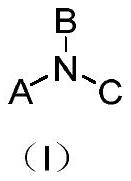
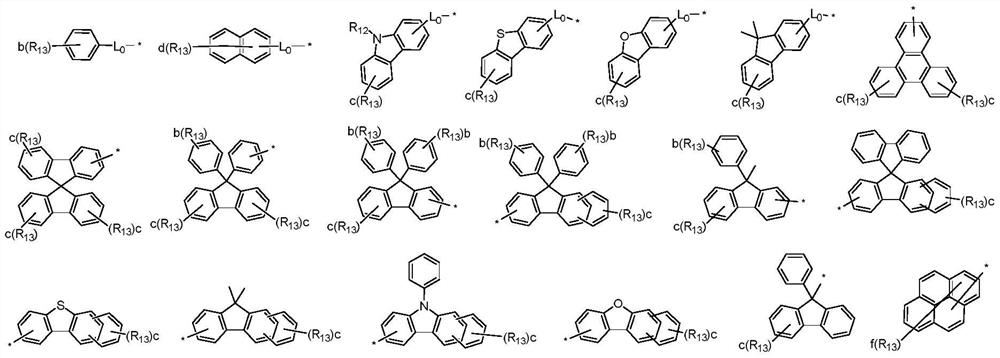
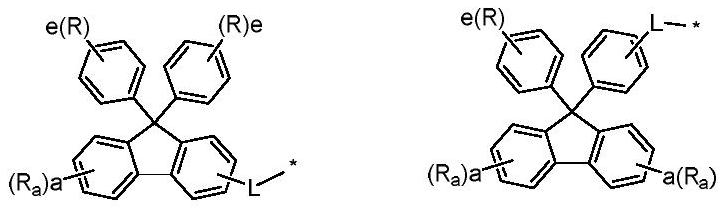An organic light emitting device
A technology of organic light-emitting devices and organic substances, which is applied in the manufacture of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state devices, etc. Luminous efficiency and driving voltage, and the effect of improving luminous efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0142] The preparation and formation methods of each layer in the organic light-emitting device are not particularly limited, and vacuum evaporation method, spin coating method, vapor deposition method, blade coating method, laser thermal transfer method, electrospray coating method, slit coating method can be used. Either of the cloth method and the dip coating method, the method of vacuum vapor deposition is preferably used in the present invention.
[0143] The organic light-emitting device of the present invention can be widely used in the fields of panel display, lighting source, flexible OLED, electronic paper, organic solar cell, organic photoreceptor or organic thin film transistor, signboard, signal lamp and the like.
[0144] The second hole transport layer made of the material of formula (I) and the covering layer made of the material of formula (IV), the corresponding compounds can be obtained by the following methods:
[0145] The triarylamine compound represent...
Embodiment 1
[0154] [Example 1] Synthesis of Compound 1-1
[0155]
[0156] Step1: Synthesis of intermediate A-1
[0157] Under nitrogen protection, toluene (600mL), a-1 (20.00g, 0.06mol), b-1 (23.83g, 0.06mol), palladium acetate (0.21g, 0.93mmol), tert- Sodium butoxide (11.3 g, 0.117 mol) and tri-tert-butylphosphine (8 mL in toluene). And react under the condition of reflux for 2 hours. After the reaction stopped, the mixture was cooled to room temperature, filtered with diatomaceous earth, the filtrate was concentrated, recrystallized with methanol, filtered with suction and rinsed with methanol to obtain a recrystallized solid to obtain intermediate A-1 (30.41g, yield 78%) , HPLC detection solid purity ≧ 99.7%.
[0158] Step2: Synthesis of compound 1-1
[0159] Under nitrogen protection, toluene solvent (600ml), c-1 (5.83g, 36mmol), intermediate A-1 (23.39g, 36mmol), Pd 2 (dba) 3 (330mg, 0.36mmol), BINAP (0.67g, 1.08mmol) and sodium tert-butoxide (3.23g, 33.6mmol), stirred and ...
Embodiment 2
[0161] [Example 2] Synthesis of Compound 1-22
[0162] Compound 1-22 (17.66 g) was synthesized by the method of compound 1-1 above, and the purity of the solid was detected by HPLC ≧99.7%. Mass Spectrum m / z: 730.3419 (Theoretical: 730.3396). Theoretical element content (%)C 56 h 34 D. 5 N: C, 92.02; H, 6.07; N, 1.92 Measured element content (%): C, 92.02; H, 6.07; N, 1.95.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com