Expression vector and method for detecting membrane protein interaction in bacteria
A technology for expressing vectors and membrane proteins, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of affecting the interaction of membrane proteins, spending a lot of time, etc., to achieve the authenticity and reliability of test results, improve water solubility, and reduce degradation effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1, construction of expression vector pMAL-Th8H
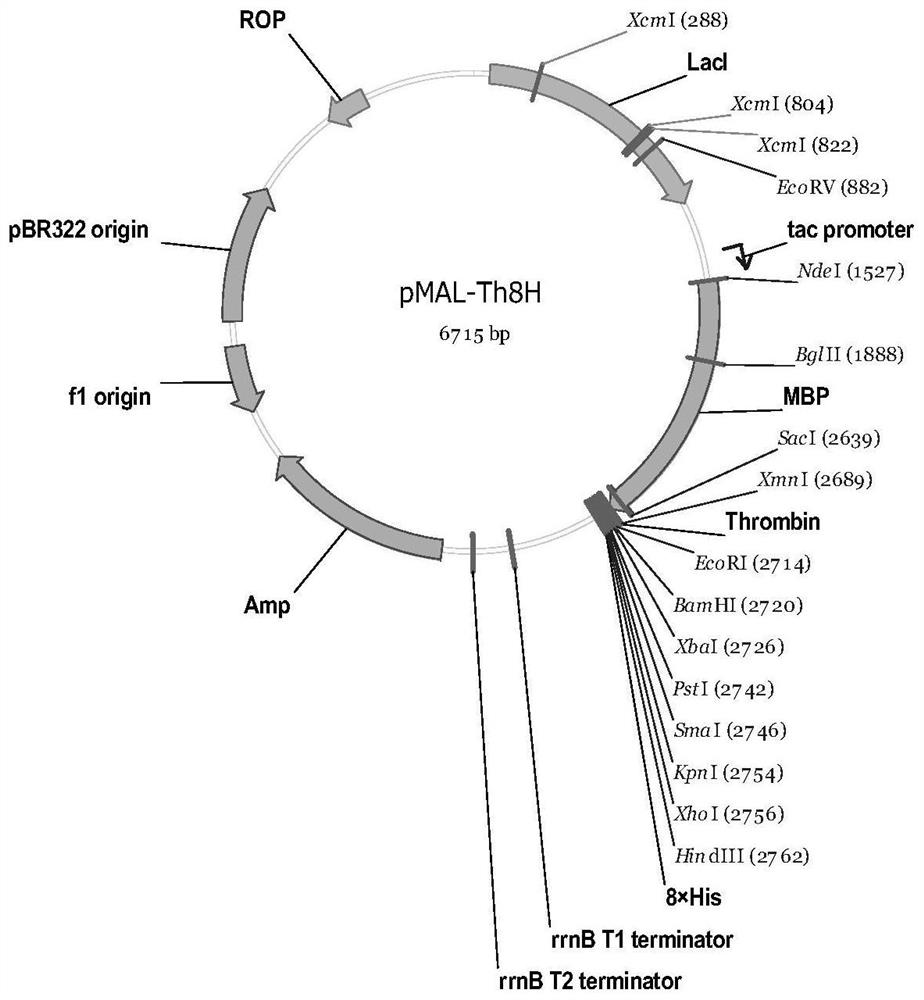
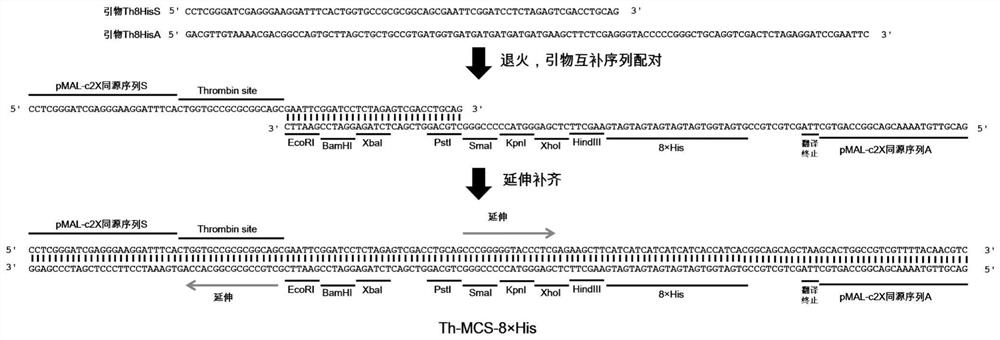
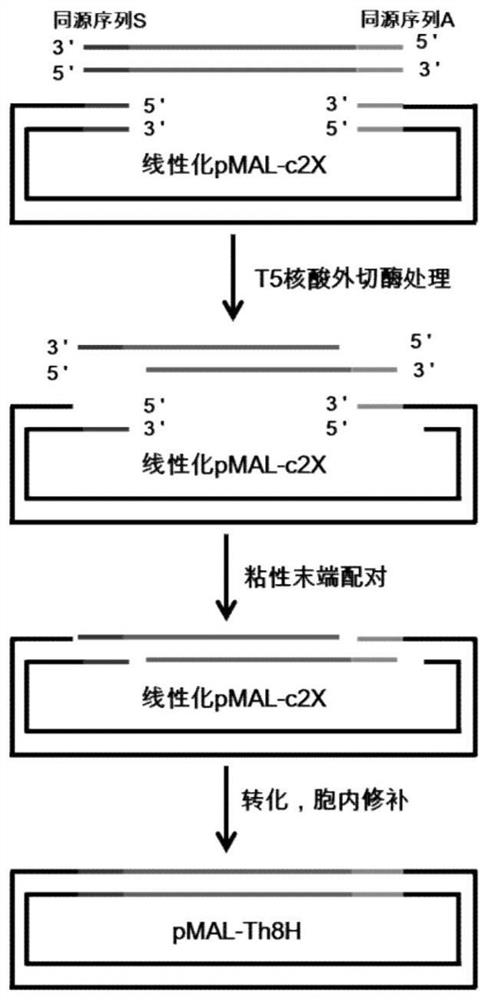
[0043] This implementation is to construct the protein expression vector pMAL-Th8H, using the commercial expression vector pMAL-c2X as the backbone, such as figure 1 As shown, the design adds the sequence of encoding thrombin (Thrombin) recognition site and 8×His tag (the number of His can be 6-10, the preferred 8 His in this embodiment) at the downstream of its MBP coding gene, and at the same time at the Thrombin position Eight common restriction endonuclease sites were inserted between the dot and 8×His, and a translation stop codon was inserted downstream of the 8×His tag. The total length of the sequence is 1275bp (including the MBP coding gene). The specific nucleotide sequence is shown in the sequence table Shown in SEQ ID NO.1.
[0044] S1. Synthesis of Th-MCS-8×His fragment. Forward and reverse primers were designed for both ends of the Th-MCS-8×His fragment, and then sent to a third-party Sangon Bioeng...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2. Expression and purification of membrane protein PP_0337 with pMAL-Th8H
