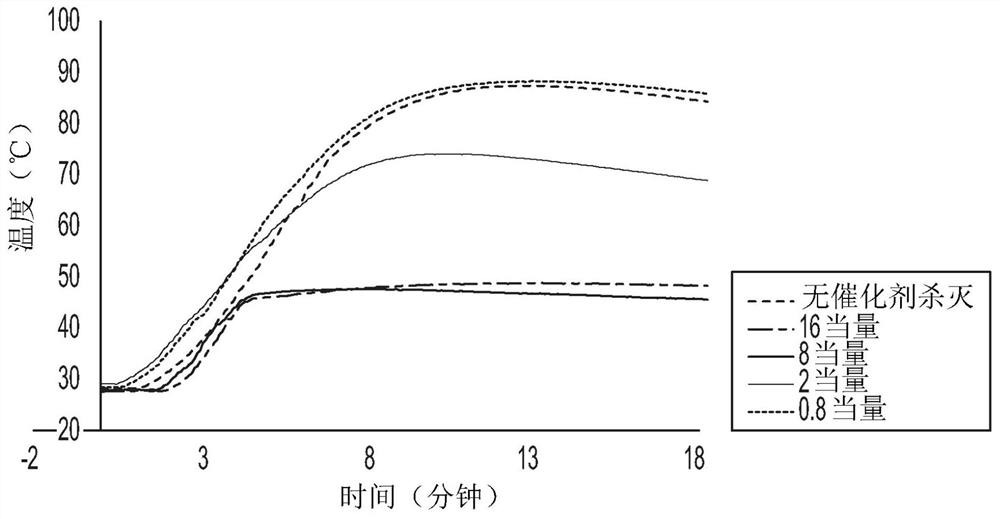
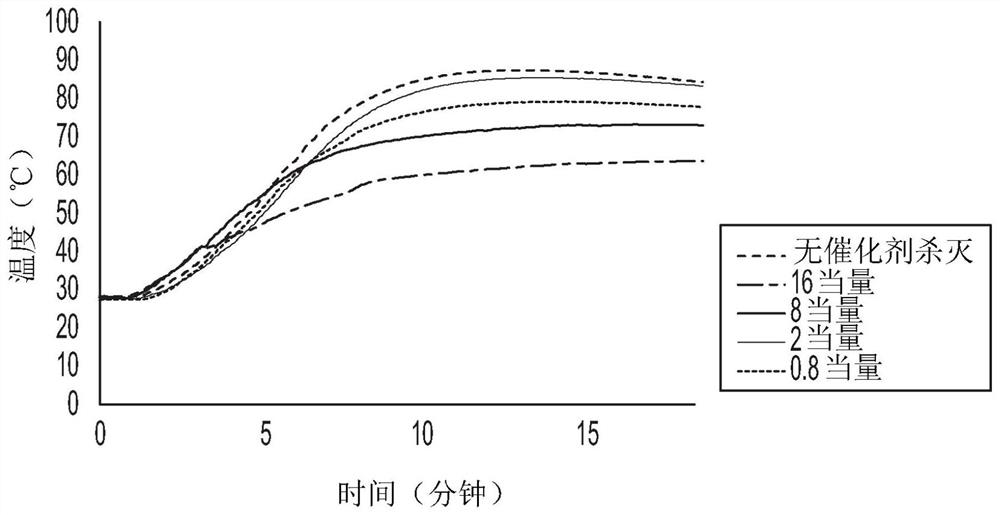
[0053] Example 1 and Comparative Example 1: Catalyst deactivation based on polyoctene test
[0054] The chemical reaction scheme for Example 1 is provided below.
[0055]
[0056] Reactions were performed in an inert atmosphere nitrogen purged glove box. In this glove box, 5.5 mL of 1-octene and 5.5 mL of Isopar-E (manufactured by ExxonMobil Chemical Company) were added to four 40 mL glass vials equipped with magnetic stirring bars. Insert the vial into the insulated slot of the magnetic stirrer block. A thermocouple was inserted through the vial's rubber septum to begin monitoring the temperature. To each of the four vials was added 40 μL of 1.0 M triethylaluminum in hexane (5 equivalents relative to Ti) followed by MgCl 2 Supported Ti-based Ziegler-Natta catalyst solution (8.00 μmol Ti). The vial was immediately sealed with a septum cap and the temperature of the reaction mixture was recorded every five seconds. When the temperature reached 40°C (approximately 10°C e...
example 2
[0058] Example 2: Comparison of HCl neutralization by different metal carboxylates
[0059] The chemical reaction scheme for Example 2 is provided below.
[0060]
[0061] M=Ca, Na, Zn, Mg
[0062] R=C 17 h 35 (stearyl), C 17 h 33 (oil based)
[0063] x=1, 2
[0064] 1 mL of Ziegler-Natta catalyst slurry solution (0.013M Ti) and 9 mL of Isopar-E were added to a 40 mL vial equipped with a stir bar and quenched with 10 mL of deionized water. After stirring at 70 °C for one hour, both the organic and aqueous layers became clear and colorless. The pH of the aqueous layer was acidic as determined by pH paper, indicating the presence of HCl formed in the hydrolysis by the Ziegler-Natta catalyst.
[0065] To neutralize HCl, a solution of the metal carboxylate (0.5, 1.0, 2.0, or 5.0 equivalents relative to the carboxylate) was injected into the vial, and the solution was stirred vigorously at 70 °C for 8 h while continuously monitoring the concentration of the aqueous layer...
example 3 and comparative example 3
[0070] Example 3 and Comparative Example 3: Precipitation Observation After Heating Ziegler-Natta Catalysts and Catalyst Killing Compounds (with and without TEA, 190°C)
[0071] Reactions were performed in a nitrogen purged inert atmosphere glove box. In a glove box, 0.25M calcium stearate, 0.25M zinc stearate and 0.25M magnesium stearate, 0.5M sodium stearate and 0.5M sodium oleate were prepared in Isopar-E. Placed in a 50mL round bottom flask. Additionally, 1 mL of HEC-3 catalyst solution (0.013M Ti) and 20 mL of hexadecane were added. For experiments using triethylaluminum, an additional 5 equivalents of TEA relative to Ti in HEC-3 were added. The solution was heated to 190° C., and then 1 mL of the different catalyst deactivator solution (approximately 250 g catalyst deactivator / g Ti) was added to the flask. Comparative Example 2 included a sample flask with no catalyst deactivator and a flask including calcium stearate as the catalyst deactivator, and Example 3 include...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com