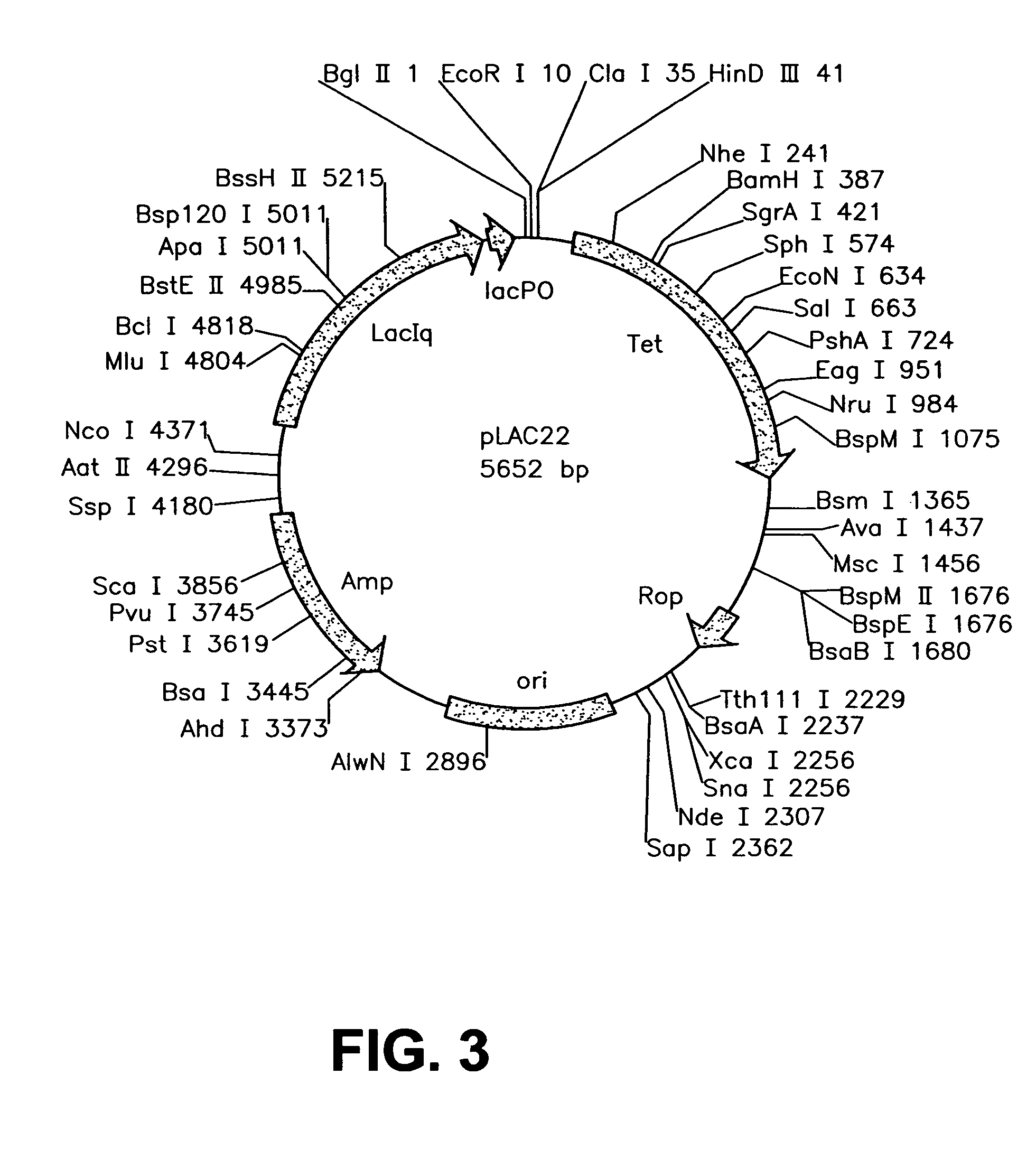
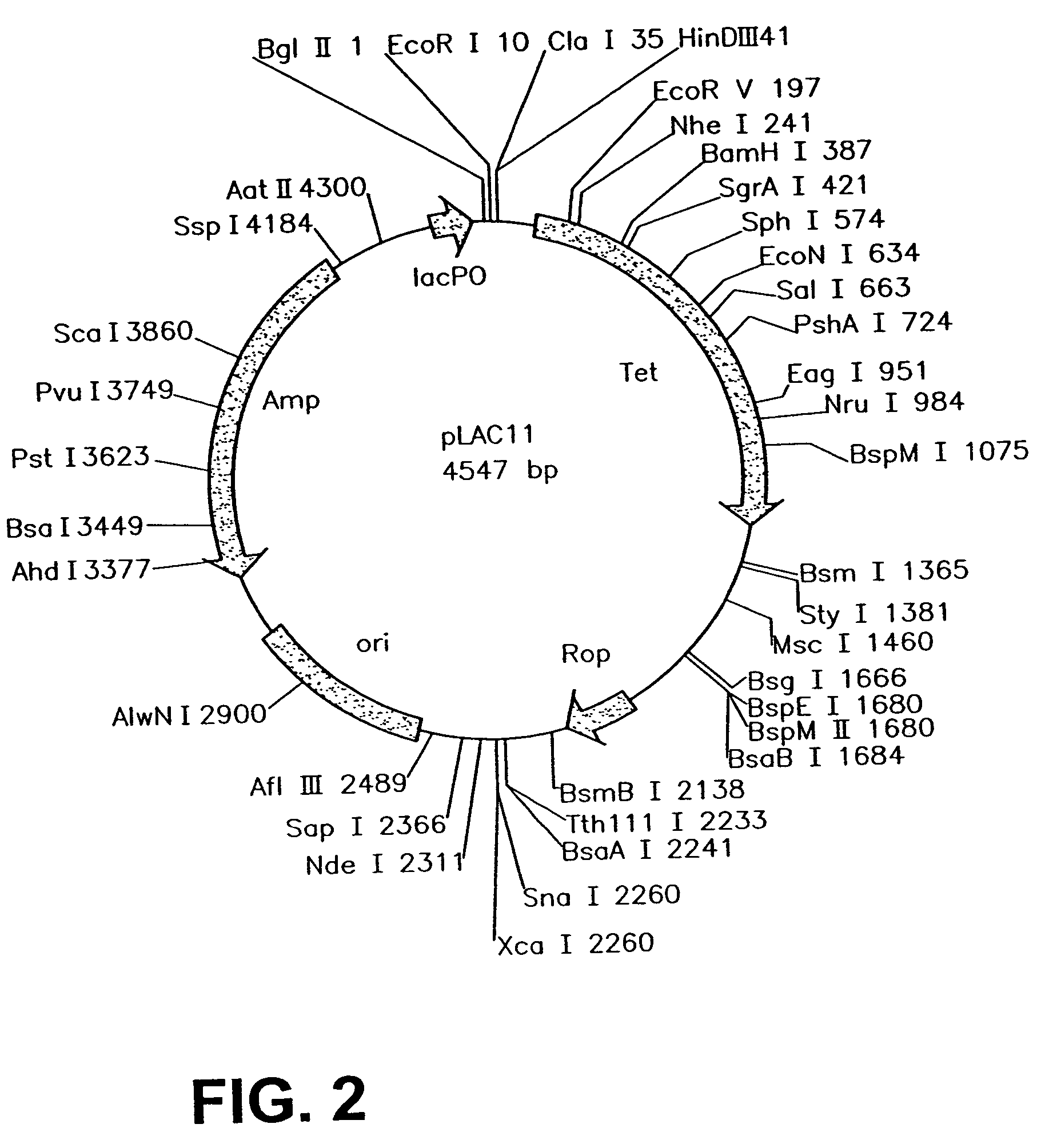
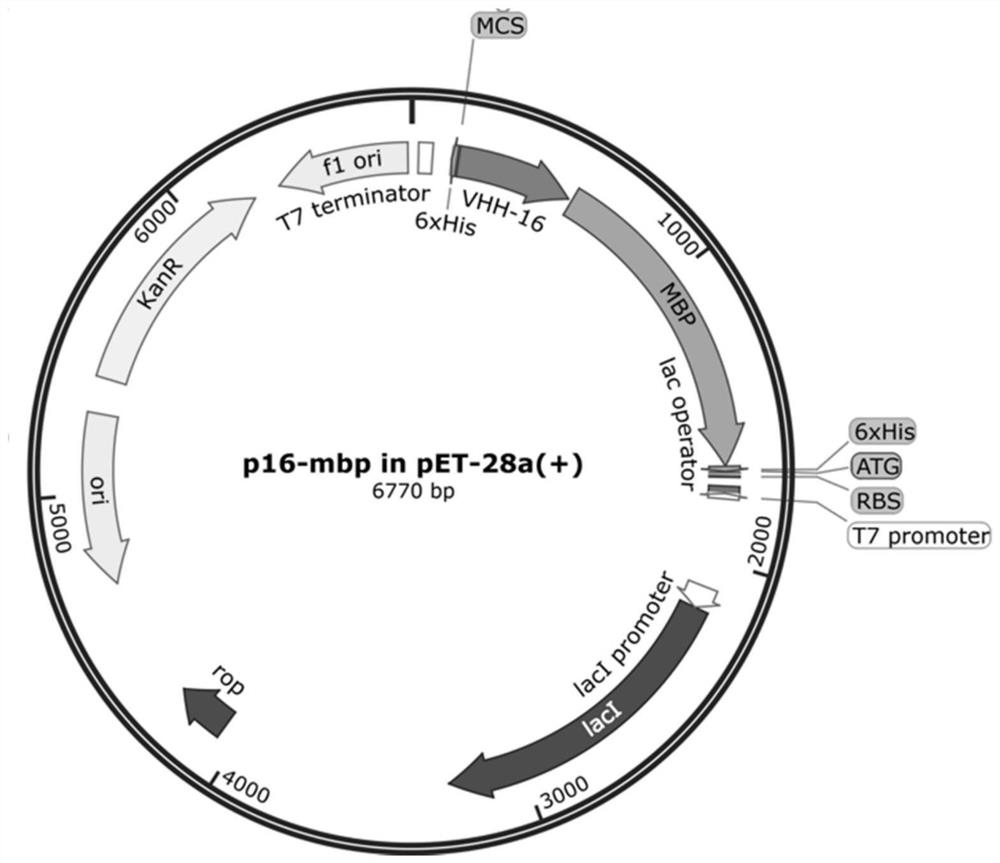
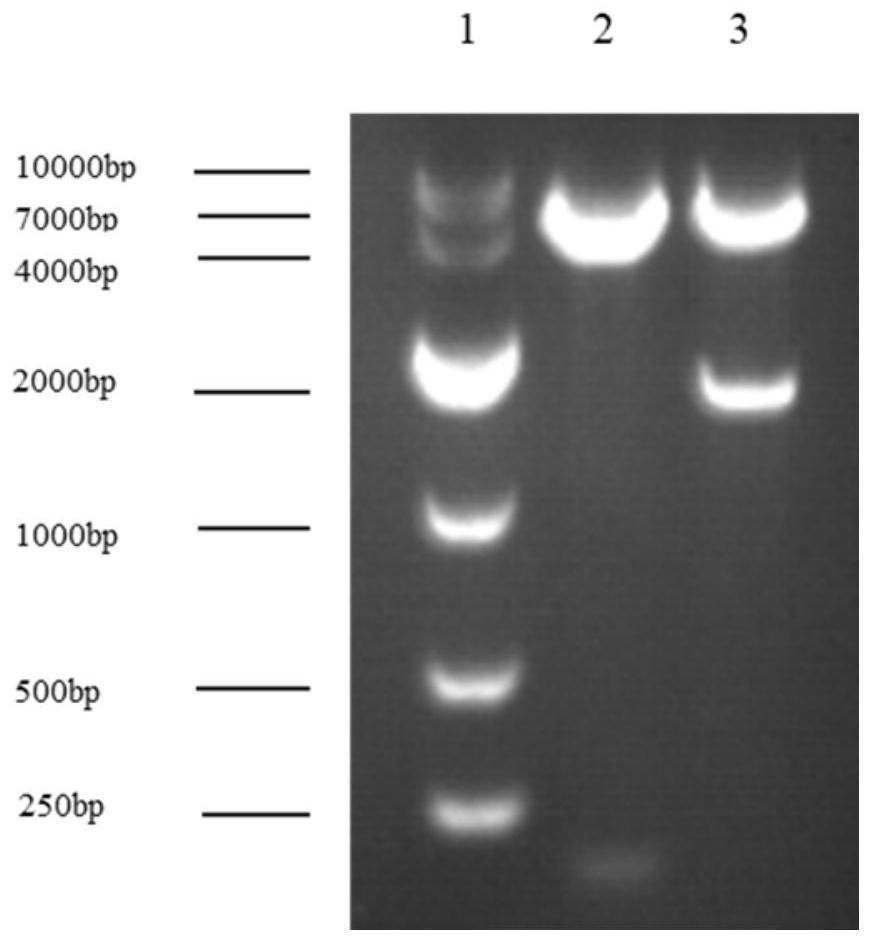
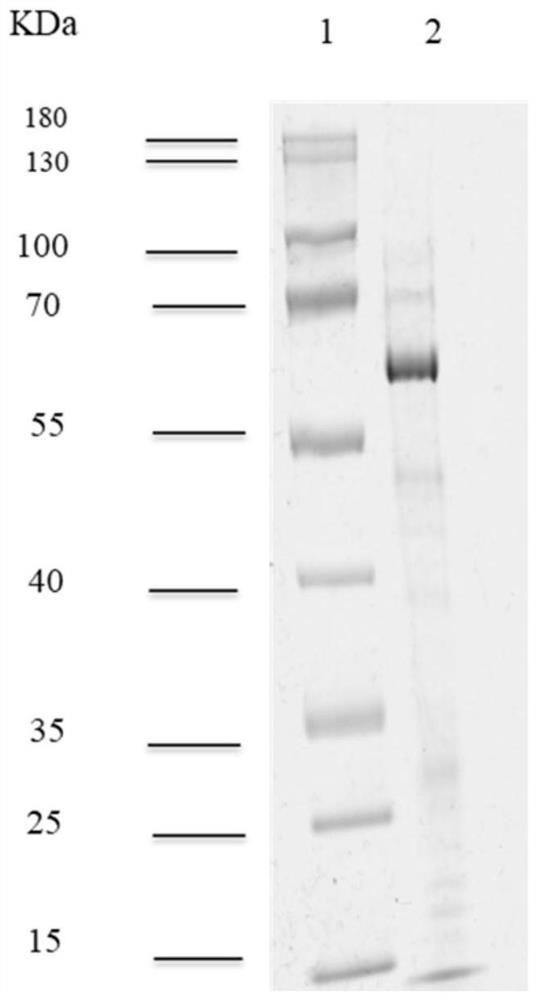
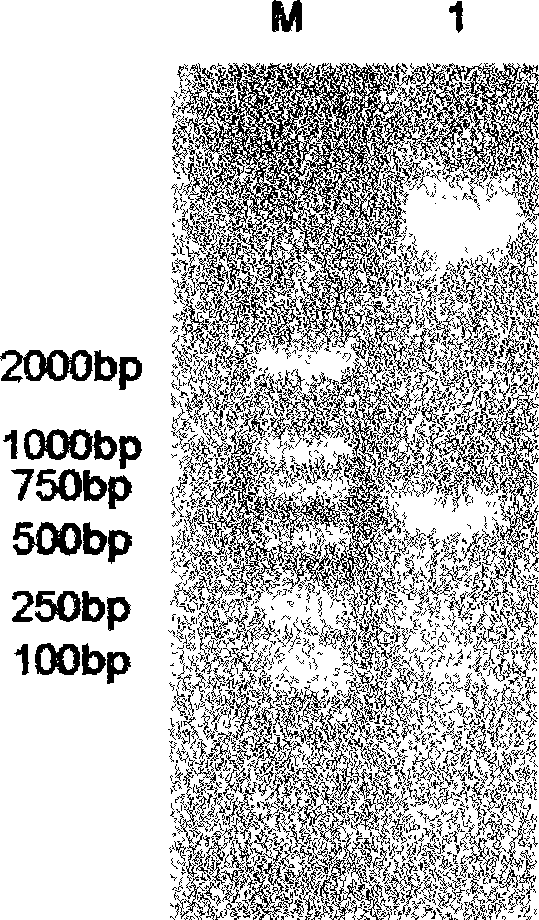Patents
Literature
63 results about "Maltose-binding protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Maltose-binding protein (MBP) is a part of the maltose/maltodextrin system of Escherichia coli, which is responsible for the uptake and efficient catabolism of maltodextrins. It is a complex regulatory and transport system involving many proteins and protein complexes. MBP has an approximate molecular mass of 42.5 kilodaltons.
