Method for extracting D-allose from nut shells by microwave radiation process
A microwave radiation method, microwave radiation technology, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, monosaccharides, sugar derivatives, etc., can solve the problems of high price of biological enzymes, high price of D-allose, etc., to improve resource utilization, Enhancement of added value and efficient extraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] In this example, D-allose is extracted from Cornus officinalis. The raw material of Cornus officinalis comes from the Funiu Mountain area in Henan, which is the plant waste of Cornus officinalis. The specific extraction process is as follows:
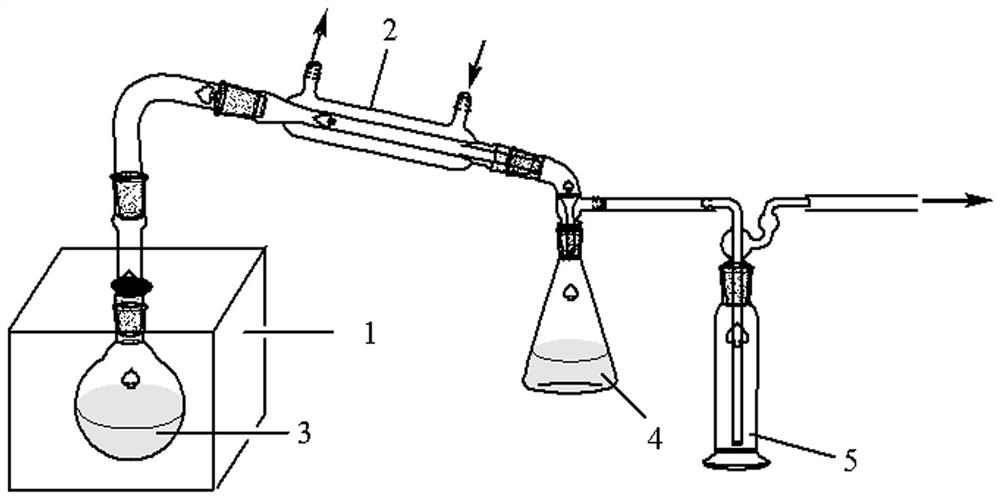
[0045] Crush Cornus officinalis seeds into particles with a particle size not greater than 5cm. After that, accurately weigh 100g of crushed Cornus officinalis seeds and 2.0g of wave-absorbing material according to the mass ratio of 1:0.02. The wave-absorbing material used here is The mass ratio is 0.5:1 The compound of ferric oxide and graphite, after fully mixing, is placed in the round bottom flask in the microwave reactor, the power of the microwave reactor is set to 800W, and the microwave reactor is turned on. Microwave radiation reaction 10min. After the reaction, the liquid in the Erlenmeyer flask was collected. The liquid is subjected to rotary distillation separation at a vacuum degree of 500mmHg and a temperature of 1...
Embodiment 2
[0050] In this example, D-allose is extracted from Cornus officinalis. The raw material of Cornus officinalis comes from the Funiu Mountain area in Henan, which is the plant waste of Cornus officinalis. The specific extraction process is as follows:
[0051] Crush Cornus officinalis seeds into particles with a particle size not greater than 2cm. After that, accurately weigh 100g of crushed Cornus officinalis seeds and 5.0g of wave-absorbing material according to the mass ratio of 1:0.05. The wave-absorbing material used here is The compound of ferric oxide and activated carbon with a mass ratio of 1:1, after fully mixing, is placed in a round-bottomed flask in a microwave reactor, the power of the microwave reactor is set to 700W, and the microwave reactor is turned on. Microwave radiation reaction 15min. After the reaction, the liquid in the Erlenmeyer flask was collected. The liquid is subjected to rotary distillation separation at a vacuum degree of 600mmHg and a temperatu...
Embodiment 3
[0053] In this example, D-allose is extracted from walnut shells. The specific extraction process is as follows:
[0054] Crush the walnut shells into particles with a particle size not greater than 3cm. After that, accurately weigh 100g of the crushed walnut shell particles and 3.0g of the wave-absorbing material according to the mass ratio of 1:0.03. The wave-absorbing material used here is The compound of cobalt oxide and graphite with a mass ratio of 0.3:1.2, after being fully mixed, is placed in a round bottom flask in a microwave reactor, the power of the microwave reactor is set to 500W, and the microwave reactor is turned on for microwave radiation React for 20 minutes. After the reaction, the liquid in the Erlenmeyer flask was collected. The liquid is subjected to rotary distillation separation at a vacuum degree of 300mmHg and a temperature of 150°C to separate part of the water and low-boiling point oil until no fraction flows out; then, the viscous solid phase obt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com