Novel crosslinkable and degradable multi-block copolymer, preparation method and application thereof
A multi-block copolymer, a new type of technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, tissue regeneration, etc., can solve the problems of unknown impact of filler on the biocompatibility of main material, many factors affecting performance, uncontrollable process, etc. The effect of unrestricted three-dimensional structure, wide application range and simple molding process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Embodiment 1 Preparation of novel photocrosslinkable degradable multi-block copolymer
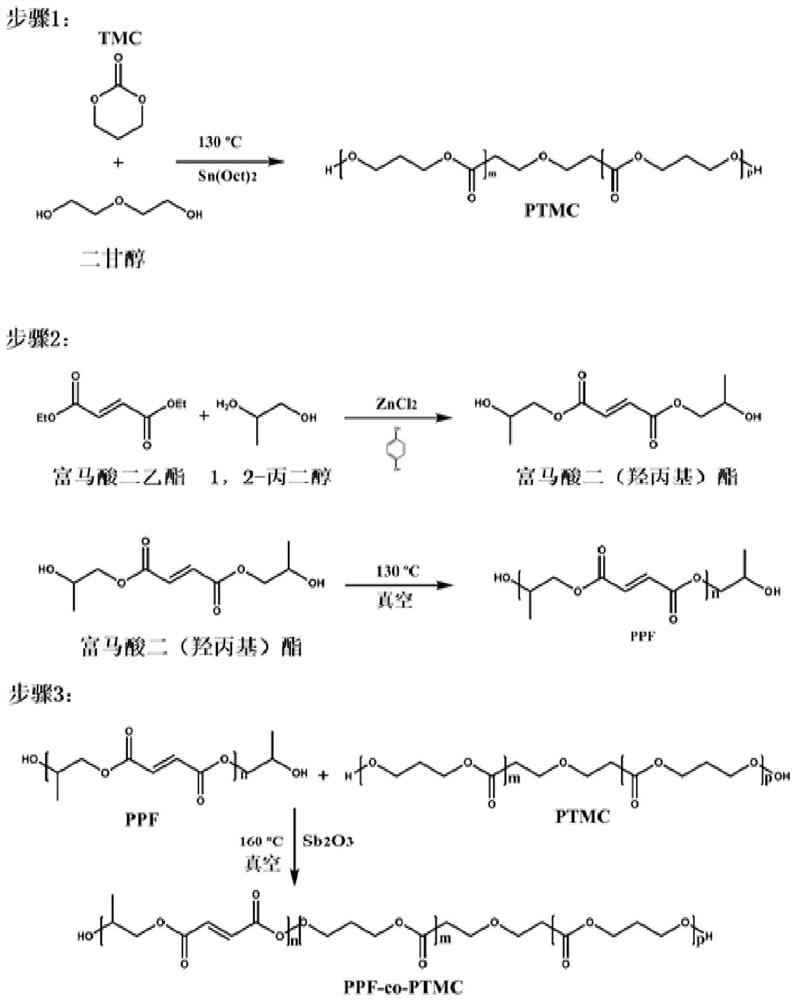
[0062] A preparation method of a novel photocrosslinkable degradable multi-block copolymer, the synthesis process is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
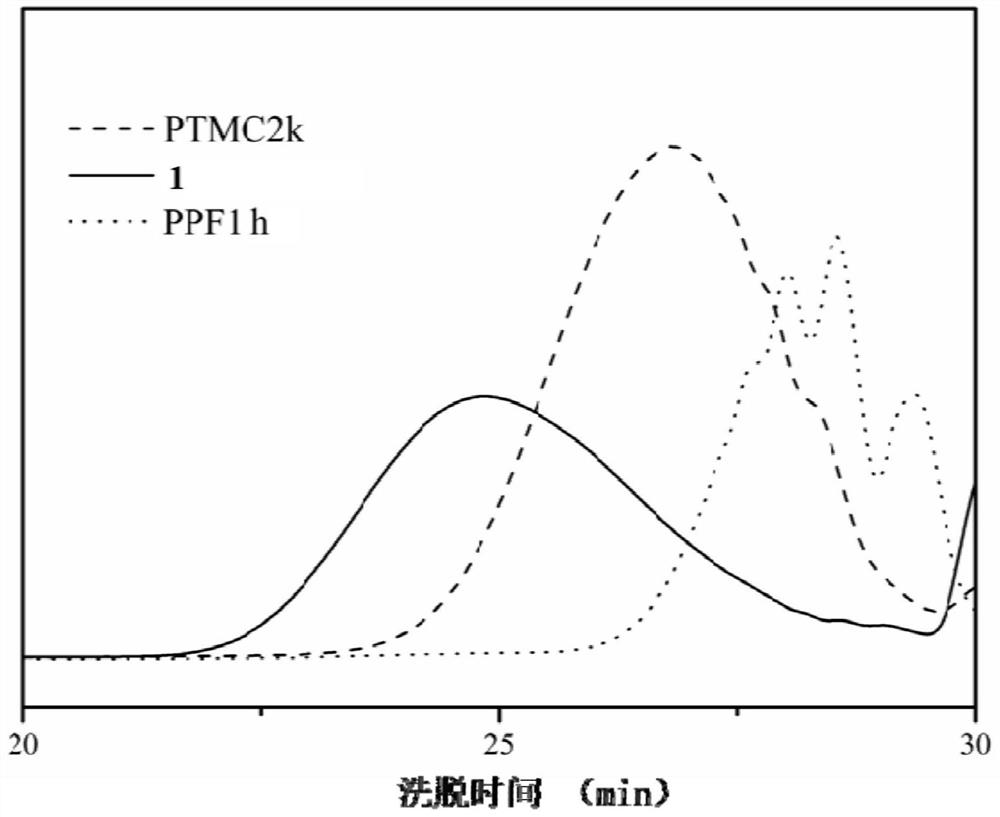
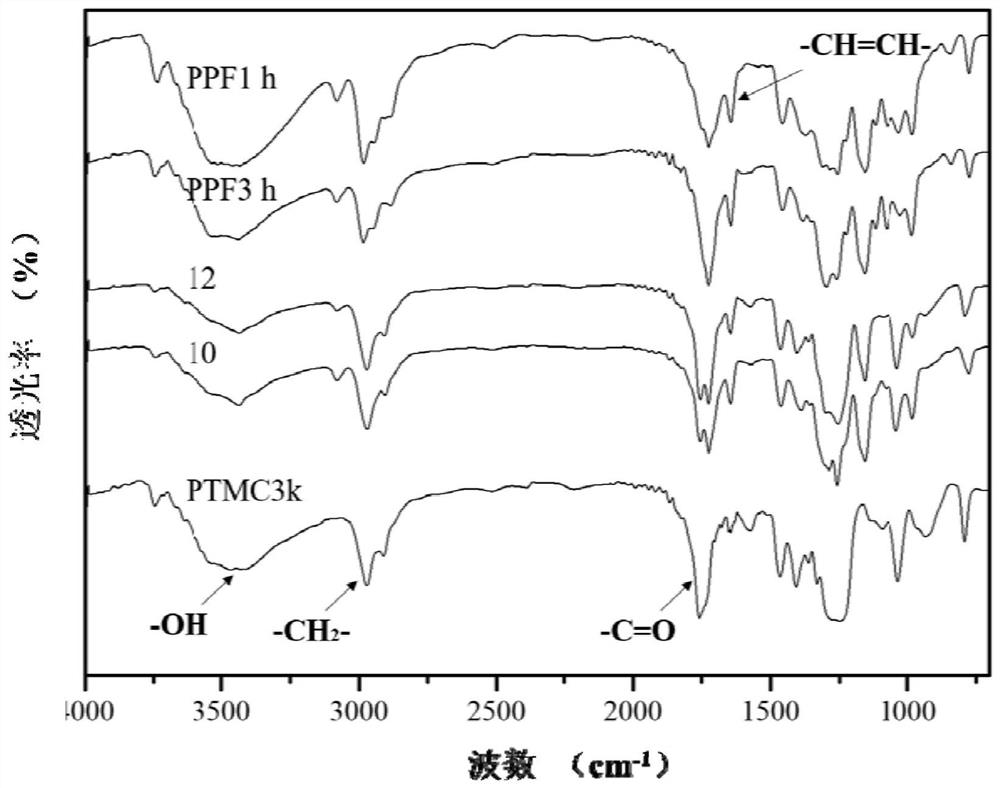
[0063] 1) Synthesis of polytrimethylene carbonate (PTMC): 50g of TMC monomer and 2.8g of diethylene glycol (diethyleneglycol) were placed in a vacuum oven at 50°C and vacuum 2 ) and 3 mL of anhydrous toluene; seal the polymerization bottle and vacuumize for 2 days to remove the toluene and water, then place it in an oil bath at 130°C for 3 days, add 100 mL of dichloromethane to dissolve the polymerization bottle after quenching, and then dissolve in 1L of petroleum ether The precipitation was repeated three times, and vacuum drying was performed to obtain polytrimethylene carbonate (PTMC2k) with a number average molecular weight of 2000 (Mn=2000).
[0064] 2) Synthesis of polytrimethylene fumarate (PPF): 50g ...