Stabilized bioactive peptides and methods of identification, synthesis, and use
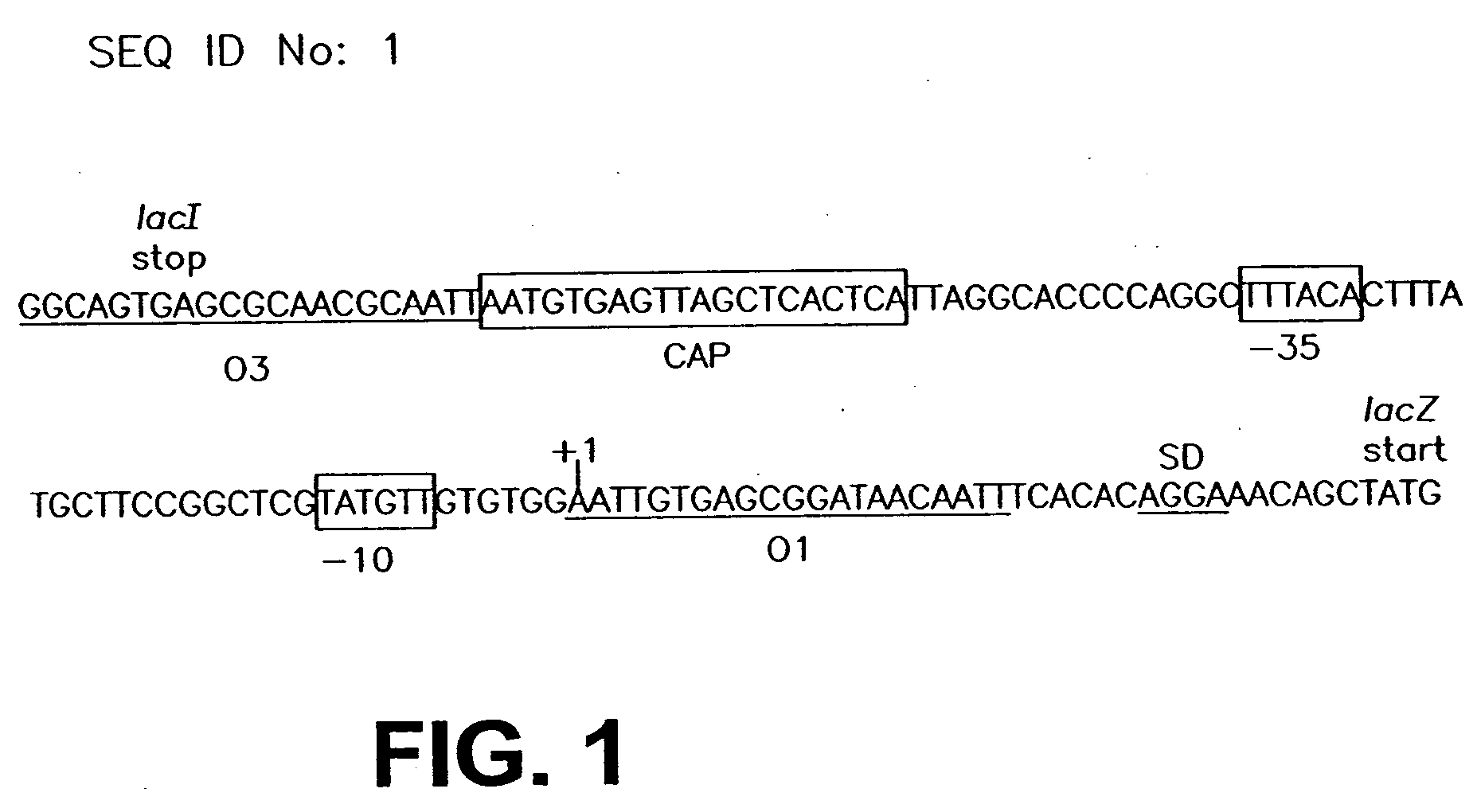
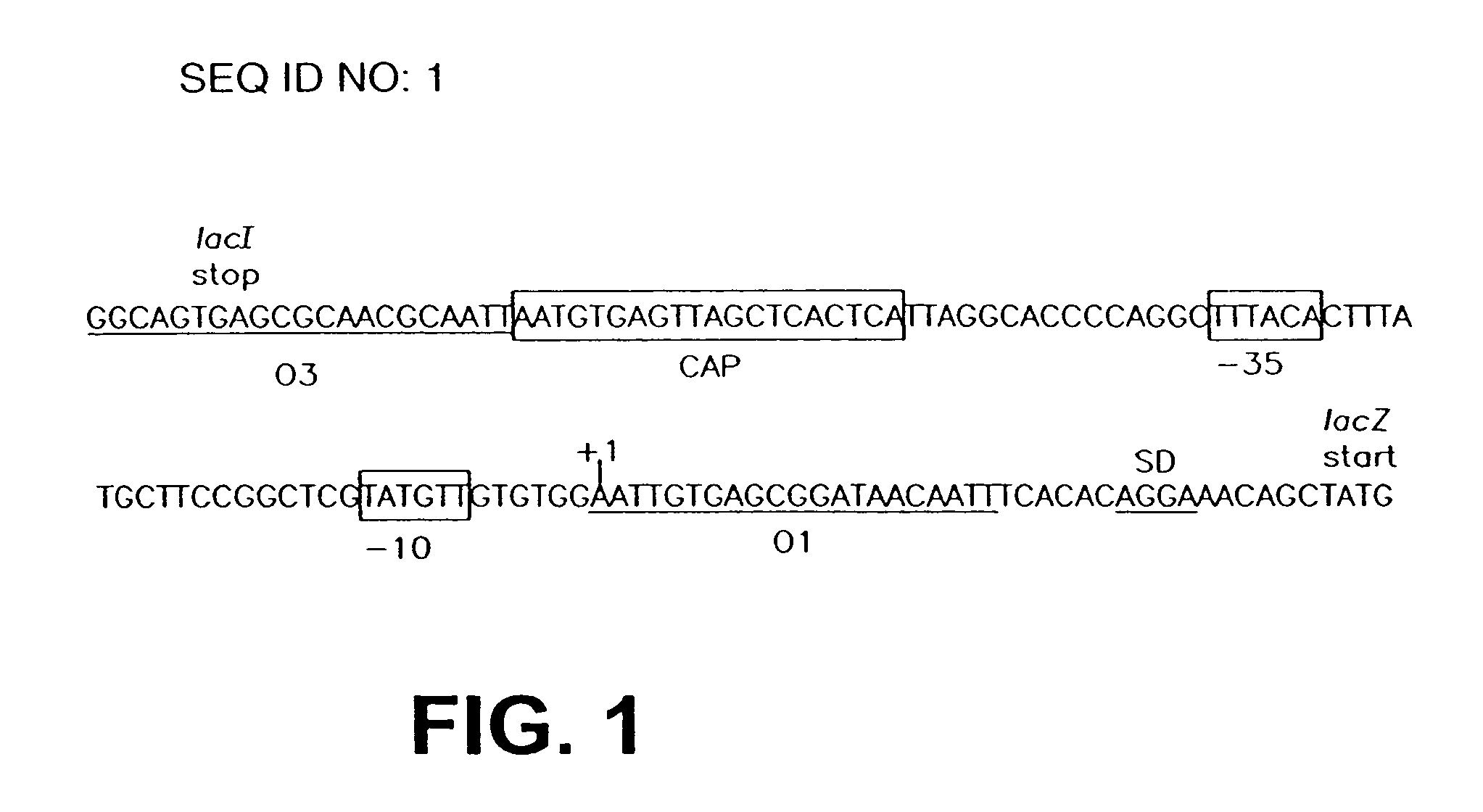
InactiveUS20060099571A1Slow down rate of intracellular degradationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsLac operonΑ helical
An intracellular selection system allows screening for peptide bioactivity and stability. Randomized recombinant peptides are screened for bioactivity in a tightly regulated expression system, preferably derived from the wild-type lac operon. Bioactive peptides thus identified are inherently protease- and peptidase-resistant. Also provided are bioactive peptides stabilized by a stabilizing group at the N-terminus, the C-terminus, or both. The stabilizing group can be a small stable protein, such as the Rop protein, glutathione sulfotransferase, thioredoxin, maltose binding protein, or glutathione reductase, an α-helical moiety, or one or more proline residues.
Owner:PEPTIDE BIOSCI
Combinant polypeptide for use in the manufacture of vaccines against Campylobacter induced diarrhea and to reduce colonization
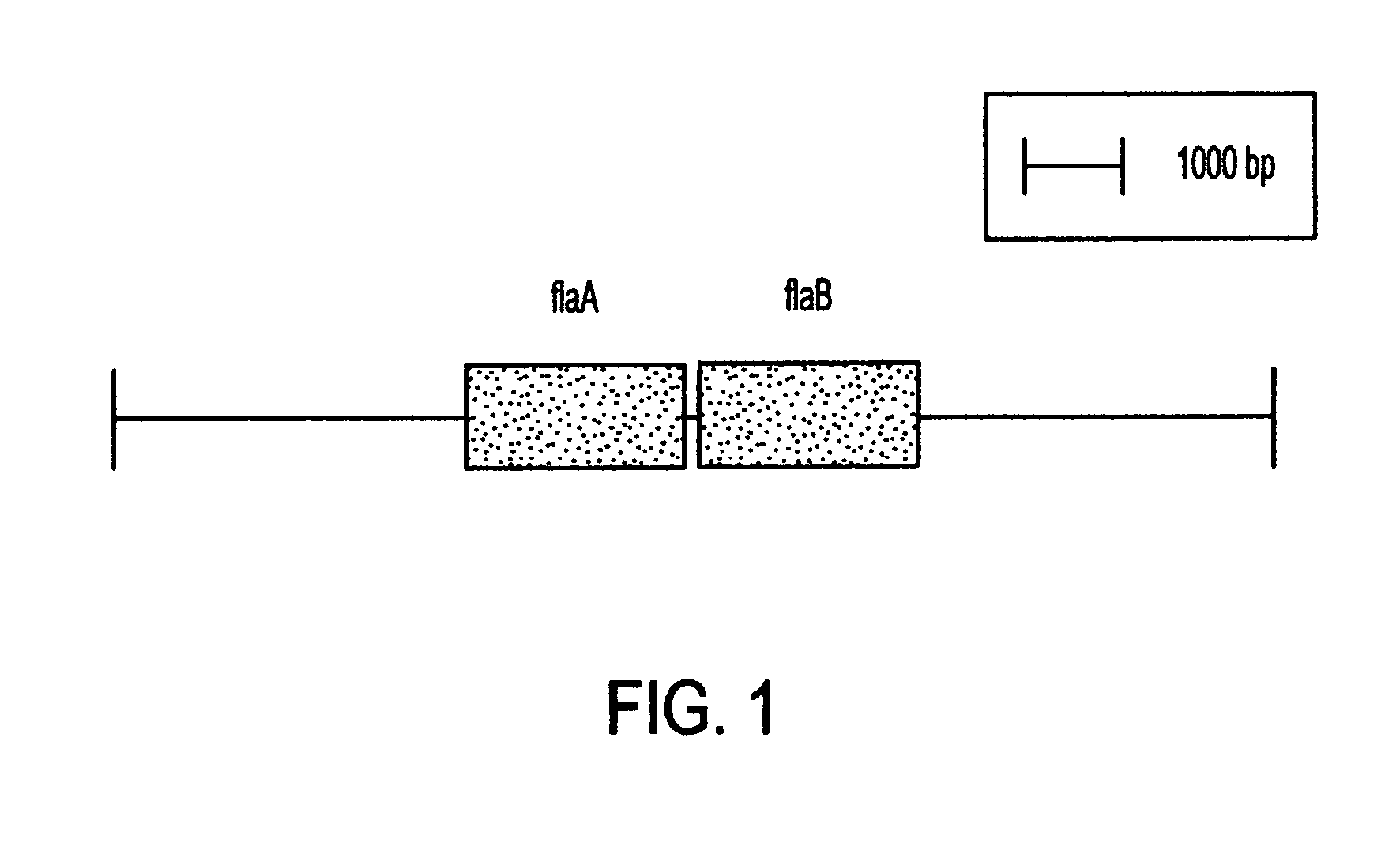
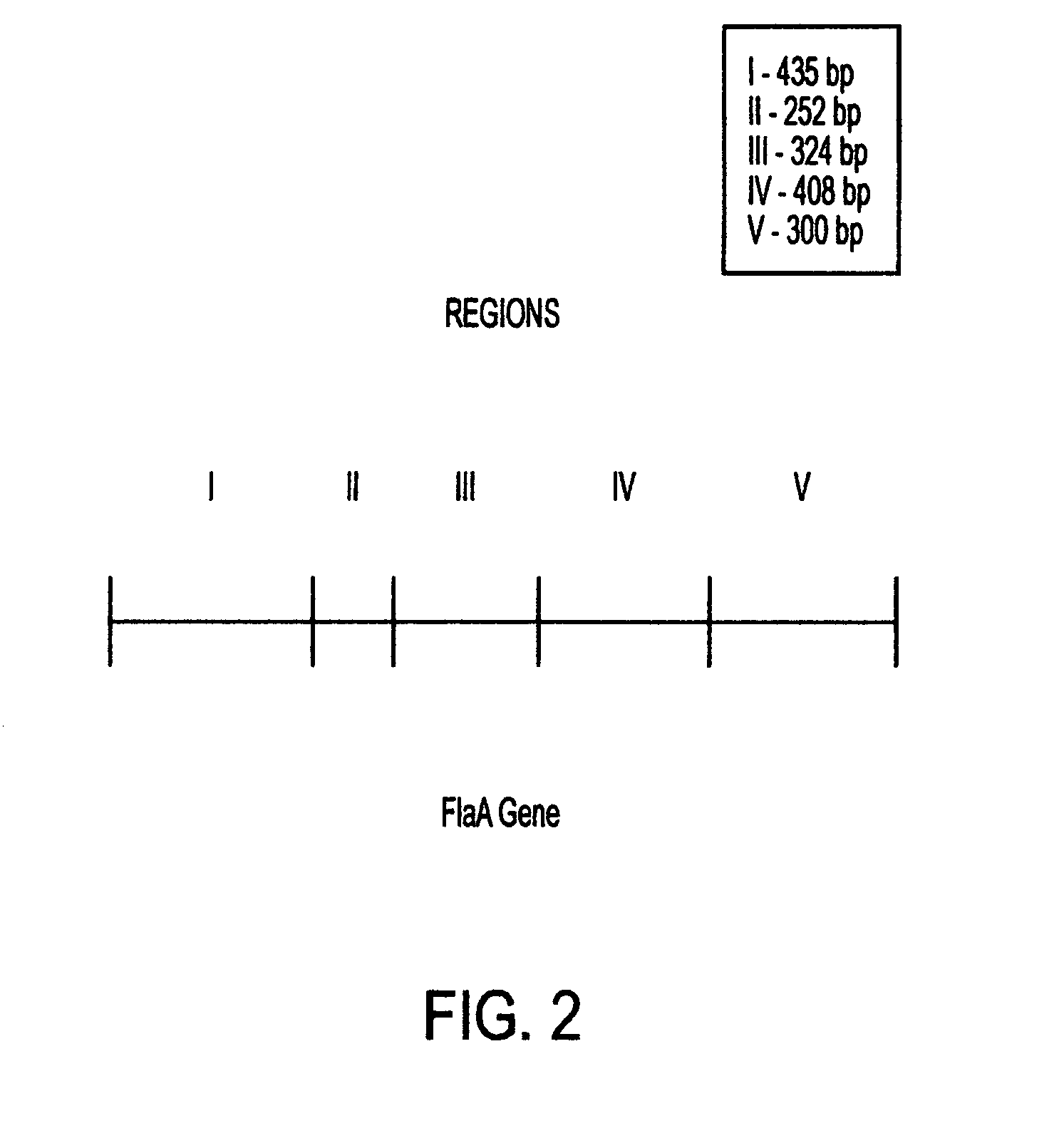
This invention comprises a recombinant protein comprising the maltose binding protein (MBP) of Escherichia coli fused to amino acids 5–337 of the FlaA flagellin of Campylobacter coli VC167 which has provided evidence of immunogenicity and protective efficacy against challenge by a heterologous strain of campylobacter, Campylobacter jejuni 81–176 in mammals. The invention further comprises a recombinant DNA construct encoding the immunodominant region (region I through III) of flagellin from Campylobacter spp. for use as a component of a vaccine against Campylobacter diarrhea. The invention therefore represents an effective treatment against Campylobacter but avoids inducing the autoimmune Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS), a post-infection polyneuropathy caused by Campylobacter molecular mimicry of human gangliosides which has hampered the development of vaccines heretofore.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Stabilized bioactive peptides and methods of identification, synthesis and use
Owner:PEPTIDE BIOSCI
Stabilized bioactive peptides and methods of identification, synthesis, and use
InactiveUS7365162B2Slow down rate of intracellular degradationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsLac operonWild type
An intracellular selection system allows screening for peptide bioactivity and stability. Randomized recombinant peptides are screened for bioactivity in a tightly regulated expression system, preferably derived from the wild-type lac operon. Bioactive peptides thus identified are inherently protease- and peptidase-resistant. Also provided are bioactive peptides stabilized by a stabilizing group at the N-terminus, the C-terminus, or both. The stabilizing group can be a small stable protein, such as the Rop protein, glutathione sulfotransferase, thioredoxin, maltose binding protein, or glutathione reductase, an α-helical moiety, or one or more proline residues.
Owner:PEPTIDE BIOSCI
Chondrosulphatase B fusion protein, and coding gene and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a chondrosulphatase B fusion protein, and a coding gene and a construction method thereof. The chondrosulphatase B fusion protein comprises maltose-binding protein. The invention also provides a method for purifying the chondrosulphatase B fusion protein. Furthermore, the invention also relates to a method for producing chondroitin sulfate B of low molecular weight.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Production of antimicrobial proteins in fusion proteins
InactiveUS7785828B1Polypeptide with affinity tagMicrobiological testing/measurementCysteine thiolatePolyhistidine-tag
The invention relates to a method of producing cysteine containing polypeptides in fusion proteins by recombinantly expressing in a host cell sequences encoding an antifungal polypeptide, a maltose binding protein, and a histidine tag. The method is carried out in the presence of a reducing agent to prevent misfolding of the fusion proteins.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Autoantibody assay method for immunological mediated I type diabetes diagnosis
InactiveCN1773282AImprove the detection rateMeet the determination requirementsPreparing sample for investigationEscherichia coliProtein target
The present invention relates to a self-body antibody detection method for immune mediated diabetes type A diagnosis, belonging to the field of biological medicine technology. Said invention includes the following steps: (1), using reverse transcriptive enzyme to make mRNA undergo the process of reverse transcription. Then using high fidelity DNA polymerase to respectively synthesize target DNA, using ligase and protein expression plasmid to make connection, making it be transformed into colibacillus to respectively express target protein; (2), using maltose-binding protein affinity chromatographic column and GST affinity chromotographic column to purify and separate out expression protein, dividing every purified expression protein into two portions; (3), coating antigen: making four antigens be mixed in the coating buffer solution, adding coating buffer solution in every enzyme-labeled well, standing still; (4), closing; and (5), using double-antigen sandwich method to determine antibody. Said invention can once detect any one or several kinds of antibodies of GAD65, IA2, Phogrin and ICA 69.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Plasmids encoding therapeutic agents
