Method for in-situ construction of surface coating layer based on metal-organic framework material
A framework material and surface coating technology, which is applied in the field of in-situ construction of surface coating layers on different substrates based on metal-organic framework materials, which can solve the problem of poor uniformity and continuity of coating thickness and the inability to accurately control coating thickness To achieve the effect of improving reaction kinetics, reducing surface film resistance and charge transfer resistance, and inhibiting dissolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0055] The preparation method of the present invention will be further described in detail in conjunction with specific examples below. It should be understood that the following examples are only for illustrating and explaining the present invention, and should not be construed as limiting the protection scope of the present invention. All technologies realized based on the above contents of the present invention are covered within the scope of protection intended by the present invention.
[0056] The experimental methods used in the following examples are conventional methods unless otherwise specified; the reagents and materials used in the following examples can be obtained from commercial sources unless otherwise specified.
[0057] The present invention will be further elaborated below through specific implementation cases. Among them, the addition amount of organic complexing agent and solvent can be adjusted according to the actual situation, so as to realize the con...
Embodiment 1
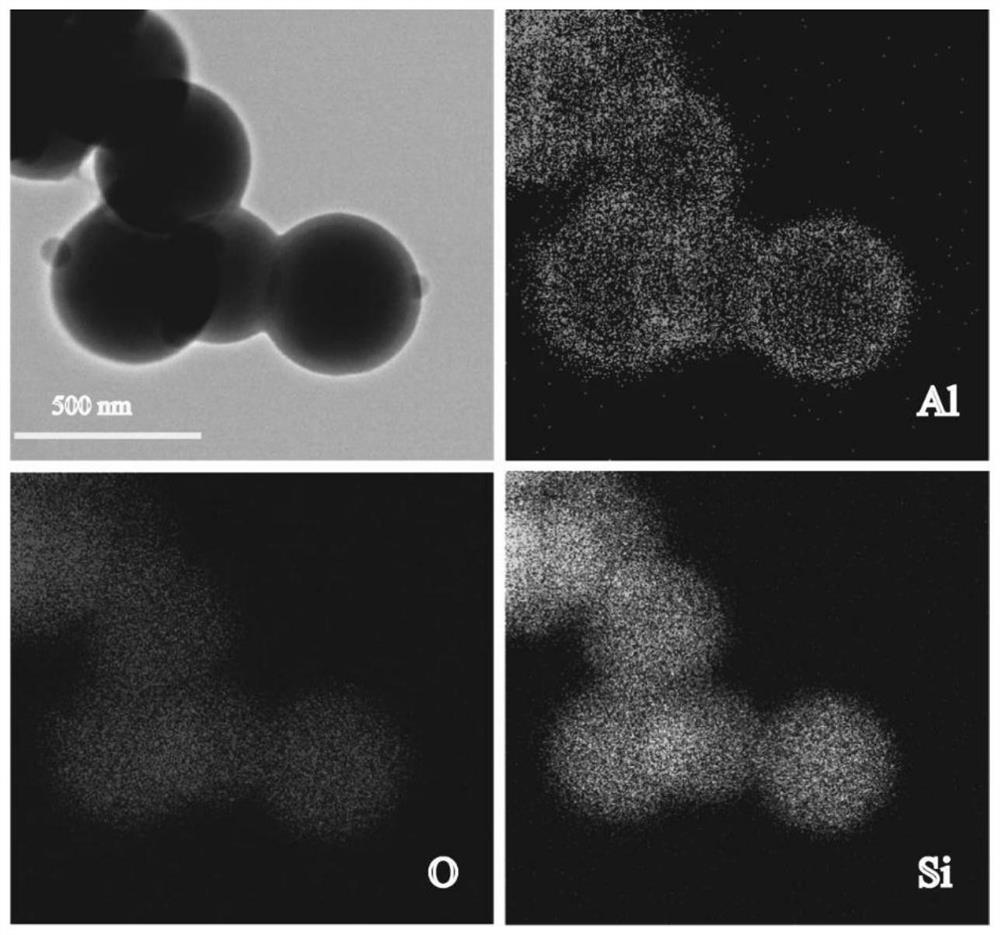
[0060] 1. Preparation of Al-MOF structure-coated silica spheres (SiO 2 )
[0061] 100mg SiO 2 Beads, 166mg of aluminum sulfate octadecahydrate, and 75mg of isophthalic acid were dispersed in 15ml of N,N-dimethylformamide solution and 5ml of absolute ethanol solution, and dispersed evenly by ultrasonication; reflux reaction at 80°C for 24h, centrifuged, After washing and drying, the silica with a core-shell structure coated based on the Al-MOF structure can be obtained.
