Immobilized lactase with hydrophobic property and method for preparing lactulose by applying immobilized lactase
A lactase and hydrophobic technology, applied in the direction of immobilized enzymes, biochemical equipment and methods, hydrolytic enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable lactulose production and high hydrolysis activity, and achieve easy recycling, simplified purification, and cost reduction Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Immobilized lactase
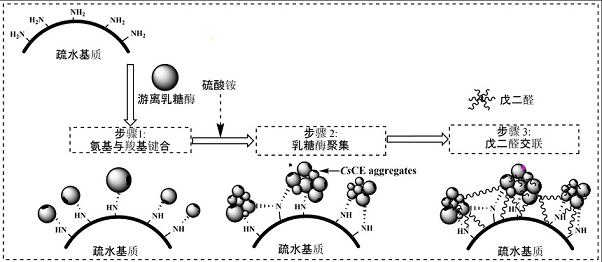
[0036] DSM's Maxilact ® Take lactase as an example, add it to the phosphate buffer solution with pH 6.8, the enzyme protein concentration is 2.5 mg / mL, and add commercially available amino resin (take Duolite A568 amino resin of DOW Company as an example), the amount of resin added to 0.5 mg / mL, react at 4°C for 12 h, then slowly add ground ammonium sulfate powder until its saturation reaches 70%, continue stirring at 4°C for 30 min, then add glutaraldehyde solution (commercially available product, 25 %, v / v) until the concentration of glutaraldehyde in the whole system was 0.5% (v / v), stirred slowly at 4°C for 4 h, then collected the immobilized lactase particles by filtration, and used phosphate buffer solution of pH 6.8 to The collected immobilized lactase particles were washed three times, and then freeze-dried. The schematic diagram of the operation of immobilized lactase is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the electron micrograph ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Preparation of Lactulose from Lactose Catalyzed by Immobilized Lactase
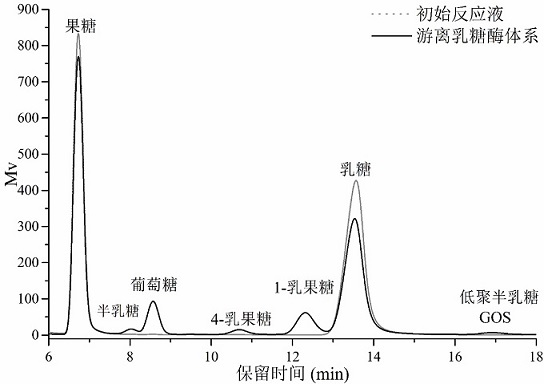
[0038]Add 250 g of lactose and 250 g of fructose to the pH 6.8 phosphate buffer, stir to dissolve (heating can be used to assist dissolution), and prepare 2 parts (A and B) each 1 L with a final lactose and fructose content of 250 g / L of the reaction substrate solution, add 2 mL of free lactase to A as a catalyst, add 5 g of immobilized lactase to B as a catalyst, stir and react for 6 h at 37°C, and take 1 mL of the reaction solution each , inactivate the enzyme in a boiling water bath for 5 min, dilute to an appropriate multiple, and then use high performance liquid chromatography to detect the composition and content of various sugars in the reaction solution system. The obtained HPLC chromatograms are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4 below. It can be seen from the analysis that the final lactulose content of group A using free enzyme is 46.18 g / L, including 38.65 g / L 1-lactulose and 7....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com