InactiveUS7252993B2Easy constructionHighly versatilePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesER retentionENCODE
Plasmids encoding anti-HIV and anti-anthrax therapeutic agents are disclosed. Plasmid pWKK-500 encodes a fusion protein containing DP178 as a targeting moiety, the ricin A chain, an HIV protease cleavable linker, and a truncated ricin B chain. N-terminal extensions of the fusion protein include the maltose binding protein and a Factor Xa protease site. C-terminal extensions include a hydrophobic linker, an L domain motif peptide, a KDEL ER retention signal, another Factor Xa protease site, an out-of-frame buforin II coding sequence, the lacZα peptide, and a polyhistidine tag. More than twenty derivatives of plasmid pWKK-500 are described. Plasmids pWKK-700 and pWKK-800 are similar to pWKK-500 wherein the DP178-encoding sequence is substituted by RANTES- and SDF-1-encoding sequences, respectively. Plasmid pWKK-900 is similar to pWKK-500 wherein the HIV protease cleavable linker is substituted by a lethal factor (LF) peptide-cleavable linker.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Method for improving solubility of foot-and-mouth disease protein for immunization
The present invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of a vaccine, and particularly relates to a method for improving the solubility of a foot-and-mouth disease protein for immunization. The method is by adding an His6-MBP protein tag in the C terminal of the foot-and-mouth disease protein by the mean genetic engineering in FMD protein by genetic engineering, so as to increase the solubility of the foot-and-mouth disease protein; the His6 represents the 6 histidine tags, and MBP represents a maltase binding protein. The present invention also provides an immune FMD protein CDG276 aiming at type A FMD prepared by the method. Compared to the FMDV VPI protein prepared by the existing genetic engineering, the FMD protein prepared by the invention has obvious increased the expression level; and due to the addition of soluble label maltose binding protein (MBP), the expressed FMDVA1 soluble protein has significantly increased solubility; therefore, the method has good application value.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Antivariant streptococcus polypeptide and use thereof and preparation method
InactiveCN101423554ALow costTo achieve the purpose of sterilizationPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemEscherichia coliSphaerotrichia divaricata
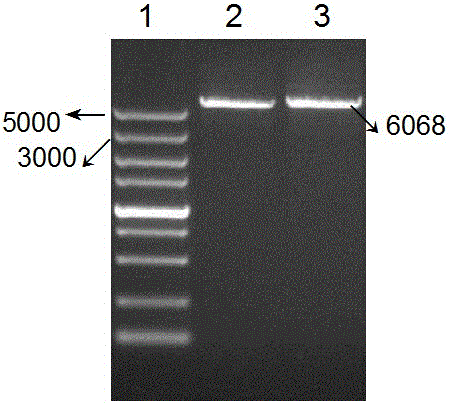
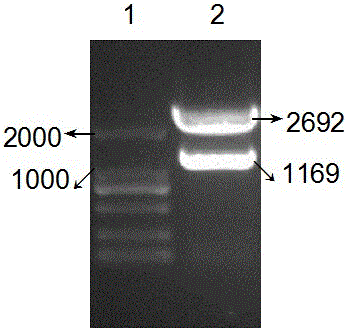
The invention belongs to the biological medicine field, and in particular relates to anti-variation streptococcus polypeptide, application and a preparation method thereof. The method is characterized in that the gene clone technique is adopted to establish MBP, Colicin Ia channel domain and CSP fudion gene, and obtain high efficiency expression in the Ia. The invention also discloses a ribonucleotide sequence for encoding recombinant polypeptide, and recombinant plasmid. The antibiotic polypeptide uses cariogenic Streptococcus mutans to forms an ion channel directly on a cell membrane of a target cell to achieve the bactericidal aim.
Owner:STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL NO 4 ARMY SURGEON UNIV PLA
Plasmids encoding therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20050202561A1Easy constructionHighly versatilePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesER retentionEukaryotic plasmids
Plasmids encoding anti-HIV and anti-anthrax therapeutic agents are disclosed. Plasmid pWKK-500 encodes a fusion protein containing DP178 as a targeting moiety, the ricin A chain, an HIV protease cleavable linker, and a truncated ricin B chain. N-terminal extensions of the fusion protein include the maltose binding protein and a Factor Xa protease site. C-terminal extensions include a hydrophobic linker, an L domain motif peptide, a KDEL ER retention signal, another Factor Xa protease site, an out-of-frame buforin II coding sequence, the lacZa peptide, and a polyhistidine tag. More than twenty derivatives of plasmid pWKK-500 are described. Plasmids pWKK-700 and pWKK-800 are similar to pWKK-500 wherein the DP178-encoding sequence is substituted by RANTES- and SDF-1-encoding sequences, respectively. Plasmid pWKK-900 is similar to pWKK-500 wherein the HIV protease cleavable linker is substituted by a lethal factor (LF) peptide-cleavable linker. Plasmid pWKK-21 is similar to pWKK-500 wherein the highly truncated ricin B chain is substituted by a one-domain ricin B chain. Oligonucleotide cassettes encoding an HIV protease-cleavable peptide linker and a method of making modified plasmids encoding modified fusion proteins are also described.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Expression vector and method for detecting membrane protein interaction in bacteria
ActiveCN112063643AEfficient purificationGood water solubilityPeptide preparation methodsBiological testingProkaryote organismsMembrane protein interactions
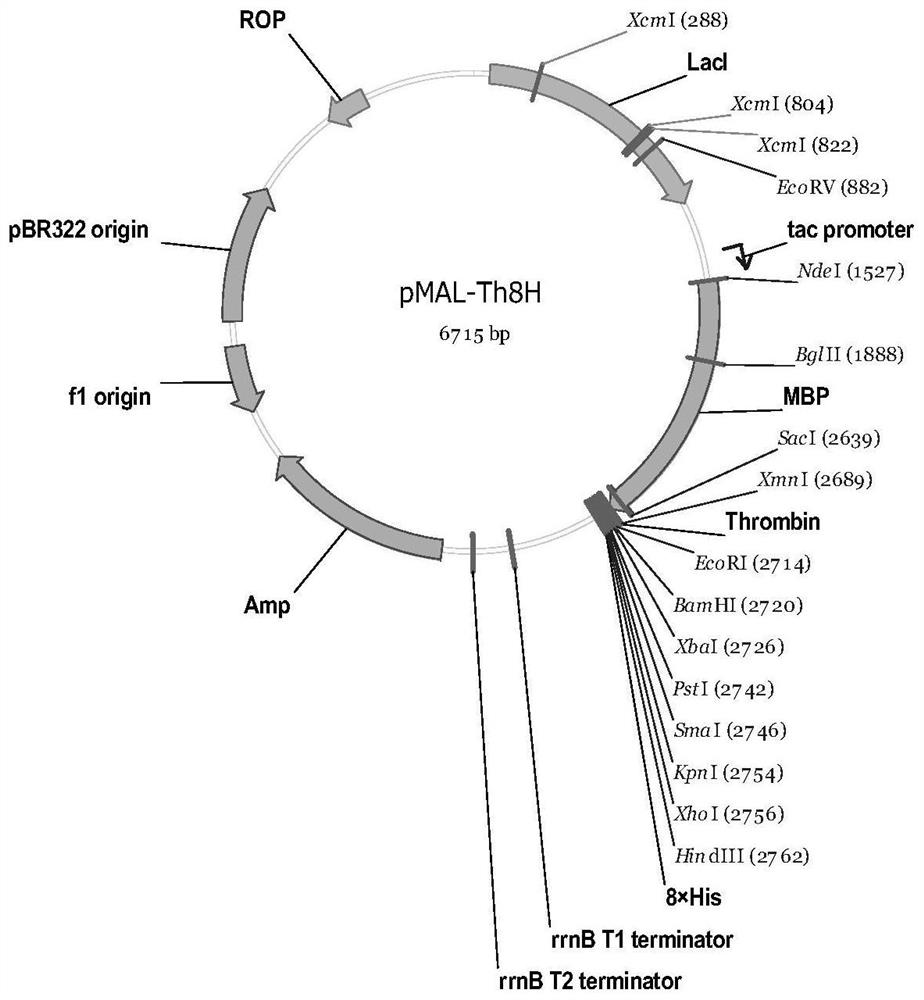