[0062] 2. Structural and Morphological Characterization of Processed Materials
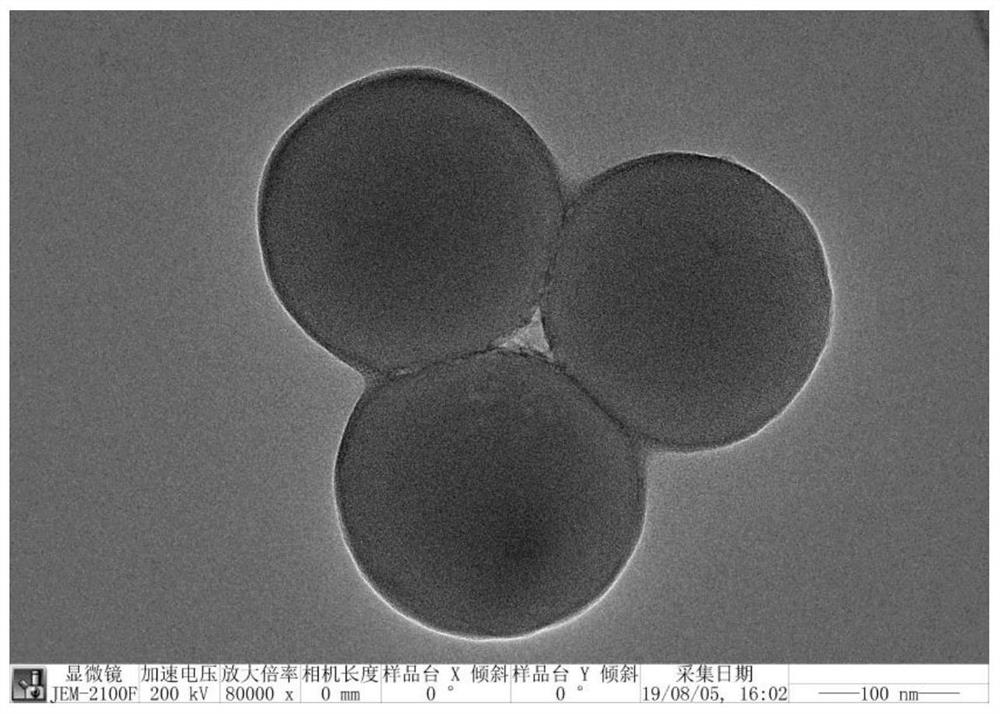
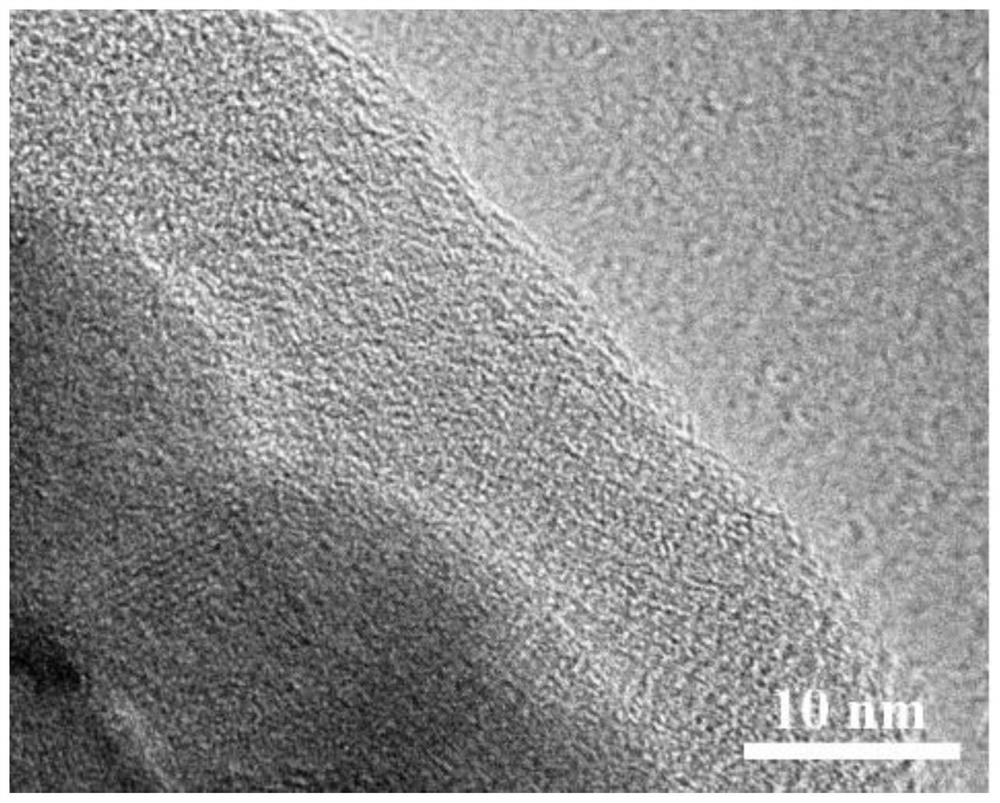
[0063] The Al-MOF structure-coated silica prepared in the above scheme has a typical core-shell structure, and its transmission electron microscope shows figure 1 shown. The core material is silica pellets with an average particle size of 414nm, the shell material is an Al-MOF structure with a thickness of 30nm, and the Al-MOF is evenly distributed on the surface of the silica.
Embodiment 2
[0065] 1. Preparation of Al-MOF structure-coated tin dioxide pellets (SnO 2 )
[0066] 100mg SnO 2 Beads (average particle size is 50nm), 166mg of aluminum sulfate octadecahydrate, 75mg of isophthalic acid are dispersed in 15ml of N,N-dimethylformamide solution and 5ml of absolute ethanol solution, ultrasonically and dispersed uniformly; at 80 ℃ reflux reaction for 24 hours, after centrifugation, washing and drying, the tin dioxide with core-shell structure coated based on Al-MOF structure can be obtained.
[0067] 2. Structural and Morphological Characterization of Processed Materials
[0068] The tin dioxide coated with Al-MOF structure prepared in the above scheme has a typical core-shell structure, and its transmission electron microscope shows figure 2 shown. The core material is tin dioxide pellets with an average particle size of 50nm, the shell material is an Al-MOF structure with a thickness of 15nm, and the Al-MOF is evenly distributed on the surface of the tin ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com