A visualized sensor for live-cell imaging of circRNA based on nucleic acid self-assembly without enzyme catalysis
A non-enzyme catalysis and self-assembly technology, applied in the field of biosensors, can solve the problems of complex instruments, limited routine applications, cumbersome operations, etc., and achieve the effect of shortening the detection time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 The establishment of a visual sensor based on GO and nucleic acid self-assembly without enzyme catalysis
[0047] 1. Experimental materials
[0048] Graphene oxide GO, SYBR Gold nucleic acid dye, nucleic acid molecular weight standard ultra-low range DNAladder, 4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), Tris, sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, potassium chloride, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid Disodium, sulfuric acid, tetramethylbenzidine, and urea were purchased from Thermo Scientific Life Technologies, and Beas-2B, MCF-7, H596, H1299, and L02 cells were obtained from Shanghai Institute of Biological Sciences. All experimental water was from Milli-Q pure water system.
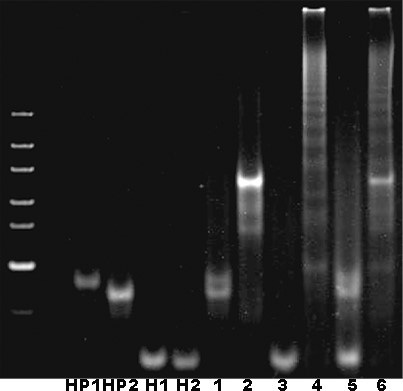
[0049] The detection hairpin strands (HP1, HP2, H1, H2) of CHA and HCR used in the experiment and the replacement strands (I' and I) of the circRNA to be detected are as follows:
[0050] SEQ ID NO: 1 (HP1): 5'-GCTATGTTGTTTCGTCTTGAGGTAGGCCGTCCAGACAAAATCCCTCAAGACGAATTCCAGACT-3' ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2 The specificity investigation of sensor
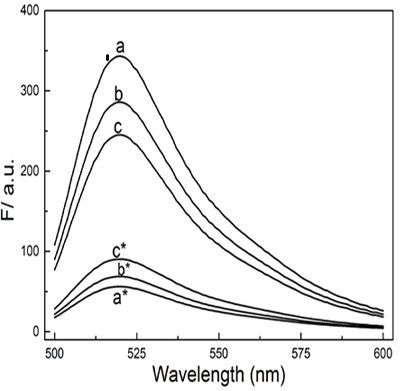
[0064] According to the biosensor constructed in Example 1, L02, H596, H1299 and Beas-2B cell lysates were added to the system for detection. The results showed that the established circRNA biosensor had better specificity ( Figure 4 ).
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3 Intracellular Imaging Investigation of Sensors
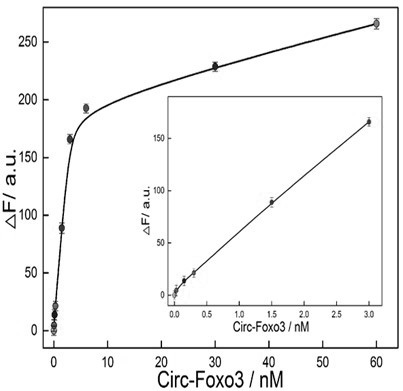
[0066] The biosensors constructed in Example 1 were added to Beas-2B and MCF-7 cells and incubated for 24 hours. CCK8 was used to detect the toxicity of the sensors to the cells. It was found that it hardly affected the viability of the cells, and subsequent intracellular fluorescence imaging experiments could be carried out. ( Figure 5 ), followed by adding the detection system to different concentrations of serum ( Image 6 A) and 2U DNase I to detect its stability in complex biological fluids ( Image 6 B), the detection system was found to have high stability. Finally, the biosensor was added to Beas-2B and MCF-7 cells and incubated for 7 hours, and the spatial position information of the intracellular target circRNA and the change of its content could be observed under a fluorescence microscope ( Figure 7 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com