Recombinant yeast for producing xanthophyll and application of recombinant yeast
A technology of recombinant yeast and lutein, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as limiting substrate conversion efficiency and product synthesis, and achieve the effects of solving competitive utilization problems, promoting synthesis, and good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: Cloning and expression of enzyme genes required for lutein biosynthesis
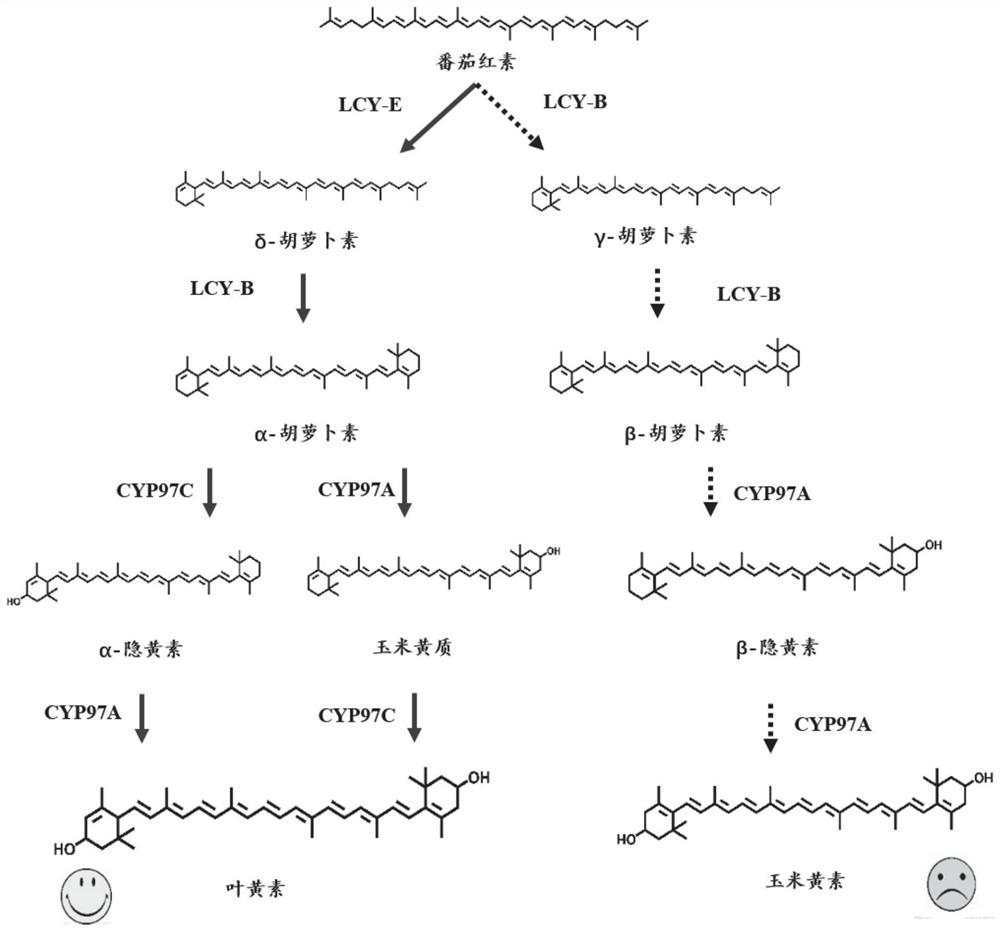
[0024] 1. The enzymes required in the lutein synthesis pathway of plants or algae, combined with the existing enzyme library in the laboratory: phytoene synthase, phytoene dehydrogenase, lycopene β-cyclase (W.Xie, X.Lv, L.Ye, P.Zhou, H.Yu, Construction of lycopene-overproducing Saccharomyces cerevisiae by combining directed evolution and metabolic engineering. Metab.Eng.30,69-78, doi:10.1016 / j .ymben.2015.04.009 (2015)), found the rest of the corresponding nucleic acid sequence or protein sequence in NCBI (see Table 1), through the codon optimization website, according to the corresponding yeast host codon optimization, the optimized gene sequence Send it to Gene Company for synthesis, and obtain three enzymes that can be successfully expressed in yeast, namely: lycopene ε-cyclase, carotene β-hydroxylase, and carotene ε-hydroxylase.