The invention discloses an expression vector and a method for detecting membrane protein interaction in bacteria. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, constructing a double-label protein expression vector with a maltose binding protein label (MBP) and a histidine label (8*His), and expressing and purifying insoluble membrane protein by using the vector to increase the solubility ofthe membrane protein; and then, detecting the interaction between the membrane protein and other proteins by utilizing a pull down technology. Meanwhile, the method can also be used for screening proteins interacting with the membrane protein in bacterial whole-cell proteins. The method for detecting the interaction of the membrane proteins in the bacteria breaks through the technical difficultyof insolubility of the membrane proteins in prokaryotes, provides an experimental means for researching the functions of the bacterial membrane proteins, and has important application value.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Preparation method of aquaporin AqpZ
InactiveCN103173468AEfficient expressionAvoid toxicityDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
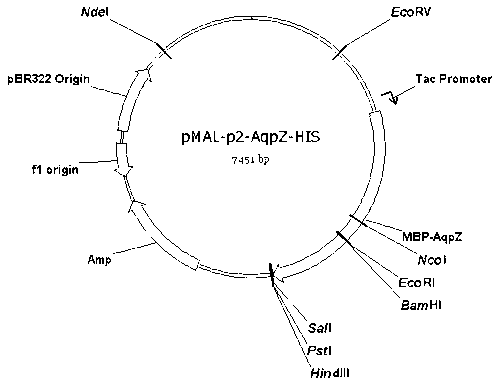
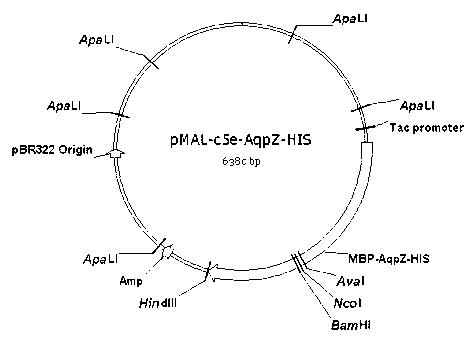
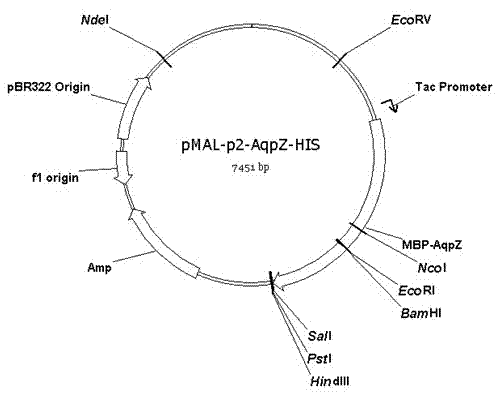
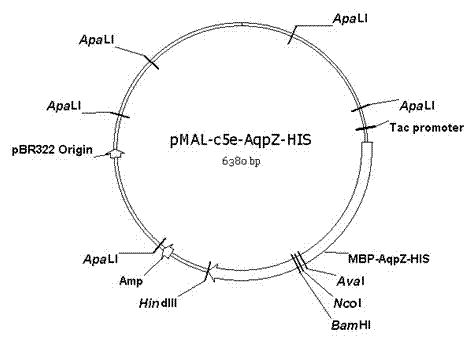
The invention discloses a preparation method of an aquaporin AqpZ. The method comprises the following steps: 1, amplifying Escherichia coli aquaporin AqpZ-HIS; 2, constructing a recombinant expression vector, carrying out construction and inducible expression of engineering strains, and carrying out ultrasonic fragmentation to obtain fusion protein MBP-AqpZ-HIS thalli; and 3, purifying to obtain the aquaporin AqpZ. The method realizes the efficient expression of a maltose-binding protein-aquaporin AqpZ-His-tag fusion protein in Escherichia coli, and overcomes problems comprising the toxicity of traditional AqpZ over-expression to host cells and insoluble inclusion body formation; and high-purity aquaporin AqpZ can be obtained only through two-time simple affinity chromatography separation of the aquaporin expressed through the method, so the method is simple to operate and is suitable for the industrialized production of the aquaporin AqpZ.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
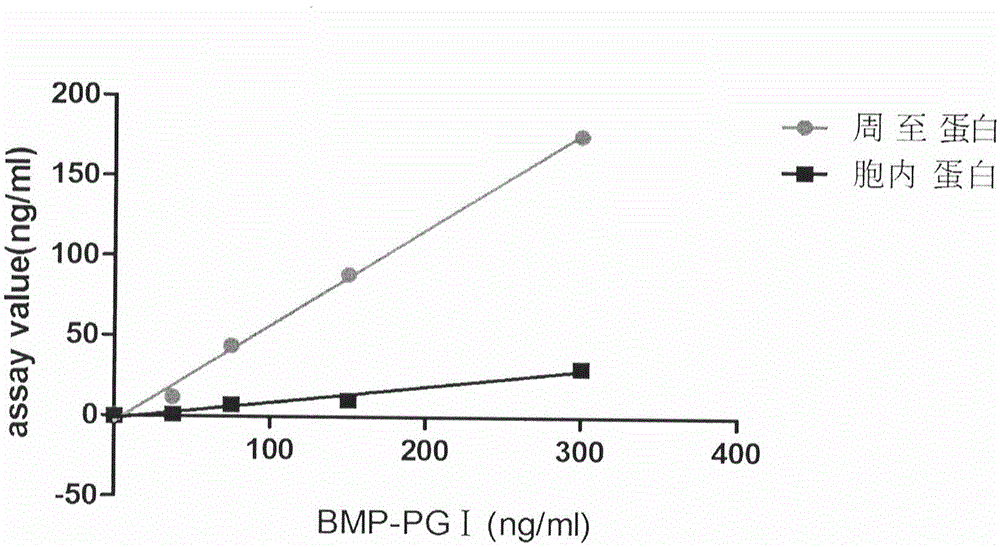
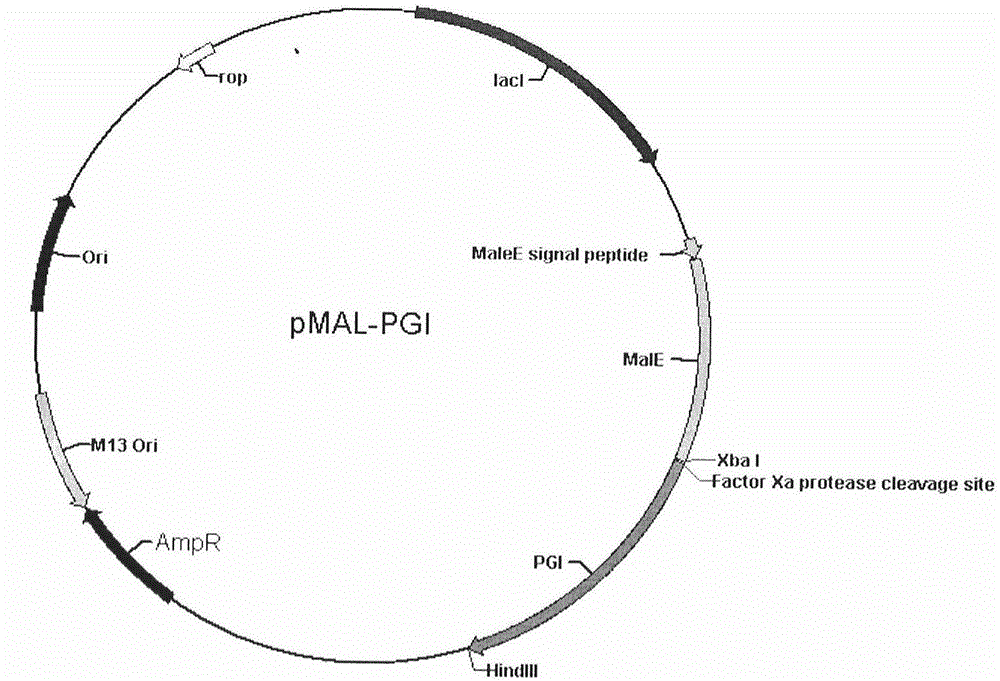
Human pepsinogen I (PGI)-maltose-binding protein (MBP) fusion protein soluble secretory expression and use
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, relates to soluble secretory expression of a human pepsinogen I (PGI)-maltose-binding protein (MBP) fusion protein in escherichia coli and provides a preparation method of the fusion protein. The invention also discloses a use of the recombinant BMP-PGI fusion protein in preparation of a monoclonal antibody and a pepsinogen I kit calibrator. Through use of a Ptas promoter, a malE signal peptide and a maltose binding protein, soluble secretory expression of PGI in escherichia coli is realized so that immunogen activity of the recombinant PGI protein of a prokaryotic expression system is greatly improved and a recombinant PGI preparation cost is effectively reduced.
Owner:BEIJING JIAWAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for embedded membrane expression and aquaporins (AqpZ) purification in escherichia coli
InactiveCN102643849AEfficient expressionAvoid toxicityMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
The invention discloses a method for embedded membrane expression and aquaporins (AqpZ) purification in escherichia coli. According to the method, firstly, AqpZ- histidine (HIS) of the escherichia coli is amplified, then, recombination expression vectors and inducible expression engineering bacterial strains are constructed, fusion protein myelin basic protein (MBP)-AqpZ-HIS thalli are obtained through ultrasonic crushing, and finally, the AqpZ is obtained through purification. The method has the advantages that the efficient expression of maltose-binding protein-AqpZ-poly histidine binary tag fusion protein is realized in the escherichia coli, and the problems of insoluble inclusion body forming and host cell toxicity caused by the traditional overexpression AqpZ are solved; and in addition, high-purity AqpZ can be obtained only through two turns of simple affinity chromatography separation on the AqpZ expressed by the method, the operation is simple, and the method can be applied to industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
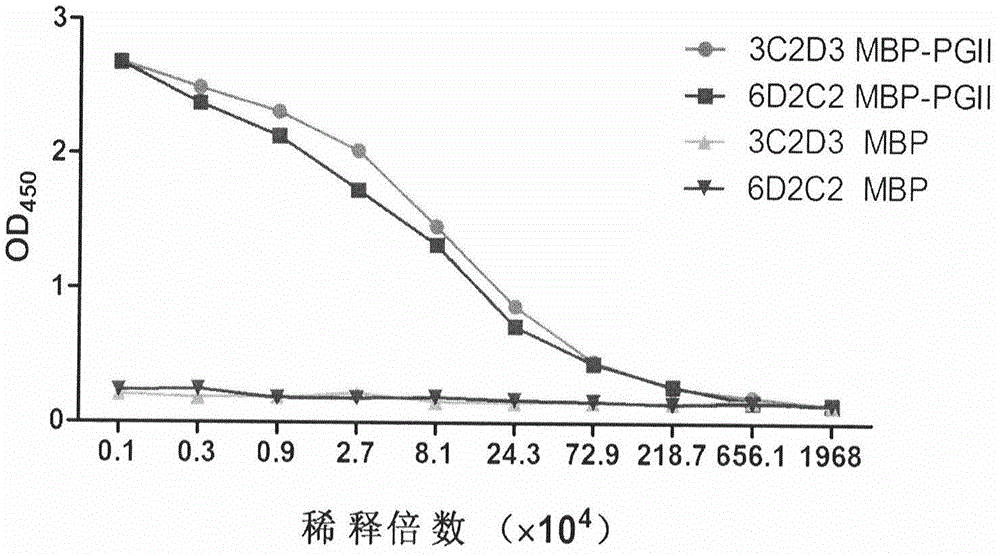
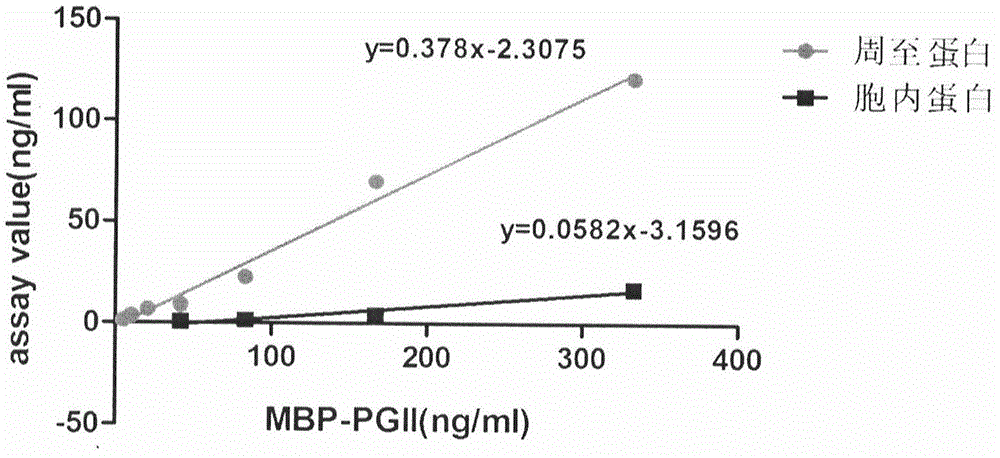
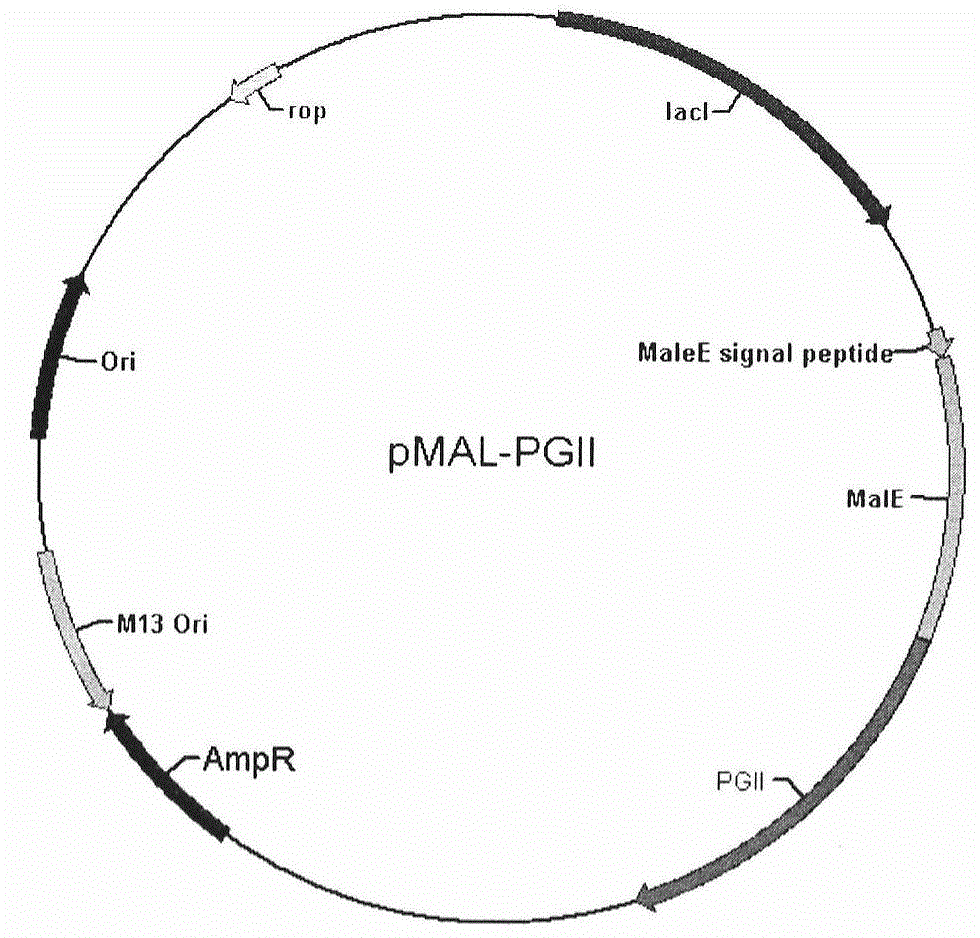
Soluble secretory expression of PG II-MBP fusion protein and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and particularly relates to soluble secretory expression of a fusion protein of a human pepsinogen II (PG II) and a maltose binding protein (MBP) in escherichia coli, provides a preparation method of the fusion protein, and also discloses application of a recombinant BMP-PG II fusion protein to preparation of monoclonal antibodies and calibration materials of pepsinogen II kits. Through the adoption of elements such as a Ptac promoter, an malE signal peptide and the maltose-binding protein, the soluble secretory expression of PG II from periphery to inside of escherichia coli is implemented; the immunogen activity of the recombinant human PG II protein from a prokaryotic expression system is greatly improved; and the preparation cost of the recombinant PG II is effectively reduced.
