Application of lithocholic acid (LCA) in preparation of drug for relieving liver fibrosis
A technology of liver fibrosis and lithocholic acid, which is applied in the application field of medicine, can solve the problems of disappearance of biological energy and damage of cell membrane, and achieve the effect of reducing secretion, increasing intestinal relative abundance and reducing relative abundance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
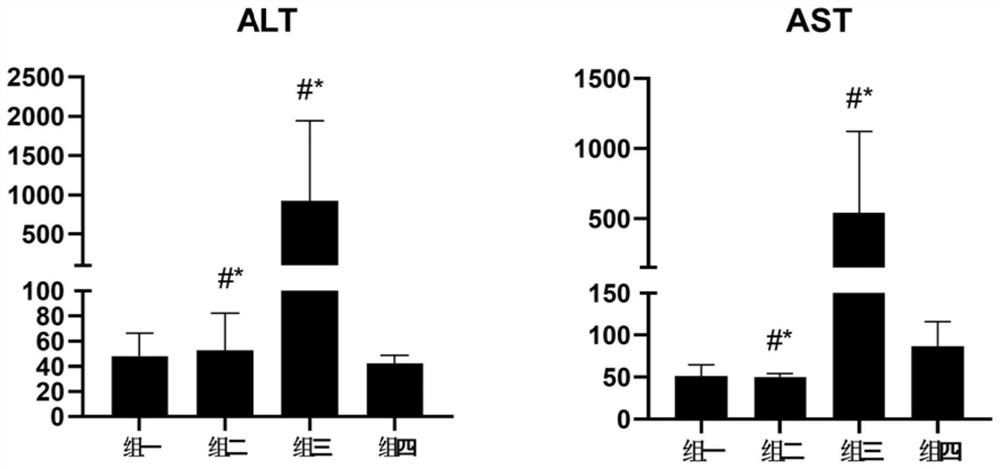
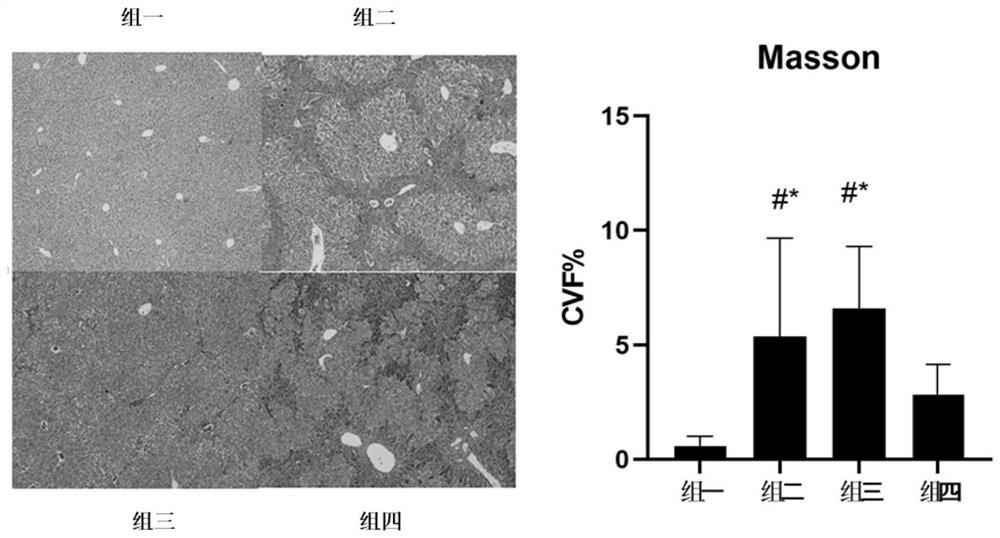
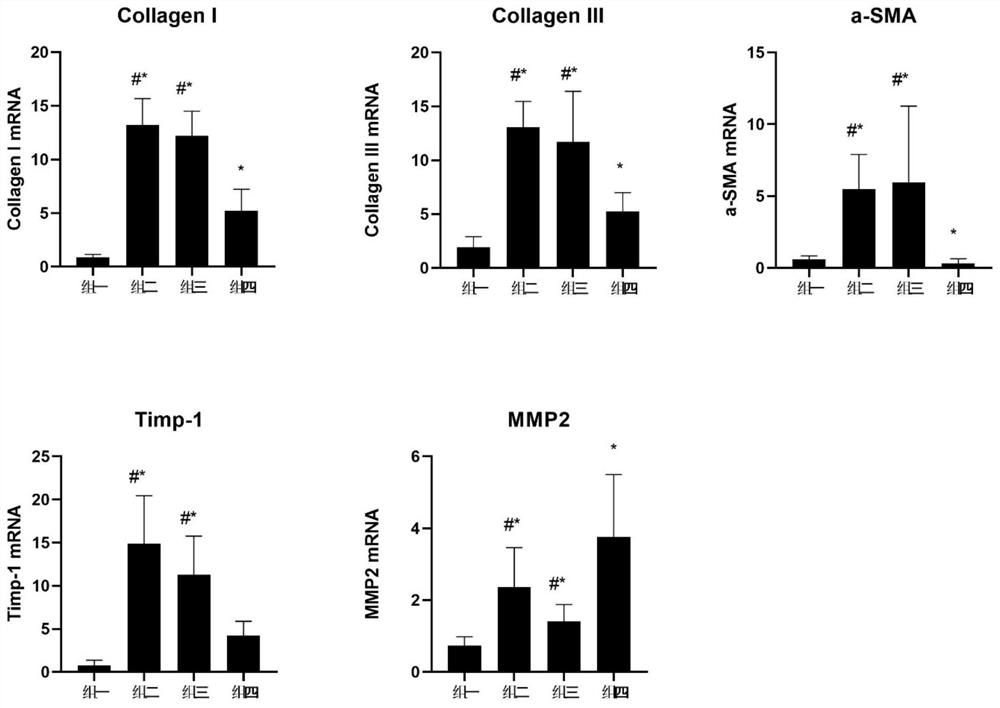
[0018] Example 1 LCA can inhibit liver inflammation and alleviate liver fibrosis
[0019] experimental method
[0020] 40 mice were randomly divided into 4 groups, 10 in each group.
[0021] Group 1: intraperitoneal injection of normal saline twice a week, gavage of deionized water twice;
[0022] Group 2: carbon tetrachloride model group (CCl4): olive oil 1:4, 1ul / g dose was injected intraperitoneally twice a week to mice. Oral administration of deionized water twice a week;
[0023] Group 3: Antibiotic treatment model intervention group (CCl4+LCA+VA): olive oil 1:4, 1ul / g dose was intraperitoneally injected to mice twice a week, and LCA was given to mice at a dose of 1mg / 15g by intragastric administration every week 2 times. Kill mouse intestinal flora with antibiotics (vancomycin 0.5g / L+ampicillin 1g / L is VA);
[0024] Group 4: Model intervention group (CCl4+LCA): olive oil 1:4, 1ul / g dose per intraperitoneal injection twice a week to mice, LCA 1mg / 15g dose intragastri...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2 Interaction between LCA and intestinal flora
[0029] experimental method:
[0030] For each of the above groups, the fresh feces of the mice in each group were collected 24 hours before treatment, and frozen at -80°C. The intestinal flora among the mice in each group was detected by 16sRNA technology, and the differences in the flora among the groups were compared.
[0031] Experimental results:
[0032] It was found that the relative abundance of harmful bacteria Dubosiella (Dubosiella) decreased in the intestinal tract of LCA-administered mice, and the relative abundance of probiotics Lactobacillus and Bacteroides increased ( Figure 5 ). Antibiotics were used to kill intestinal symbiotic bacteria, and the effects of LCA on inhibiting liver inflammation and alleviating fibrosis disappeared. Demonstrate that the interaction of the gut microbiota-bile acid-liver triangle is the cornerstone of LCA action.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Example 3 LCA achieves anti-fibrosis effect by inhibiting liver NKT cell activator to reduce TNF-a concentration
[0034] experimental method:
[0035] The fresh liver of the mouse was taken, and the single cell suspension of the liver was prepared, and the immune cells in the liver: NKT cells, NK cells and macrophages, and the macrophages in the blood of the mice were detected by flow cytometry. The serum of the mice was detected by flow cytometric CBA.
[0036] Experimental results:
[0037]It was found that LCA can inhibit the activation of NKT cells, and the activation of NKT cells is manifested as down-regulation of NKT cells in liver tissue, which is related to the loss of specific antigens after NKT cell activation. After antibiotics kill the gut flora, the percentage of NKT cells increases. The change of TNF-α concentration in each group in serum is consistent with above-mentioned result ( Figure 5 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com