Hydrogel for inflammatory resistance and repair and preparation method of hydrogel
A hydrogel, anti-inflammatory technology, applied in medical science, bandages, etc., can solve the problems of difficult-to-moisture necrotic tissue, waste of use cost, poor liquid delivery performance, etc., to improve liquid absorption and liquid delivery performance, and promote autolysis. Debridement and healing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
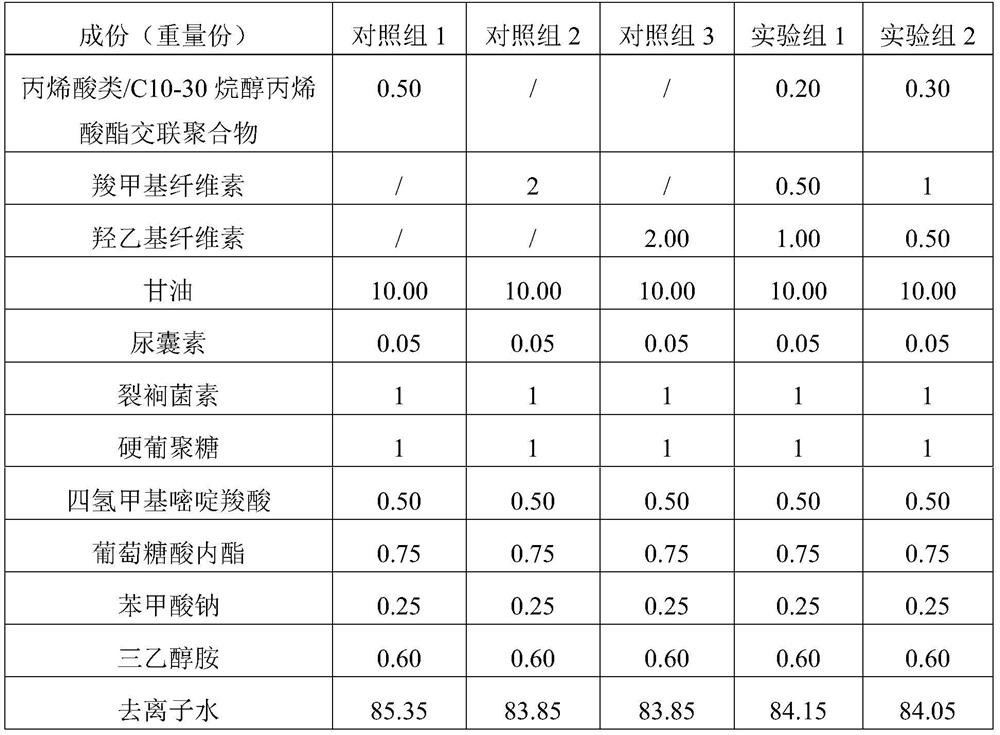
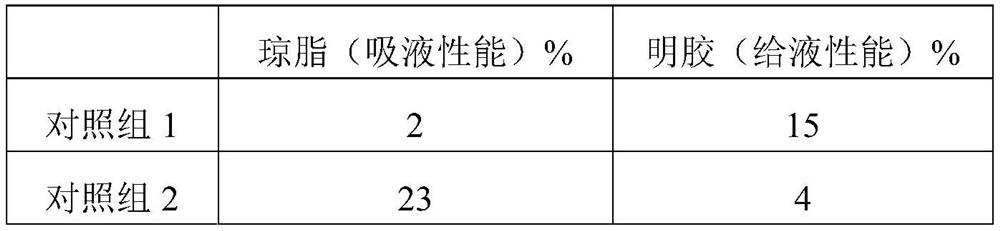
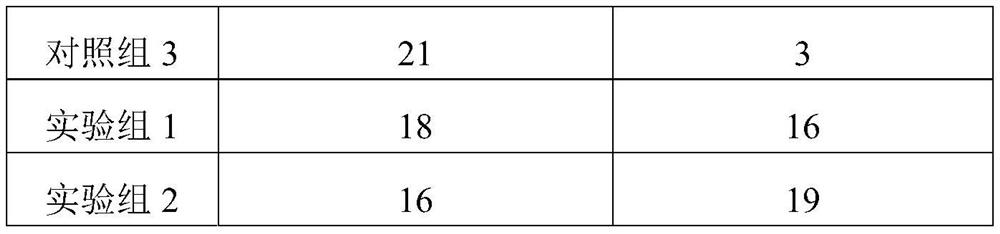
[0028] Influence of Compound Selection of Gel Matrix on Liquid Affinity
[0029] This test mainly measures the liquid absorption and liquid delivery properties of hydrogels by measuring the amount of liquid absorbed from agar and the amount of liquid delivered to gelatin. Agar simulated a lightly exuding wound, and gelatin simulated a dry, scabbed wound.
[0030] The hydrogels were prepared according to the following recipe.
[0031]
[0032] The preparation process is as follows:
[0033] S1. Soak the acrylic / C10-30 alkanol acrylate crosslinked polymer with an appropriate amount of deionized water and set aside;
[0034] S2. Mix and disperse carboxymethylcellulose, hydroxyethylcellulose and glycerin respectively, and set aside;
[0035] S3. Add an appropriate amount of deionized water into the reaction kettle, heat it to 65-75°C, add the pre-dispersed raw materials for S1 and S2, and after stirring, homogenizing, and vacuum defoaming, the product is in a uniform state; ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Effects of compounding of antiseptic system on antiseptic performance and cytotoxicity
[0062] The hydrogels were prepared according to the following recipe.
[0063]
[0064]
[0065] The preparation process is the same as in Example 1.
[0066] Anti-corrosion performance test:
[0067] Test method: Refer to the United States Pharmacopoeia USP42-NF37, 2019, chapter 51 for antiseptic efficacy test.
[0068] Test bacteria: Bacteria: Escherichia coli (ATCC No.8739); Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC No.6538); Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC No.9027); Fungi: Candida albicans (ATCC No.10231); Mold (ATCC No. 16404).
[0069] Judging criteria: bacteria: the logarithmic value of the number of bacteria from the initial day to 14 days cannot be less than 2.0, and the number of bacteria cannot increase from day 14 to day 28; fungi: the number of fungi cannot increase from day 14 to day 28.
[0070] test results:
[0071] Total number of bacteria (CFU / gram)
[0072] ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] The repairing effect of functional additives on skin damage and evaluation of anti-inflammatory efficacy
[0091] The hydrogels were prepared according to the following recipe.
[0092]
[0093]
[0094] The preparation process is the same as in Example 1.
[0095] Skin damage repair test:
[0096] experimental method:
[0097] 1. Solution preparation:
[0098] LPS (lipopolysaccharide): use serum-free 1640 culture medium to prepare a mother solution with a concentration of 500,000 / mL, filter and sterilize with a 0.22 μm filter membrane, store in a -20°C refrigerator, and dilute to a working solution of 10,000 / mL before use.
[0099] Hydrogel solution: Prepare a 5% experimental sample with LPS working solution, filter and sterilize with a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and store in a refrigerator at -20°C.
[0100] 2. Dosing treatment
[0101] Seed Raw264.7 cells in a 24-well plate at 1*105 / mL at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivate for 24 hours under the same conditions, add s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com