Owner:BEIJING JIAWAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for high-level expression of bacterial laccase in Escherichia coli
InactiveCN101736026BAchieving soluble expressionShort fermentation timeMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesInclusion bodiesHigh level expression
The invention provides a technical method for forming maltose binding protein-bacterial laccase fusion protein by fusing maltose binding protein and bacterial laccase and expressing the maltose binding protein-bacterial laccase fusion protein at low temperature. The method comprises the following steps: A, constructing a maltose binding protein-bacterial laccase gene; B, screening a positive converter; C, expressing fusion protein; D, identifying soluble fusion protein; E, purifying the fusion protein; and F, measuring parameters of enzyme kinetics of the bacterial laccase. The method realizes the high-level expression of the protein-bacterial laccase fusion protein in Escherichia coli cells. The soluble bacterial laccase can be expressed in high level and also maintains the same enzyme activity as unfused bacterial laccase. The problem that a large number of insoluble inclusion bodies are formed when the bacterial laccase is expressed in high level in the Escherichia coli cells is solved. The method has the advantages of simple operation, short fermentation time and low cost. The bacterial laccase also can be directly immobilized on maltose affinity chromatograph resin for various enzymatic reactions.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
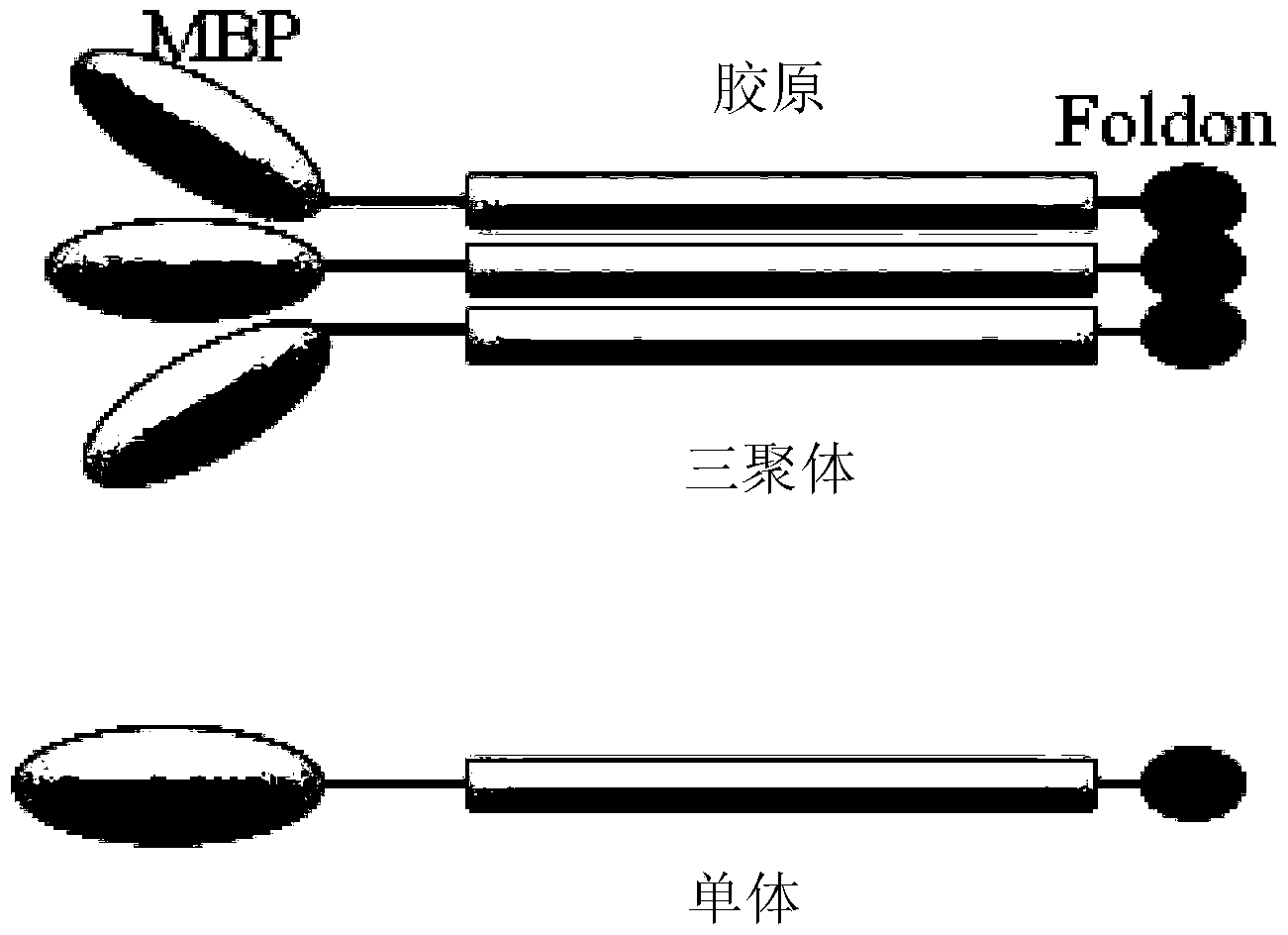
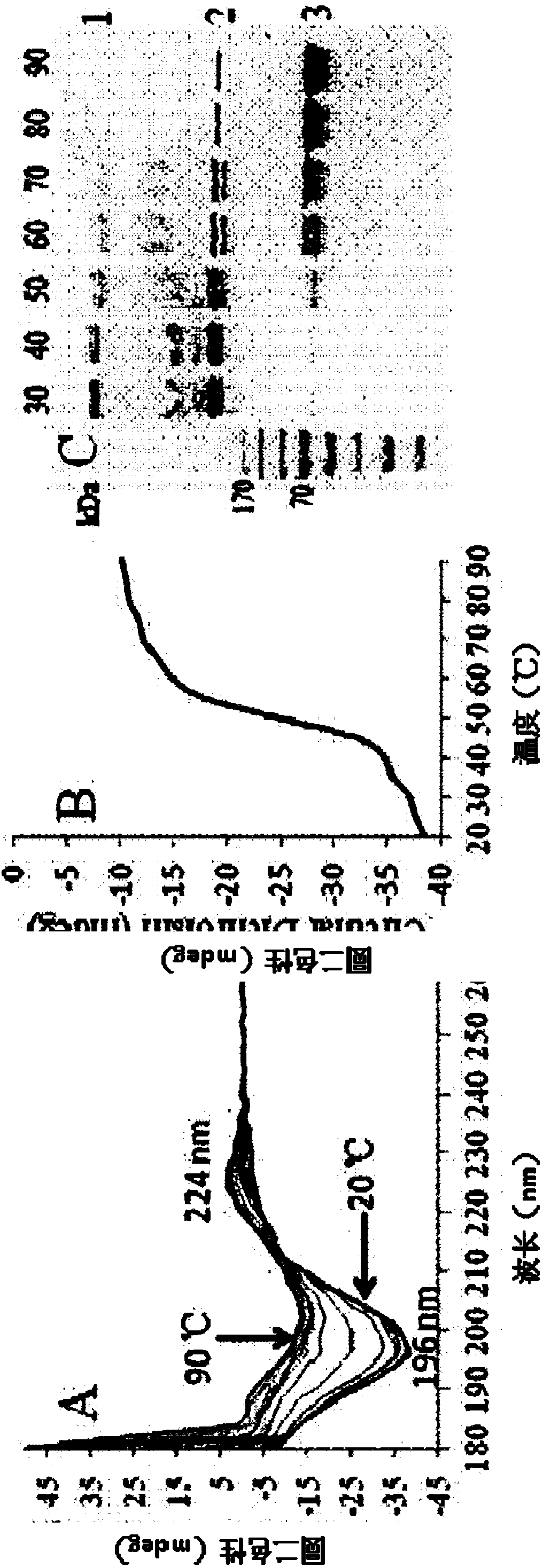
Recombinant collagen-mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant collagen-mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) composite material. The composite material comprises mRNA for coding specific protein factors and a protein carrier loading the mRNA, wherein the protein carrier sequentially comprises a maltose-binding protein and a collagen from an amino terminal to a carboxyl terminal; the mRNA is in covalent linkage with cysteine in the glycine-proline-cysteine sequence of the collagen of the protein carrier through an amino group modifying the 3' terminal. The composite material is capable of continuously and controllably releasing the specific protein factors to a wound part.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Protein stabilization by domain insertion into a thermophilic protein
ActiveUS8592192B2Improve dynamic stabilityCompromise in its activityEnzyme stabilisationImmunoglobulinsProtein targetADAMTS Proteins
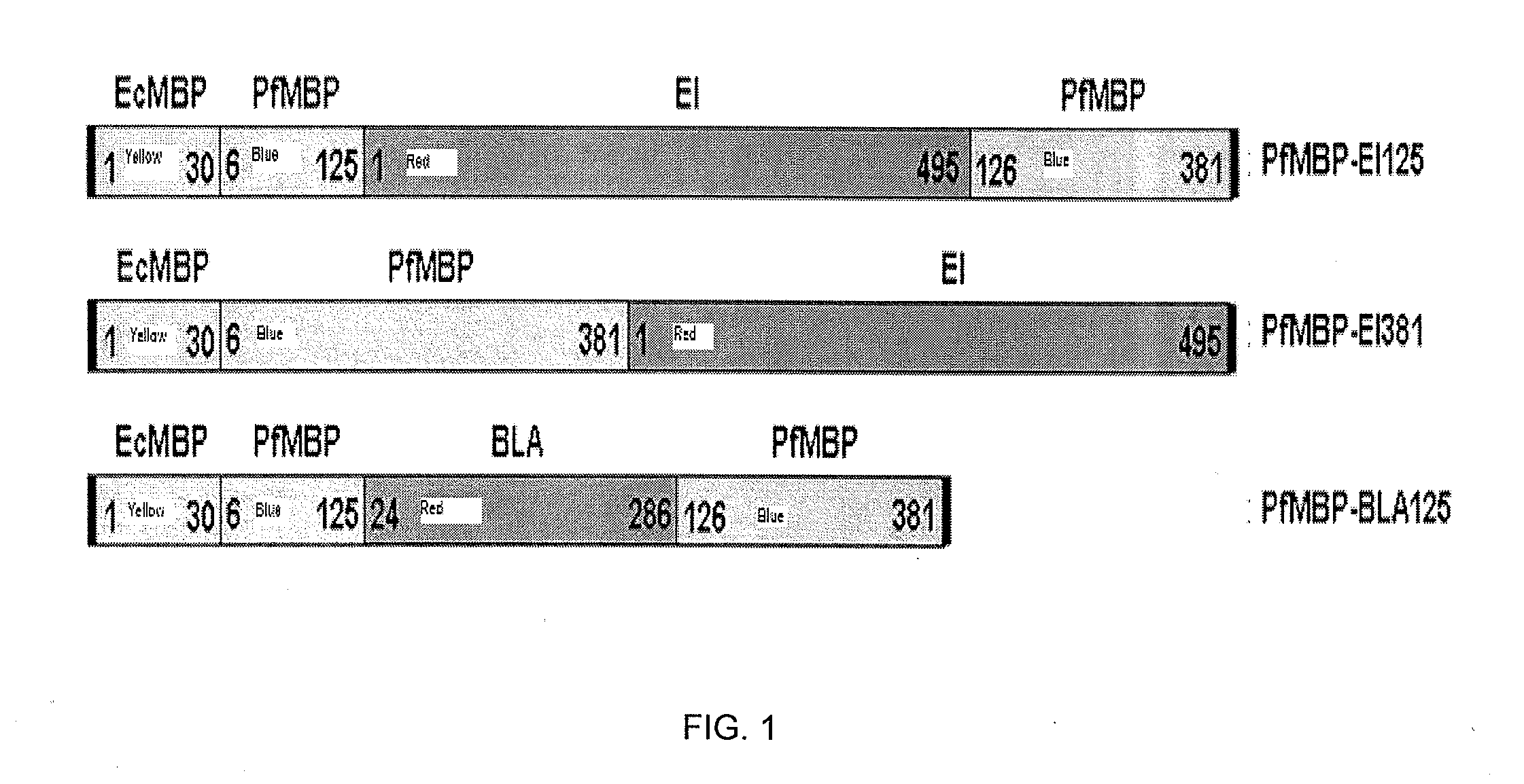
A strategy to improve protein stability by domain insertion. TEM 1 beta-lactamase (BLA) and exo-inulinase, as model target enzymes, are inserted into a hyperthermophilic maltose binding protein from Pyrococcus furiosus (PfMBP). Unlike conventional protein stabilization methods that employ mutations and recombinations, the inventive approach does not require any modification on a target protein except for its connection with a hyperthermophilic protein scaffold. For that reason, target protein substrate specificity was largely maintained, which is often modified through conventional protein stabilization methods. The insertion was achieved through gene fusion by recombinant DNA techniques.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Recombinant Escherichia coli capable of realizing soluble expression of linoleate isomerase and application of recombinant Escherichia coli
PendingCN108660102ASolve the problem of excessive inclusion bodiesHigh expressionBacteriaCis-trans-isomerasesEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
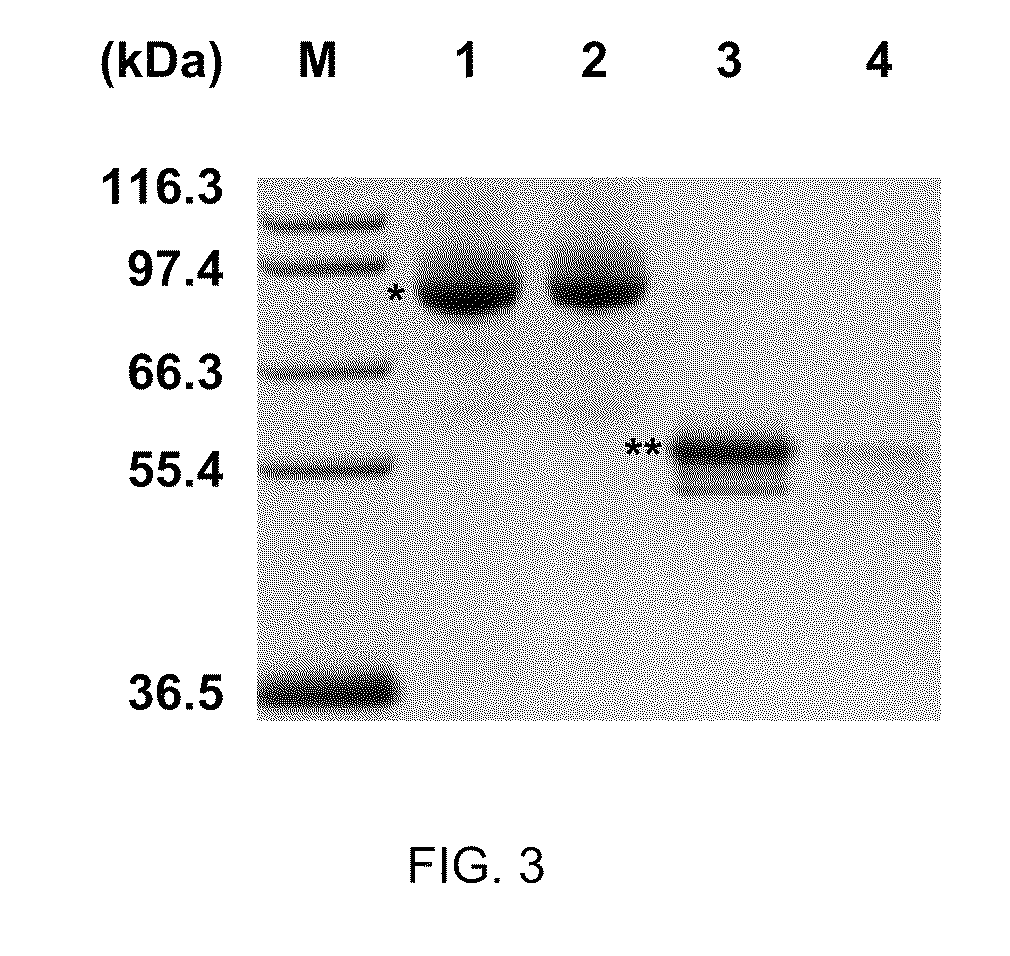
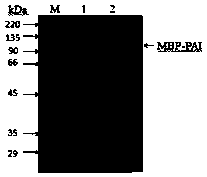
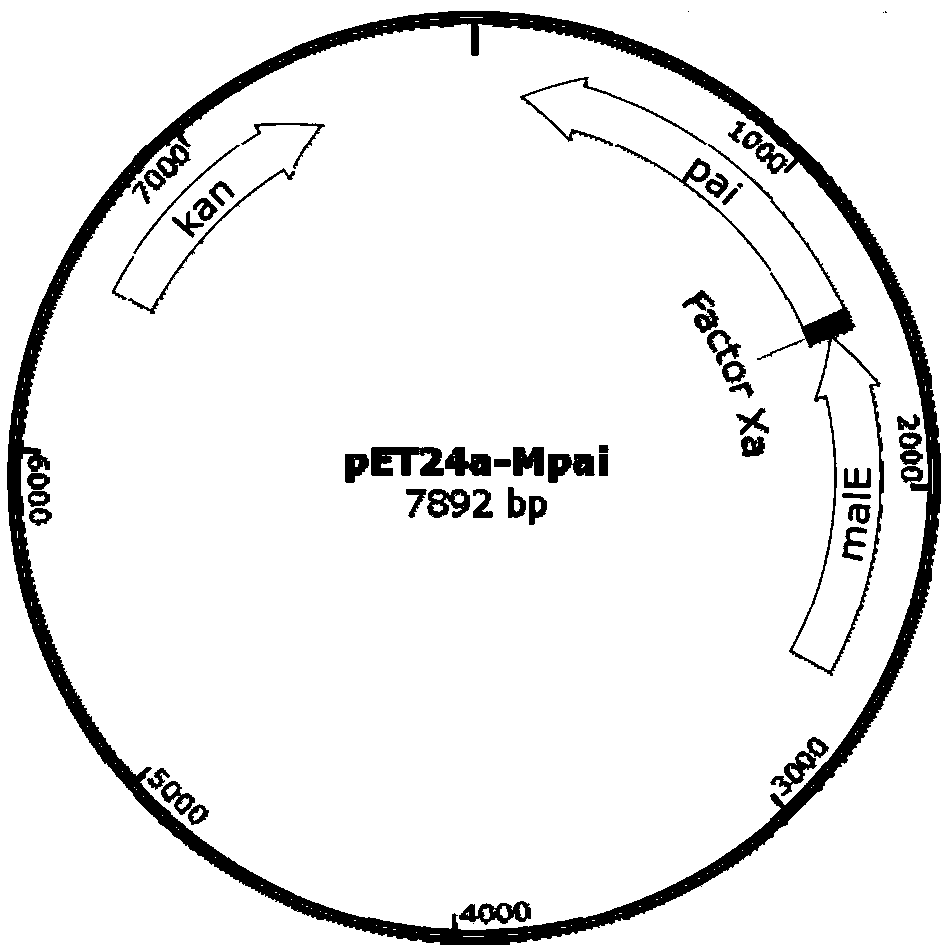
The invention discloses recombinant Escherichia coli capable of realizing soluble expression of linoleate isomerase and application of the recombinant Escherichia coli, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The recombinant Escherichia coli is constructed by the following steps: inserting genes mal E of a coded maltose-binding protein MBP into the upstream of genes pai of linoleateisomerase PAI, and constructing the recombinant Escherichia coli containing an MBP-PAI fusion expression vector. The expression quantity of the PAI of the obtained recombinant Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) (pET24a-Mpai) is far higher than that of other strains recorded in the prior art, and most of the recombinant proteins MBP-PAI exist in a soluble protein form. Therefore, the recombinant Escherichia coli disclosed by the invention is capable of realizing high-efficiency soluble expression of the MBP-PAI, and the problem of excessive inclusion bodies is solved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Novel anti-H5 subtype avian influenza virus nanoantibody and application thereof
ActiveCN113527476ASolving the insoluble puzzleImprove accuracyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against virusesFusion Protein ExpressionAvian virus