Embodiment 2~12
[0066] Embodiment 2~12 preparation of novel photocrosslinking degradable multi-block copolymer
[0067] The preparation method of novel photocrosslinkable degradable multi-block copolymer among the embodiment 2~12 is identical with embodiment 1, and difference is only in the synthetic reaction time of PPF (i.e. fumarate bis(hydroxypropyl) ester adds vacuum and heats up after The polycondensation time), the number average molecular weight of PTMC and the PTMC feed ratio (that is, the ratio of PTMC quality to the sum of PTMC and PPF mass), as shown in Table 1.
[0068] Differences between the preparation method of the novel photocrosslinkable degradable multi-block copolymer in Examples 2-12 of Table 1 and Example 1
[0069]
[0070]
[0071] NOTE: The number average molecular weight of PTMC is controlled by the monomer to initiator molar ratio.
Embodiment 13
[0073] Synthesis of polytrimethylene fumarate (PPF): 50g diethyl fumarate (diethyl fumarate) and 65.97g 1,2-propanediol (1,2-propandiol) were added to the three-necked flask successively, under nitrogen atmosphere ( Flow rate: 3~5 bubbles per second) Stirring at 150rpm for 20min, then adding 0.39g of zinc chloride (ZnCl 2 ) mixed with 0.064g hydroquinone; stirred at 100°C and stirred at 300rpm for 30min and then heated up to 150°C for 7h and then cooled to 100°C (first step reaction) to obtain di(hydroxypropyl) fumarate ( bis (hydroxypropyl) fumarate); apply vacuum, react at 100°C for 1 hour, then raise the temperature to 130°C for 7 hours (the second step reaction), and obtain PPF.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com