Peanut bacterial wilt resistance grading identification method and application thereof
A technology of peanut bacterial wilt disease and identification method, which is applied in the identification of peanut bacterial wilt resistance classification and the field of plant disease resistance identification, can solve the problems of no fixed standard, cumbersome classification and identification, etc., and achieves easy operation and efficient technical support , the result is accurate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: Isolation of pathogenic bacteria of bacterial wilt
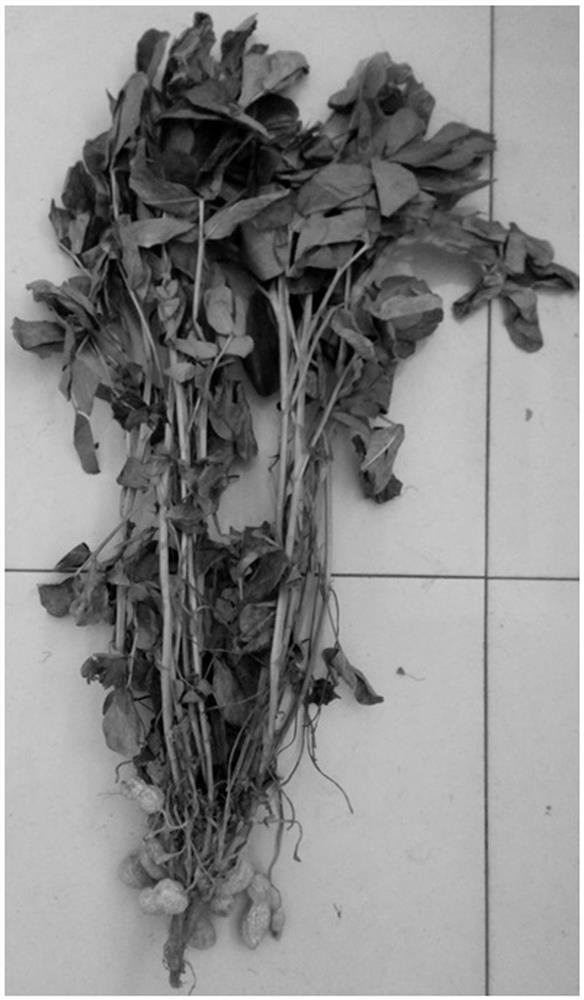
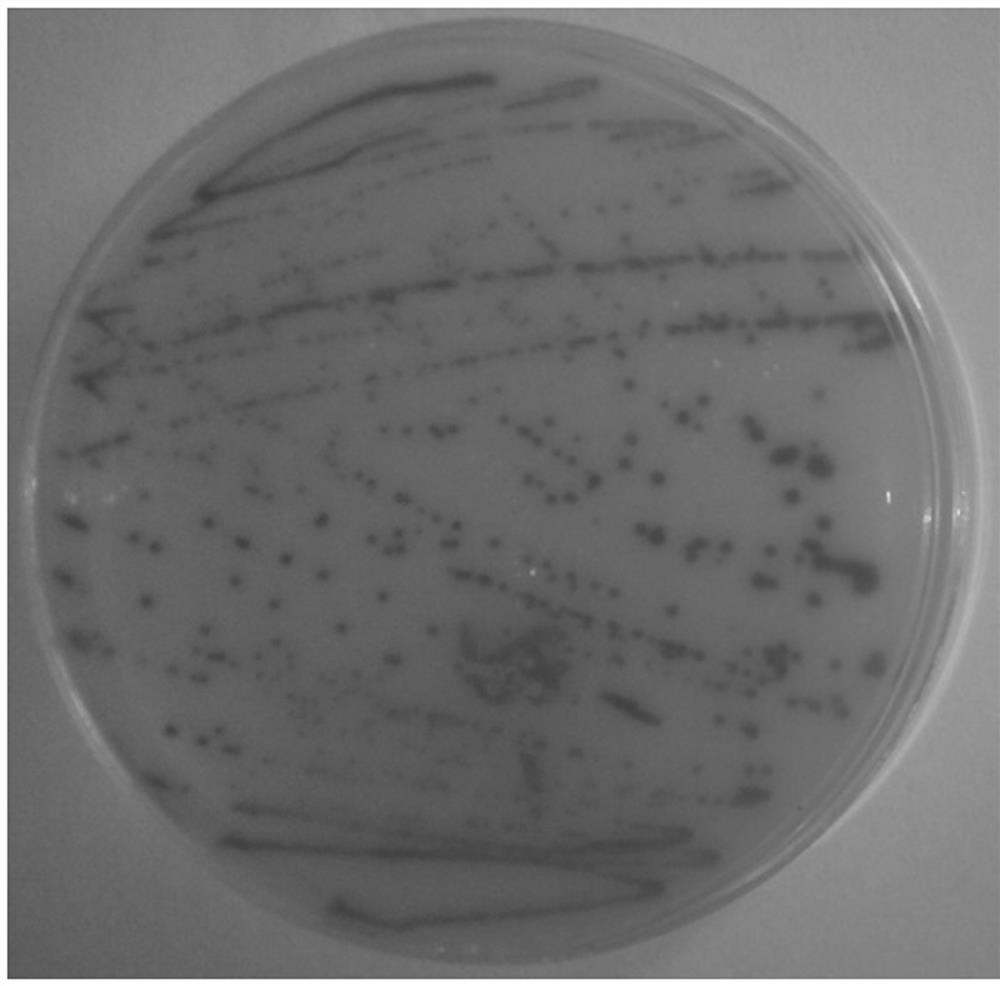
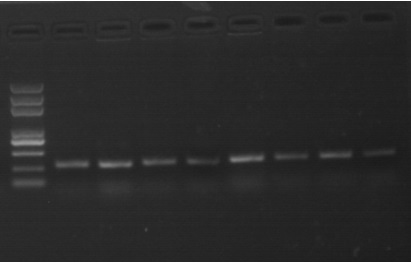
[0036] Bacteria wilt diseased peanut plants ( figure 1 ) roots, cut them crosswise with a knife, immersed them in sterile water for 6 h, and collected the extract; shake the extract evenly, and draw 200 μL and apply it on a TZC plate (1L plate medium formula: 10 g of bacto-peptone, 5 g of glucose , casamino acid 1g, yeast extract 1g, agar 15g, TZC 50mg, the rest was made up with sterile water, pH 7.2), streak culture at 28°C for 48 h, the colony morphology is as follows figure 2 shown. Pick a single red colony from the plate and put it in 200 μL LB liquid medium, culture it with shaking at 220 rpm for 48 h at 28 °C; centrifuge at 1500 rpm for 10 min to collect the bacteria and extract the DNA of the bacteria. Specific primers 759 / 760 for identification of R. solanacearum strains were used to amplify bacterial DNA, wherein the primer sequence was 759: 5'-gtcgccgtcaactcactttc-3'; 760: 5'-gtcgccgtcagcaa...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Grading of resistance to bacterial wilt of high-yielding peanut varieties