The invention discloses a novel anti-H5 subtype avian influenza virus nanoantibody and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the nanoantibody is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. An antibody gene is connected with a maltose binding protein (MBP) gene through a connecting peptide, an expression vector is constructed, and the expression of a fusion protein is induced to promote the soluble expression of the anti-H5 avian influenza virus nanoantibody fusion protein in an expression system, so the problem that the anti-H5 avian influenza virus nanoantibody protein is insoluble in a prokaryotic system is solved, and accuracy and repeatability are improved. The nanoantibody can be used for detecting, diagnosing, preventing or treating avian influenza viruses, especially H5 subtype avian influenza viruses. The nanoantibody has great significance for monitoring the H5 avian influenza of chicken.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method of shearing fusion protein by escherichia coli intracellular protease
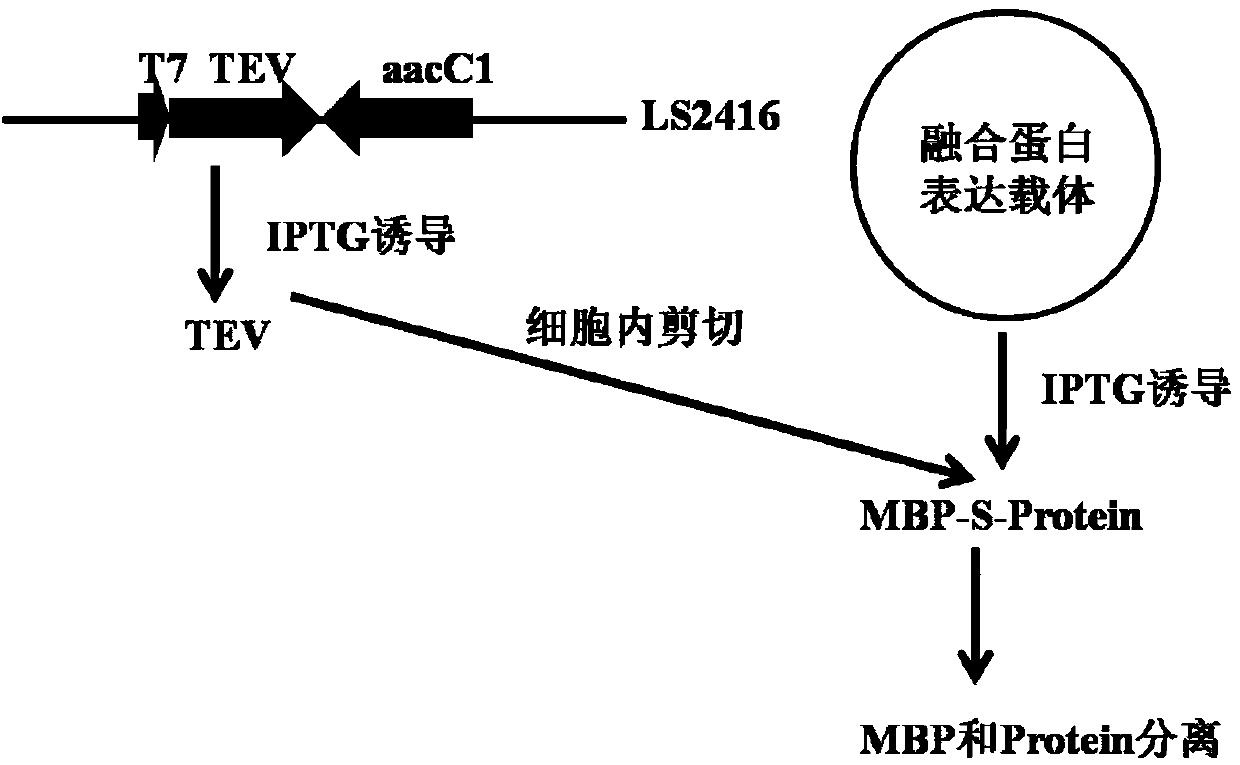
InactiveCN103993030AActivity does not affectRetain activityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetThiogalactosides
The invention relates to a method of separating a target protein by shearing a fusion protein by escherichia coli intracellular protease. Used host bacteria is obtained by integrating a TEV (tobacco etch virus) protease gene driven by a strong promoter T7 to escherichia coli expression host bacteria BL21(DE3) by virtue of a recombinant engineering method. An expression vector is obtained by cloning maltose-binding protein and stuffer fragment to the expression vector pET30(+). A target gene not containing a terminator replaces the stuff segment to obtain a target gene fusion expression vector, and the tail end of the fusion protein contains 6 histidines of the vector. After the expression vector is transformed to the host bacteria, under induction of isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside, the fusion protein and the TEV protease based on a chromosome are expressed at the same time; the TEV is acted on an enzyme cutting site between the maltose-binding protein and the target protein for separating the target protein. According to the intracellular shearing method, steps of fusion protein separating, TEV enzyme digesting, and the like are omitted.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Protein stabilization by domain insertion into a thermophilic protein
ActiveUS20100227374A1Improve dynamic stabilityImprove stabilityEnzyme stabilisationImmunoglobulinsProtein targetProtein insertion
A strategy to improve protein stability by domain insertion. TEM 1 beta-lactamase (BLA) and exo-inulinase, as model target enzymes, are inserted into a hyperthermophilic maltose binding protein from Pyrococcus furiosus (PfMBP). Unlike conventional protein stabilization methods that employ mutations and recombinations, the inventive approach does not require any modification on a target protein except for its connection with a hyperthermophilic protein scaffold. For that reason, target protein substrate specificity was largely maintained, which is often modified through conventional protein stabilization methods. The insertion was achieved through gene fusion by recombinant DNA techniques
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
cDNA encoding a polypeptide including a hev ein sequence
InactiveUS6083687APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA libraryEscherichia coli
A cDNA clone (HEV1) encoding hevein was isolated via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using mixed oligonucleotides corresponding to two regions of hevein as primers and a Hevea brasiliensis latex cDNA library as a template. HEV1 is 1018 nucleotides long and includes an open reading frame of 204 amino acids. The deduced amino acid sequence contains a putative signal sequence of 17 amino acid residues followed by a 187 amino acid polypeptide. The amino-terminal region (43 amino acids) is identical to hevein and shows homology to several chitin-binding proteins and to the amino-termini of wound-induced genes in potato and poplar. The carboxyl-terminal portion of the polypeptide (144 amino acids) is 74-79% homologous to the carboxyl-terminal region of wound-inducible genes of potato. Wounding, as well as application of the plant hormones abscisic acid and ethylene, resulted in accumulation of hevein transcripts in leaves, stems and latex, but not in roots, as shown by using the cDNA as a probe. A fusion protein was produced in E. coli from the protein of the present invention and maltose binding protein produced by the E. coli.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Avirulent C-type clostridium botulinum gene engineering subunit vaccine and production method thereof
ActiveCN110075288AEnsure safetyGuaranteed validityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenHeavy chain
The invention relates to an avirulent C-type clostridium botulinum gene engineering subunit vaccine and a production method thereof. The prepared avirulent C-type clostridium botulinum subunit vaccineis produced by adopting recombinant protein (rMBP-BoHC), which is subjected to codon optimization and contains a maltose-binding protein (MBP) tag, of an avirulent area HC (BoHC) of a clostridium botulinum toxin (BoNTs) heavy chain, so that not only is the safety of the vaccine guaranteed furthest, but also the effectiveness of the vaccine is maintained. Meanwhile, an antigen of the vaccine can be expressed in a soluble mode, so that the avirulent C-type clostridium botulinum gene engineering subunit vaccine has the advantages of being simple in preparation technology, low in immunizing dose,good in immune efficacy and the like, and is an ideal candidate vaccine for upgrading and updating current C-type clostridium botulinum vaccines of the nation.
