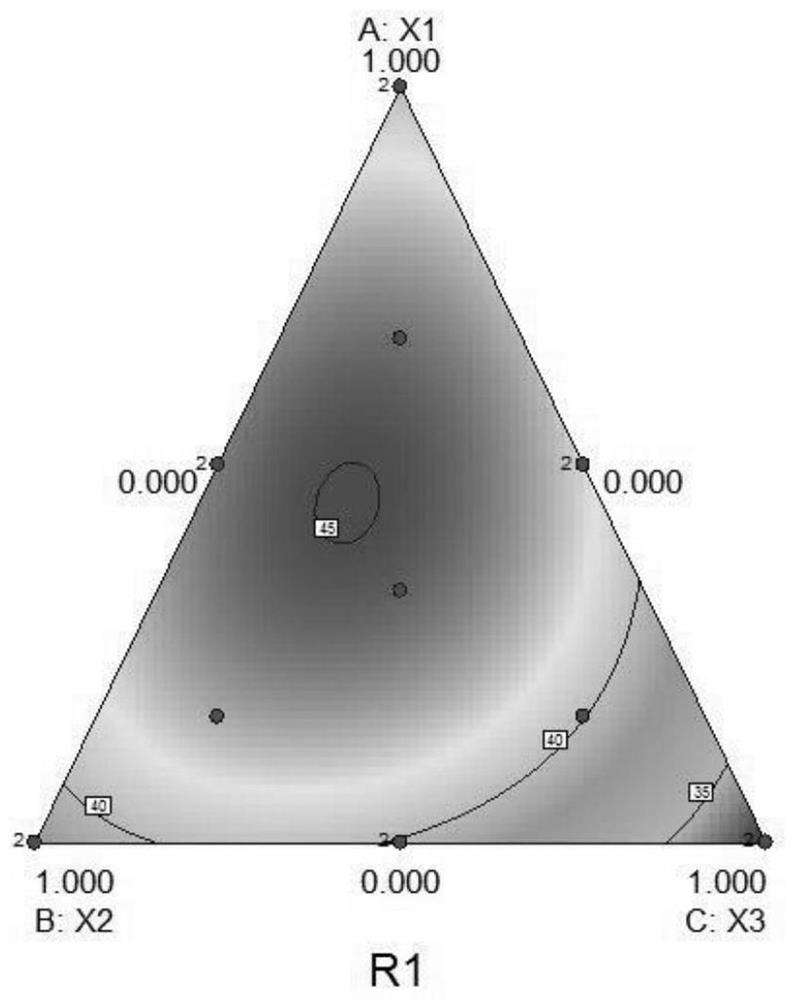
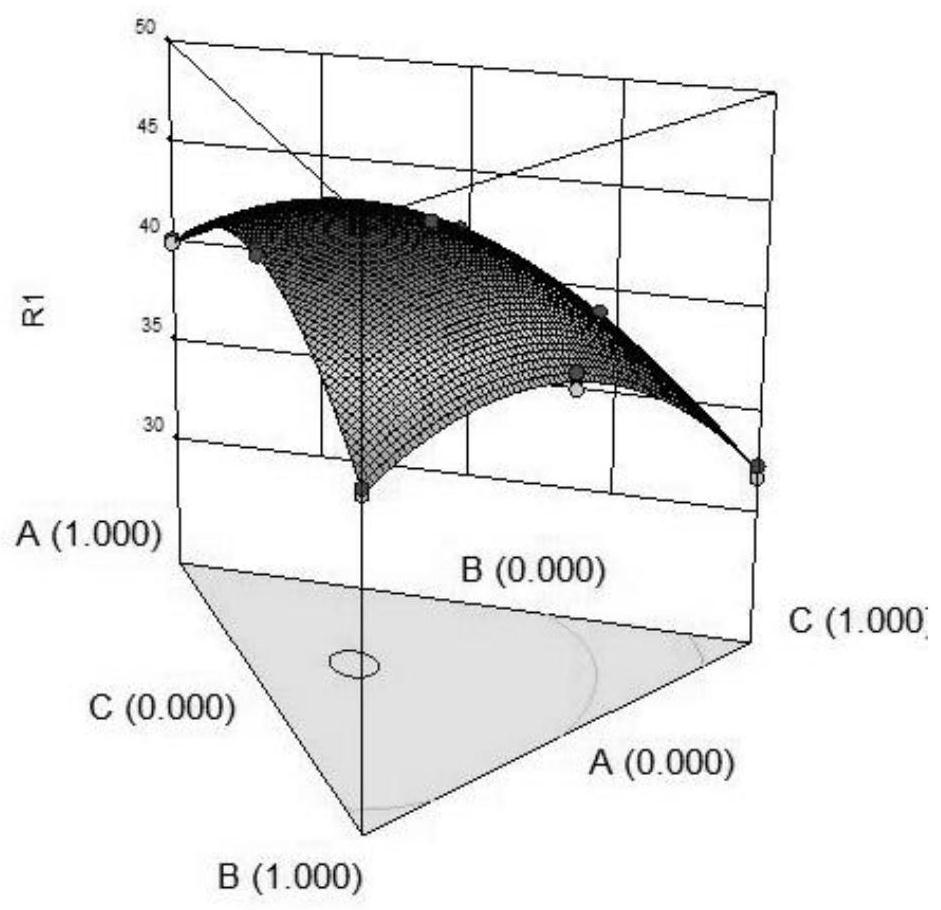
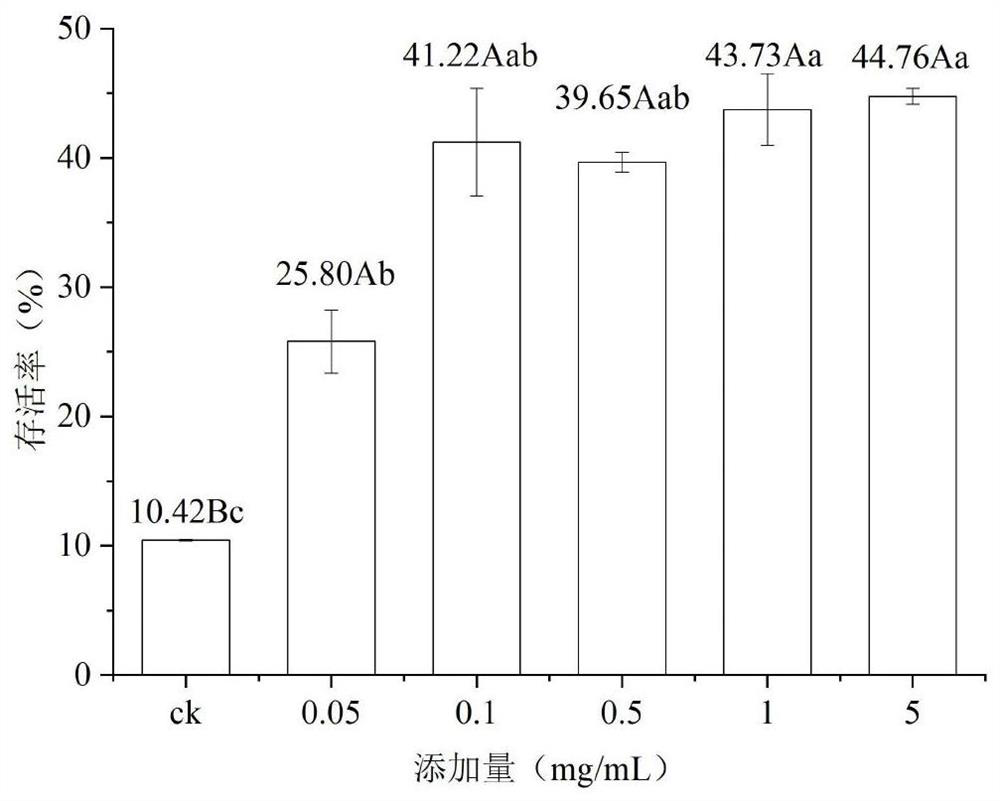
Red yeast rice vinasse heat-resistant peptide agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology for red yeast rice and red yeast rice powder, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism-based methods, fungi, etc., can solve the problems of many insoluble substances, low utilization rate, pollute the ecological environment, etc., and achieve rich varieties. , The effect of improving the utilization rate of protein and the degree of hydrolysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] A preparation method of red yeast rice anti-heat peptide agent, comprising the following steps:
[0026] Take fresh red yeast rice grains and dry them, and then carry out ultrafine pulverization to obtain red yeast rice grains powder;
[0027] The red yeast rice powder is prepared into a red yeast rice suspension with a mass percentage fraction of 6-10% with deionized water, and the pH value of the red yeast rice suspension is adjusted to 4-5, and the mass percentage fraction is 1-1.5% of the cellulase is degraded for more than 8 hours, then reacted in a high-temperature reactor, and then homogenized with micro-jet to obtain micronized red yeast rice grains;
[0028] adjusting the pH value of the micronized red yeast rice grains to 5.8-6.5, degrading with amylase and then precipitating at a pH value of 4.5 to obtain a precipitate;
[0029] The precipitate is enzymolyzed with a protease complex to obtain the primary product of the anti-heat peptide agent of red yeast ri...
Embodiment 1