[0038] Select 9 high-yielding peanut varieties: Huayu 665, Huayu 669, Huayu 960, Huayu 967, Huayu 968, Huayu 969, Huayu 6620, Huayu 9620, and Huayu 9625 for bacterial wilt resistance Graded identification test. The bacterial wilt resistant peanut variety "Rihua 1" and the bacterial wilt susceptible peanut variety "Huayu 40" were selected as controls. Plants of all peanut varieties were planted in the experimental base located in Laixi, Qingdao.
[0039] 1. The acquisition of peanut branches:
[0040] The seeds of all peanut varieties were sown in the soil at the same time in a conventional manner, and daily management was adopted. The individuals of each variety were randomly sampled on the 55th day after sowing, and long cuts were cut from the top of the second pair of side branches of the selected peanut plants. For the branches with leaves, put them into the sampling box and sto...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The disease-resistant variety "Rihua 1" was selected as the male parent (♂) and the highly susceptible variety "Huayu 967" was used as the female parent (♀) to cross the F3 generation, and the individuals in the recombinant inbred line (RIL) population were subjected to RIL Identification of disease resistance levels. All hybrid F3 generation seeds were planted in the experimental base located in Laixi, Qingdao.
[0055] Sampling in 55 days after sowing, two shoots are cut from the second pair of side branch tops of each plant, then according to the method described in embodiment 2, carry out the activation and inoculation of bacterial wilt disease bacterium, count hybridization F3 generation on the 5th day after inoculation The disease-resistant phenotype of the plants. At this time, the control variety "Rihua 1" showed no symptoms, and the susceptible varieties "Huayu 40" and "Huayu 967" had obvious symptoms. Identification results such as Figure 7 As shown, accord...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com