Owner:CHINA INST OF VETERINARY DRUG CONTROL
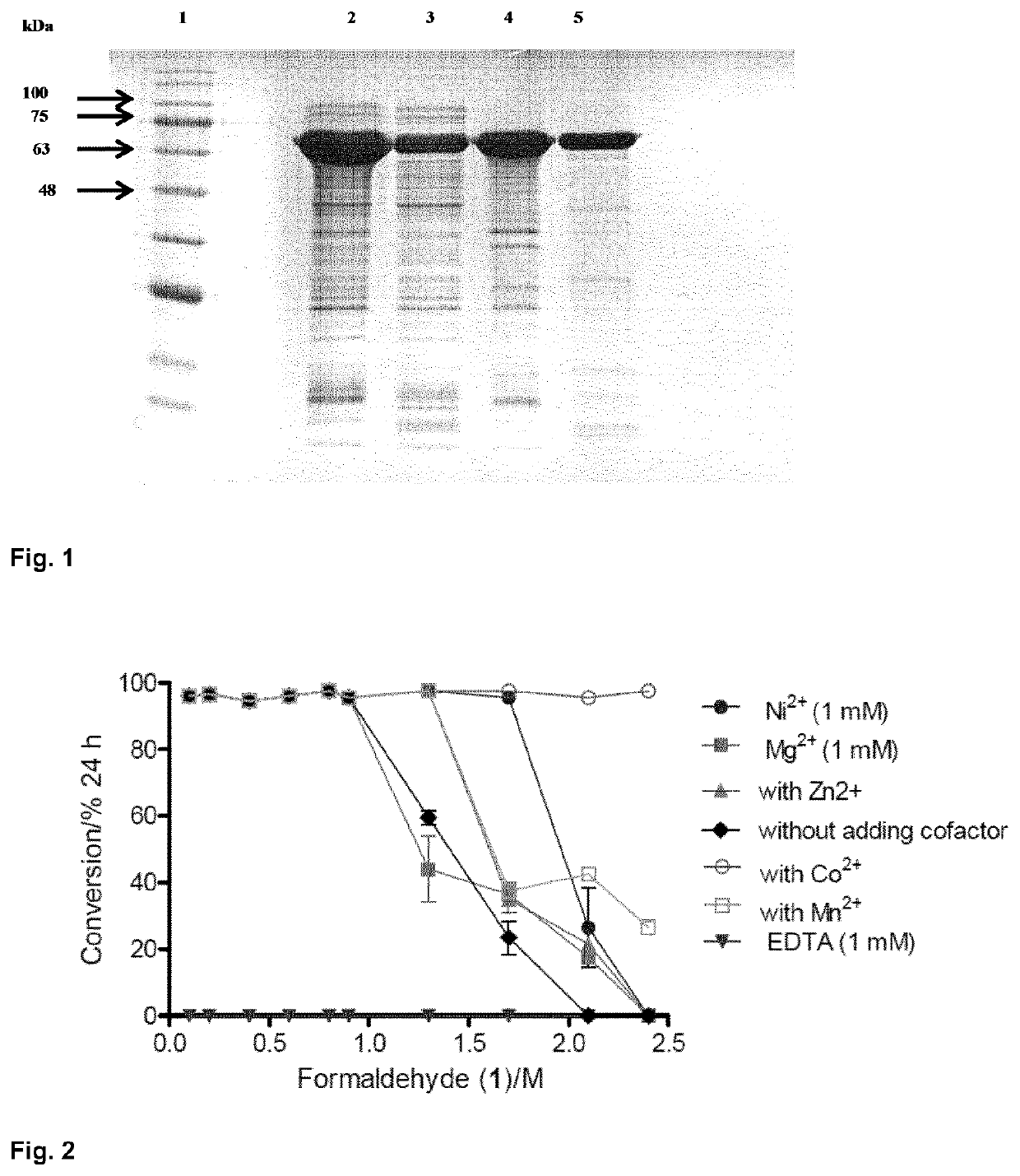
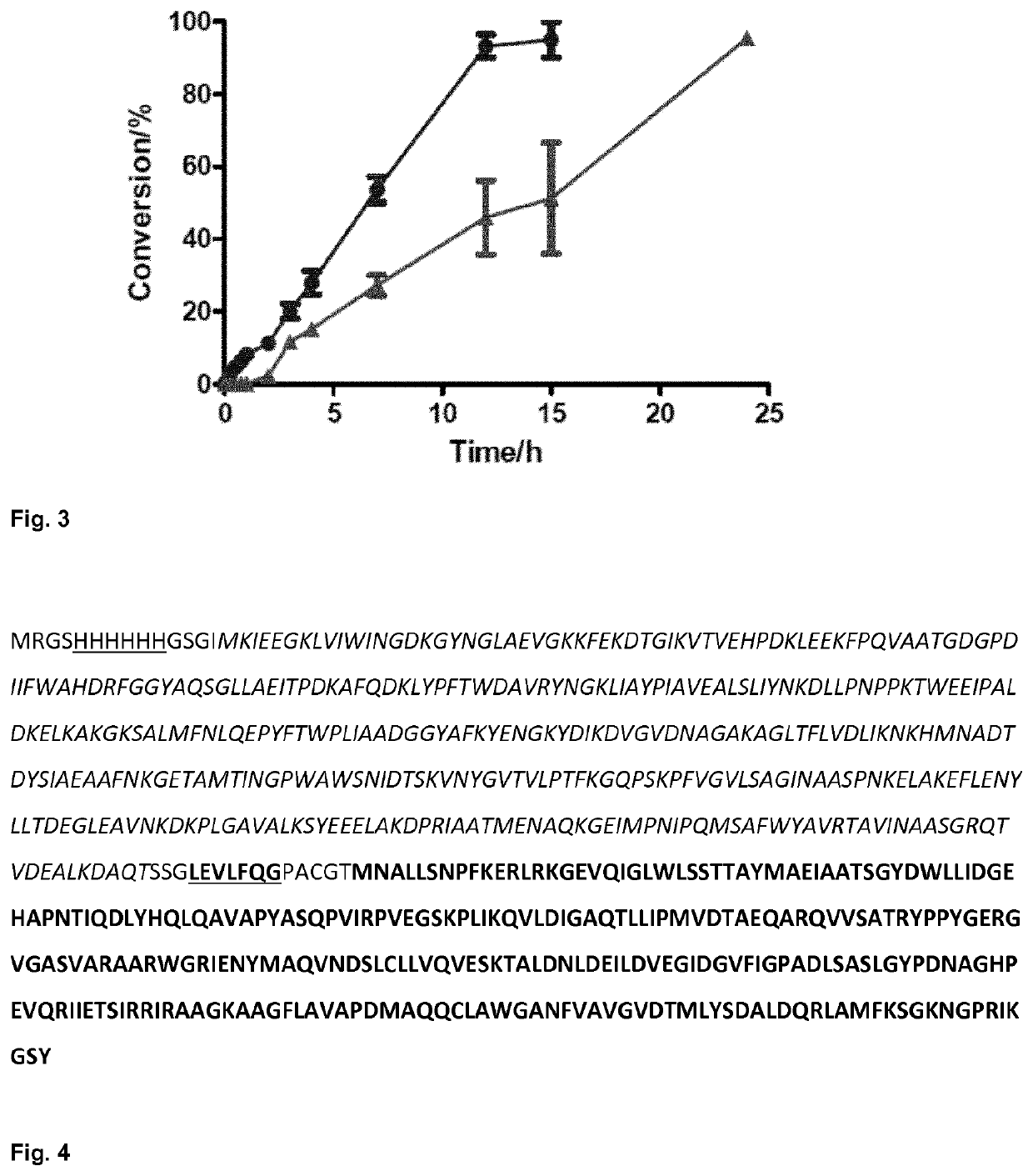
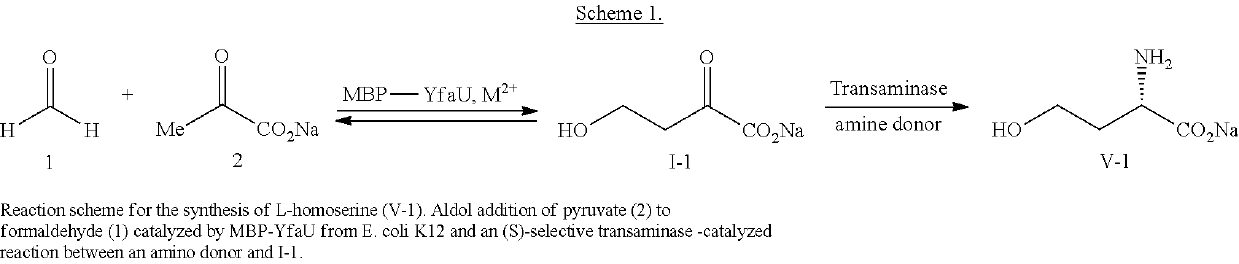
Fusion proteins comprising an aldolase enzyme joined to a maltose binding protein
ActiveUS10683493B2Vector-based foreign material introductionPolypeptide with MBP-tagBond formationPyruvic acid
The present invention refers to an enzyme consisting of a fusion protein particularly useful as shown through-out the present invention for carrying out the carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction known as the aldol Reaction, preferably for carrying out an aldol reaction by using aldehydes as substrates and preferably pyruvate or a salt thereof, for producing hydroxyketoacids. Said enzyme is made by binding an aldolase to a maltose binding protein. The enzymes display full activity under “highly denaturing” substrate loadings (aldehydes, >1 M).
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +2
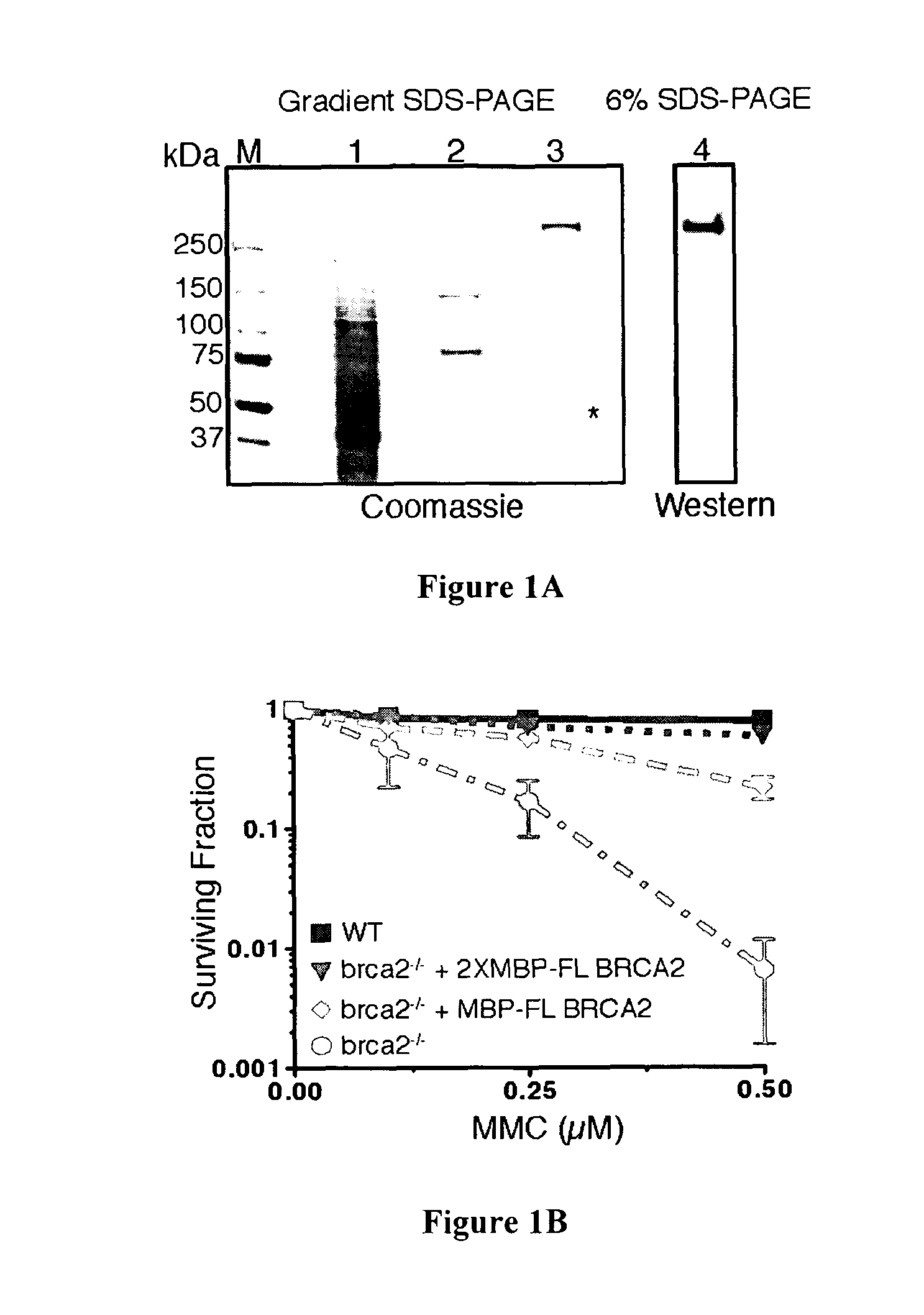
Expression and purification of fusion protein with multiple MBP tags
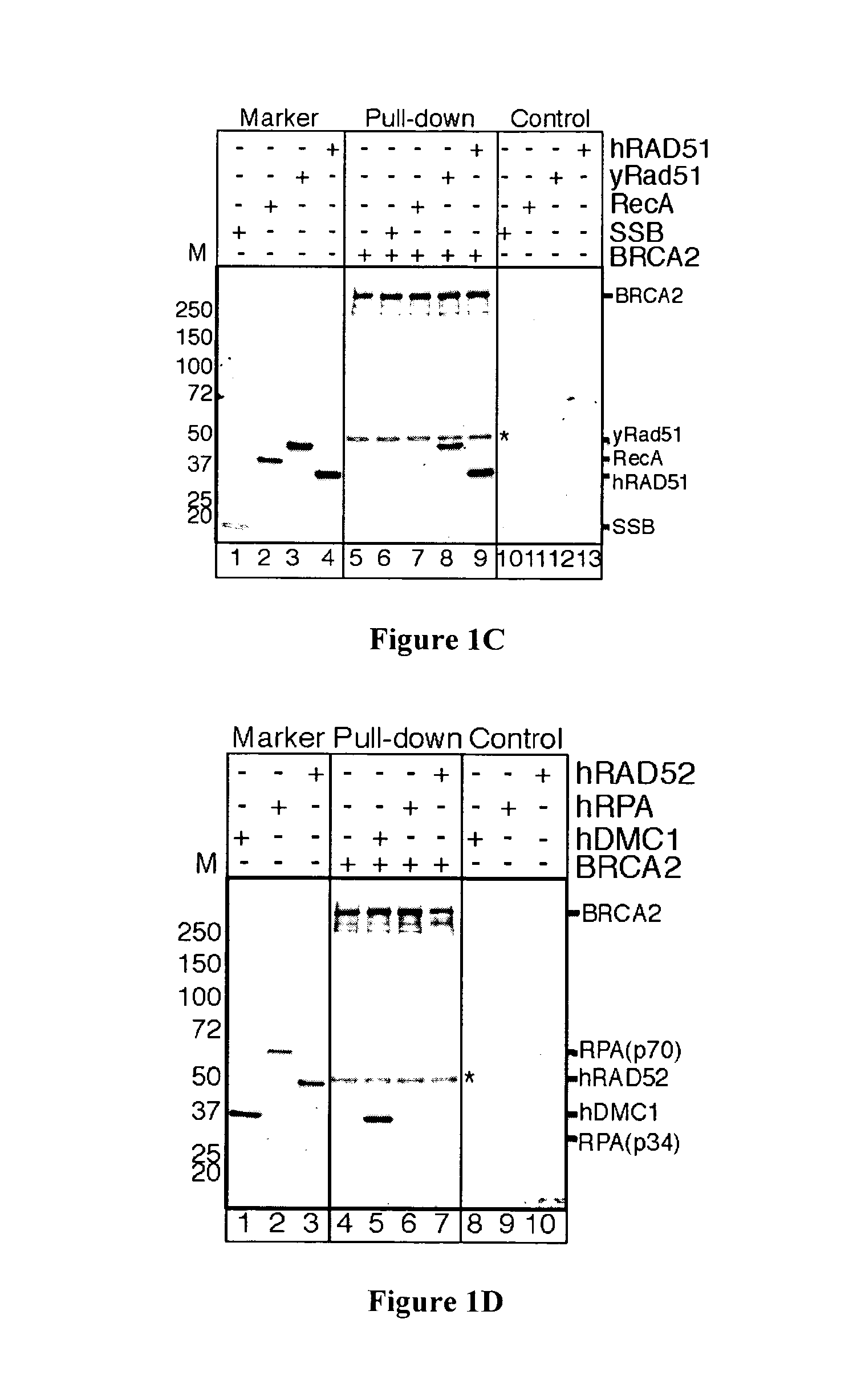
The present invention provides a new method for recombinantly expressing a protein of interest, such as the human BRCA2 protein, BLM protein, CtIP protein, or EXOI protein, by expressing the protein in the form of a fusion protein comprising two maltose-binding protein (MBP) or glutathione-S-transferase (GST) tags. The expression cassette useful for this method and the fusion protein produced by this method are also described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
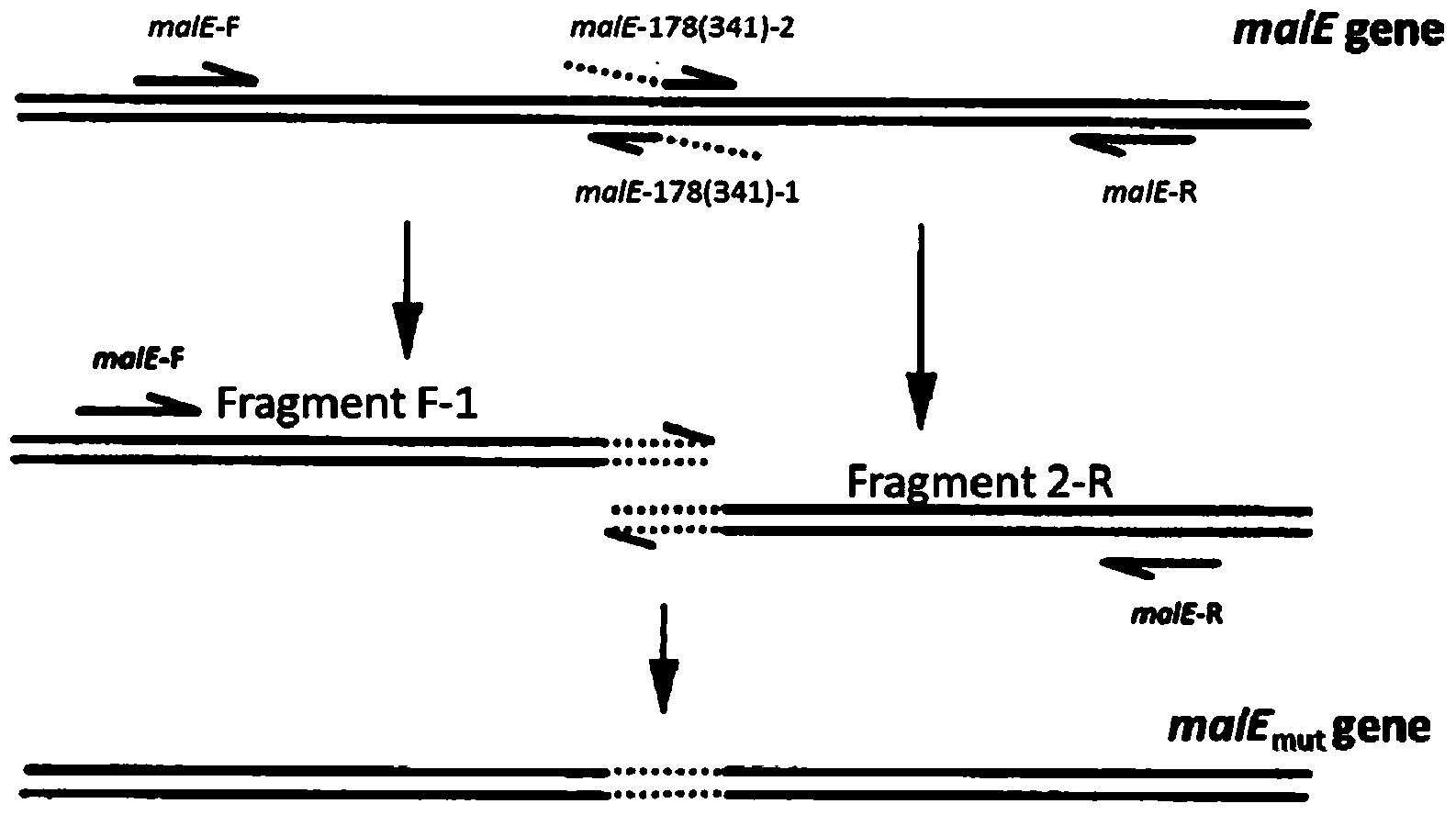
Glycosylated maltose binding protein, and preparation method and application thereof
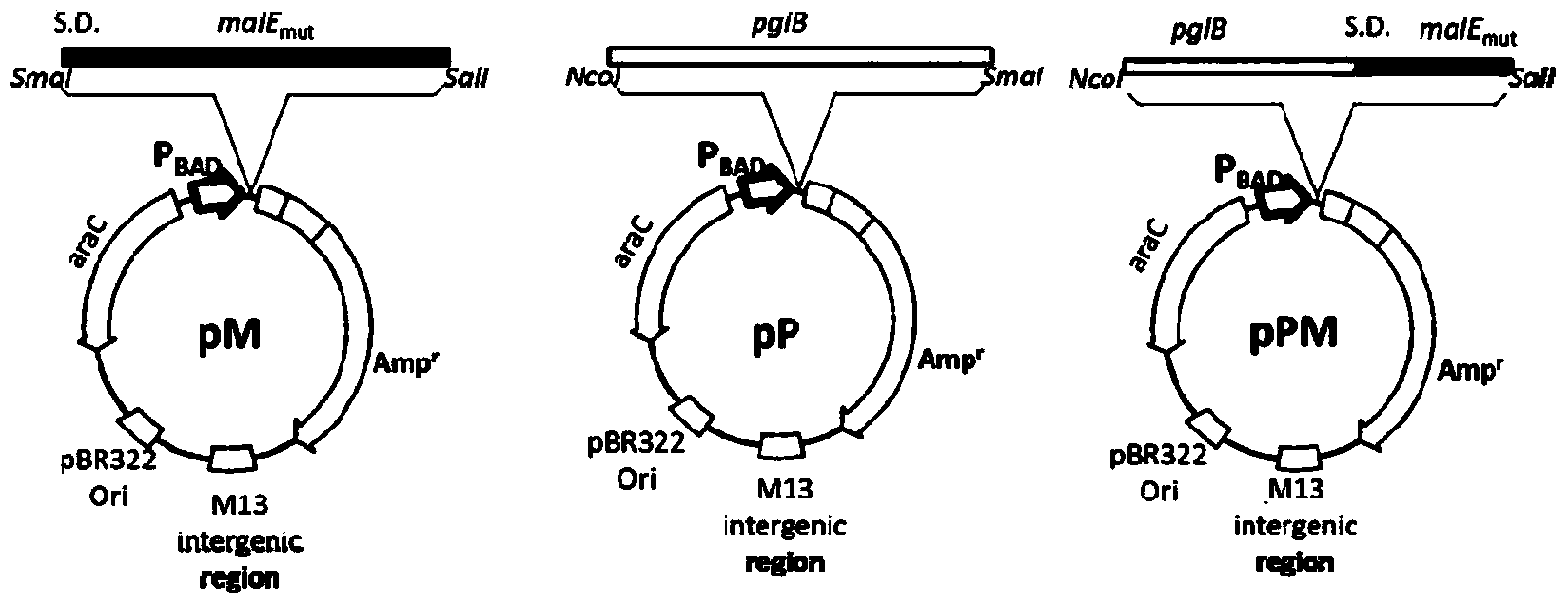
The invention relates to glycosylated maltose binding protein, and a preparation method and an application thereof. A maltose binding protein expression gene malE-Mut has a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.1. As a TD antigen, the sugar-protein conjugate vaccine can generate long-lasting immunity in the body of a healthy adult. The vaccine is also effective for the high-risk populations.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation method of swine H1N1 subtype influenza virus hemagglutinin recombinant protein and liquid phase chip detection kit for virus antibody