[0050] A method for preparing an anti-heat peptide agent from red yeast rice, which specifically takes the following steps: take an appropriate amount of fresh red yeast rice and dry it at 60°C, and then perform ultrafine grinding until the D50 is 40-50μm, and more than 90% The particle size of the red yeast rice powder is less than 150 μm, and the red yeast rice powder is obtained. After ultrafine pulverization, the utilization rate of red yeast rice grains is 67.23%, which is significantly better than 60.78% obtained by ordinary pulverization. The red yeast rice powder is formulated with deionized water into an 8% red yeast rice suspension by mass percentage, the pH value of the red yeast rice suspension is adjusted to 4.5, and 1% cellulose by mass percentage is added Enzymatically degrade for 24 hours, then react in a high-temperature reactor at 120°C for 20 minutes under high pressure, and use a micro-fluidic reactor to homogenize three times at a pressure of 100 MPa to ob...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The difference from Example 1 is that the red yeast rice powder is formulated with deionized water into a suspension of 6% by mass percentage, and the pH value of the suspension of the red yeast rice is adjusted to 4.0. After being degraded with cellulase, react in a high-temperature reactor at 110°C for 20 minutes under high pressure, and use a micro-fluidic reactor at a pressure of 150 MPa to homogenize 3 times to obtain micronized red yeast rice grains. After this step, the utilization of red yeast rice grains protein The rate was further increased to 76.43%. The pH value of the micronized red yeast rice is adjusted to 6.5, and the reaction conditions for enzymatic hydrolysis with amylase are as follows: amylase is added to the micronized red yeast rice in an amount of 0.5% by mass. The precipitate is enzymolyzed with a protease complex, and the protease complex used is formulated with alkaline protease, neutral protease, and papain in a weight ratio of 495:385:219 (...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Relative molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com