[0056] PP_0337 is a phosphodiesterase in the model strain Pseudomonas putida KT2440, which localizes on the cell membrane and is responsible for degrading the second messenger c-di-GMP. It is difficult to obtain soluble PP_0337 protein by conventional expression methods. In this example, the vector pMAL-Th8H constructed in Example 1 was used to express and purify the PP_0337 protein. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0057] S1. PCR amplification of the gene encoding PP_0337. Using the genome of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 as a template, the PP_0337 coding gene was amplified by PCR, and the primer sequences used were as follows:
[0058] PP_0337S: 5'-CGGGATCCATGAAAAGCCAACCCGATG-3' (SEQ ID NO.5)
[0059] PP_0337A: 5'-CCCTCGAGACGCGGATAGCGCTTCAG-3' (SEQ ID NO. 6)
[0060] The product was recovered with a PCR recovery kit, and the length of the amplified product was 2676 bp, in...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3. Using His pull down assay to detect the interaction between membrane protein PP_0337 and CheA protein
[0067] CheA protein is a chemotactic kinase widely present in various Gram-negative bacteria and plays a key regulatory role in bacterial chemotaxis motility. Previous studies have used the bacterial two-hybrid method to confirm the interaction between CheA and PP_0337 protein in Pseudomonas, but this result was observed in the host bacteria Escherichia coli, and there is no more direct and intuitive in vitro result. In this example, the PP_0337 protein obtained in Example 2 is used to visually detect whether there is an interaction between PP_0337 and the CheA protein by using pull down technology. The operation process is as follows Figure 7 shown. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0068] S1. Expression and purification of CheA protein. First, using the genome of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 as a template, the CheA coding gene was amplified ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com