[0025] Table 1: Genes required for synthesis
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Introduction of a temperature-sensitive Gal4 mutant (Gal4M9)
[0038] 1. Knock out the GAL4 gene by homologous recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In this process, a HIS3 knockout cassette for GAL4 is constructed: GAL4 upstream homologous segment-HIS3 expression cassette-GAL4 downstream homologous segment. Fragment 1 expressing HIS3 was amplified from PUG23 (GenBank: AF298783.1) with GAL4-HisF1 and GAL4-HisXF1, and the upstream homology arm was amplified from the genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741 with GAL4-CyF and GAL4-HISR1, which is the fragment 2. Use GAL4-His-XR1 and GAL4-XinF1 to amplify the downstream homology arm from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741 genome, which is fragment 3, and perform overlap extension PCR on the three fragments to obtain the HIS3 knockout GAL4 fragment (see Table 2 for primers) . The transcription activator GAL4 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae YY00 constructed in Example 1 was knocked out by using the HIS3 express...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3: Verification of Cell Membrane Localization Sequences
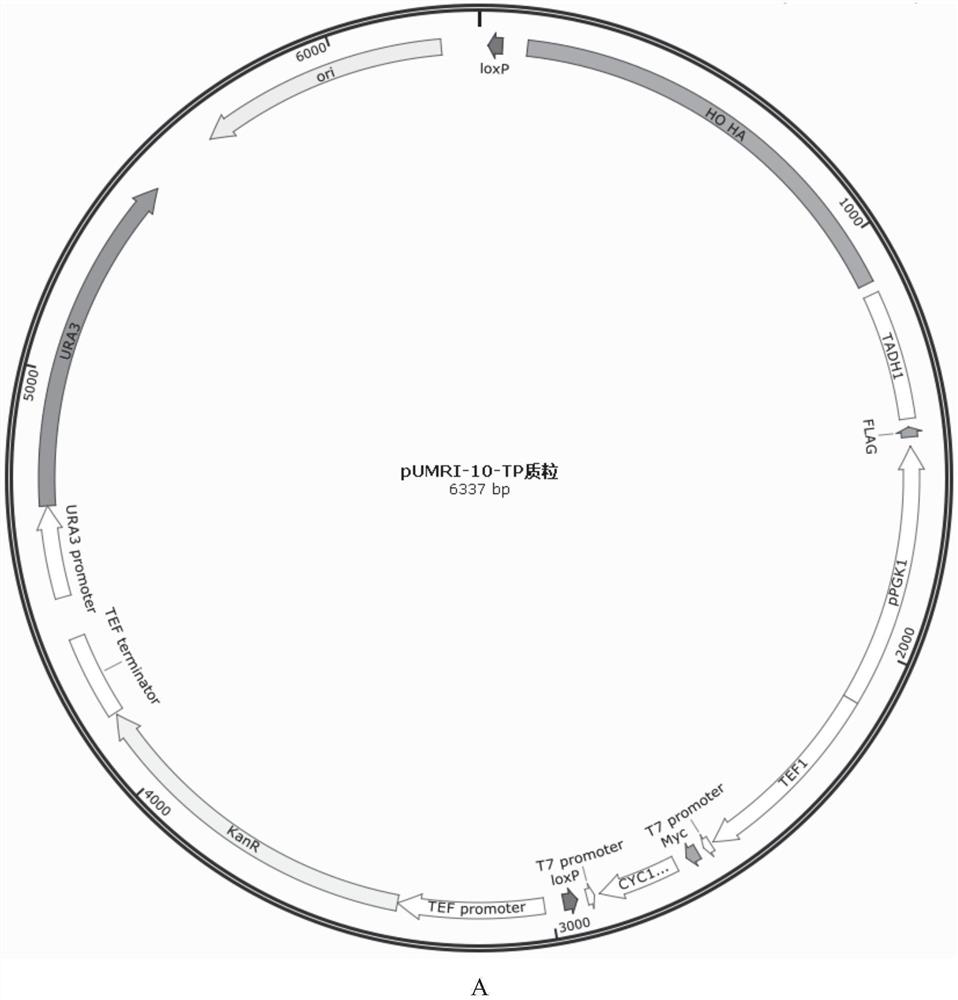
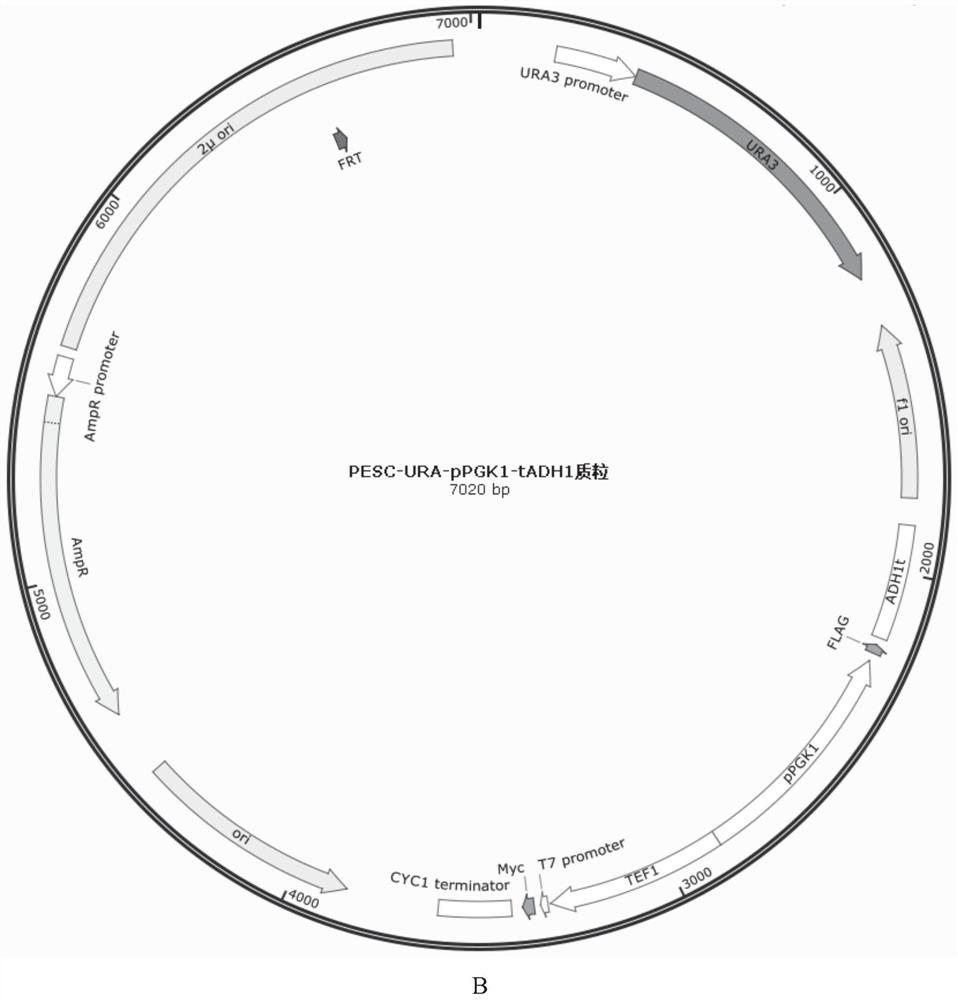
[0044] 1. Primer EGFP-F and EGFP-R Using PUG23 (GenBank: AF298783) as a template to amplify the EGFP fragment by PCR, use NotI and SpeI for the EGFP fragment and the PESC-URA-pPGK1-tADH1 plasmid (see figure 2 ) for double enzyme digestion, transformation after ligation, and cloning to obtain PESC-URA-pPGK1-EGFP-tADH1.
[0045] 2. Utilize the plasmid obtained by cloning in step 1, the primers in Table 4, and use high-fidelity enzyme (Prime STAR TM HSDNA polymerase) to construct plasmids by CPEC (Circular polymerase extension cloning) method. The CPEC reaction system (10 μl) is: Prime Star buffer: 2 μl; dNTPs (2.5mM): 1 μl; primer 1: 0.4 μl; primer 2: 0.4 μl; template: 0.2 μl; DNA polymerase: 0.1 μl; Water: 5.9 μl.
[0046] The PCR program was as follows: pre-denaturation at 98°C for 2 min; denaturation at 98°C for 10 s, annealing at Tm±5°C for 20 s, extension at 72°C at 1 kb / min, a total of 20 cyc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com