ActiveCN106749553AGood antigenicityHigh sensitivitySsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesHemagglutininEscherichia coli
The invention first provides a preparation method of a swine H1N1 subtype influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) recombinant protein. A pair of primers with HIS labels is designed by removing a signal peptide of the HA according to an HA sequence, and a prokaryotic expression plasmid with a 6*His-maltose-binding protein (MBP) combination label is constructed; the HA recombinant protein expressed in a soluble form is successfully obtained in an Escherichia coli expression system and can generate reaction with a mouse antibody with swine H1N1 subtype influenza virus HA, thereby showing that the HA recombinant protein has good antigenicity; a liquid phase chip detection technology is established by using the HA recombinant protein and is higher than ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) in sensitivity; the establishment of the method provides necessary technical supplement for detecting a swine influenza virus antibody, lays a technical basis for researching the liquid phase chip detection technologies of other epidemic disease antibodies, and provides a test reference for establishing multiple liquid phase chip detection technologies of multiple swine disease antibodies.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Serodiagnosis of lyme disease by use of two recombinant proteins in ELISA
ActiveUS10401358B1Great capacity to identifyFast and easy to performAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDepsipeptidesSerodiagnosesEscherichia coli
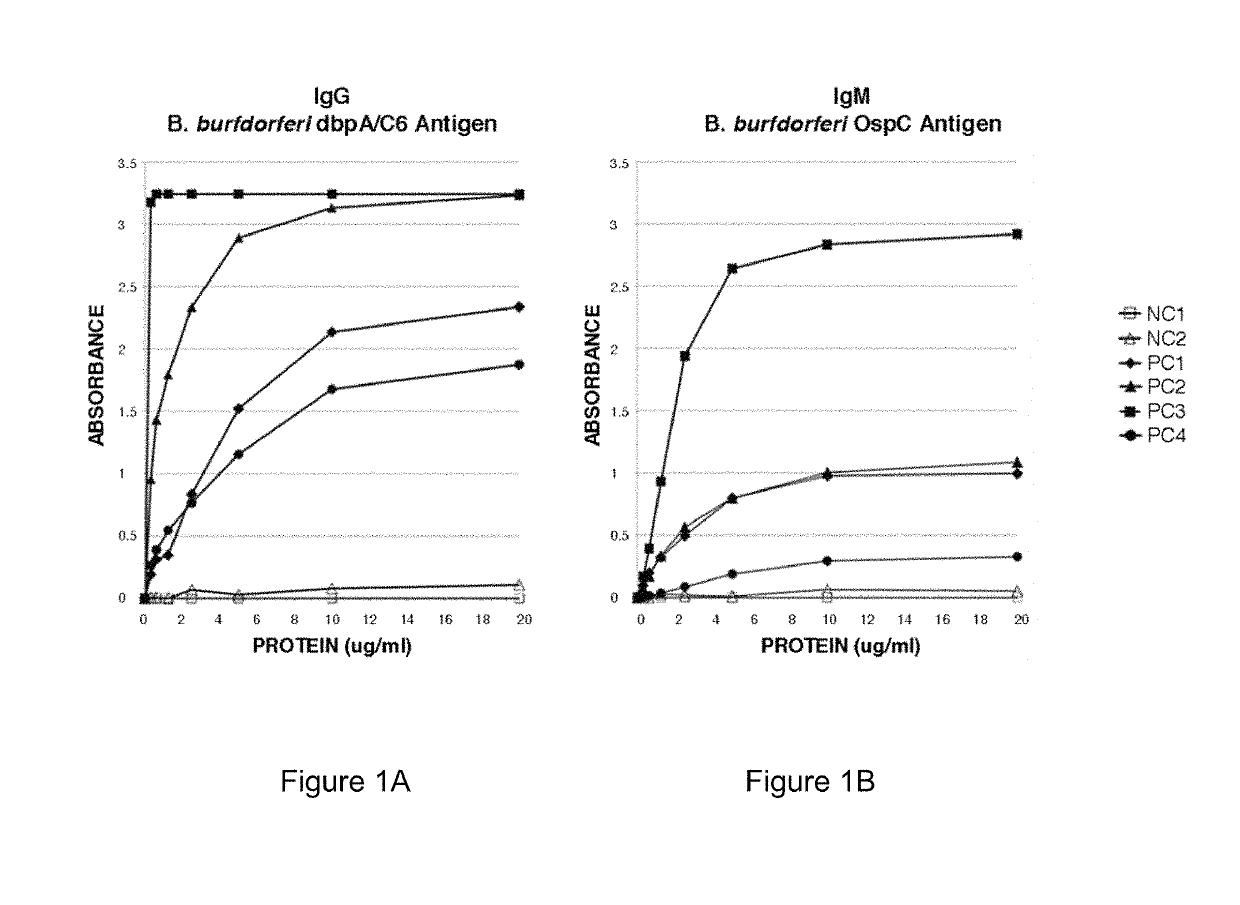
Two Borrelia burgdorferi recombinant proteins were expressed in E. coli. These two proteins were generated from (a) the full length dbpA gene combined with the invariable region 6 of the VlsE gene (dbpA / C6), and (b) the full length OspC gene combined with the coding sequence for amino acids 1-121 of the E. coli maltose binding protein gene (OspC / MBP). Methods of using these recombinant proteins for detecting anti-Borrelia burgdorferi antibodies in patient sera and diagnosis of Lyme Disease are described.
Owner:ROSS SOUTHERN LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com