A kind of oxazole derivative fluorescent probe and its preparation method and application
A technology of fluorescent probes and derivatives, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, chemical instruments and methods, luminescent materials, etc., can solve problems such as affecting self-purification ability, human health damage, environmental pollution, etc., achieving simple structure and low cost of raw materials , the effect of high purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A preparation method of an oxazole derivative fluorescent probe, the technical route is as follows:
[0034] ;
[0035] Proceed as follows:
[0036] (1) Add thionyl chloride (0.90 g, 7.50 mmol) to anhydrous benzene (40 mL) containing 2-(2-hydroxybenzene)oxazole-4-carboxylic acid (0.51 g, 2.50 mmol), and magnetically The mixture was heated to 80° C. with stirring, and the reaction was refluxed for 4 hours. Cool to room temperature, remove the unreacted thionyl chloride and solvent benzene to obtain the acid chloride of oxazoles;
[0037] (2) The acid chloride (1.50 mmol) of the oxazoles prepared in step (1) was dissolved in anhydrous dichloromethane, and then 2-aminomethylpyridine (0.33 g, 3.00 mmol) was added, and heated to 45 °C to fully react After 4 hours, cooled to room temperature, the solvent was concentrated, and purified by column chromatography to obtain 0.42 g of oxazole derivative fluorescent probe.
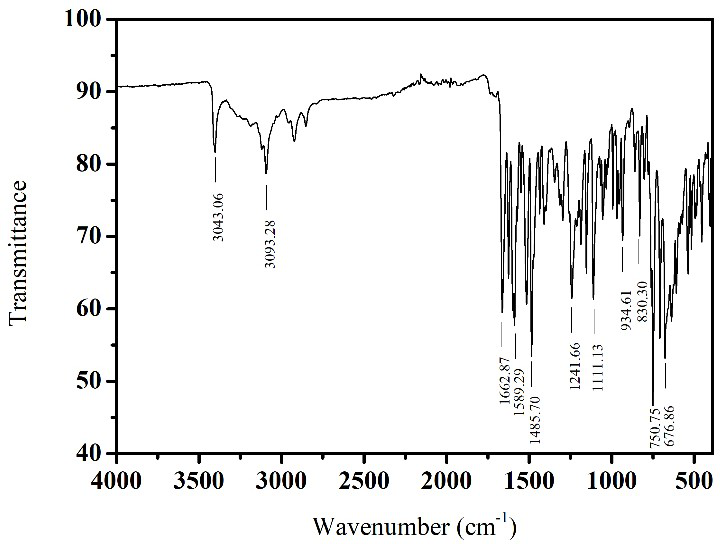
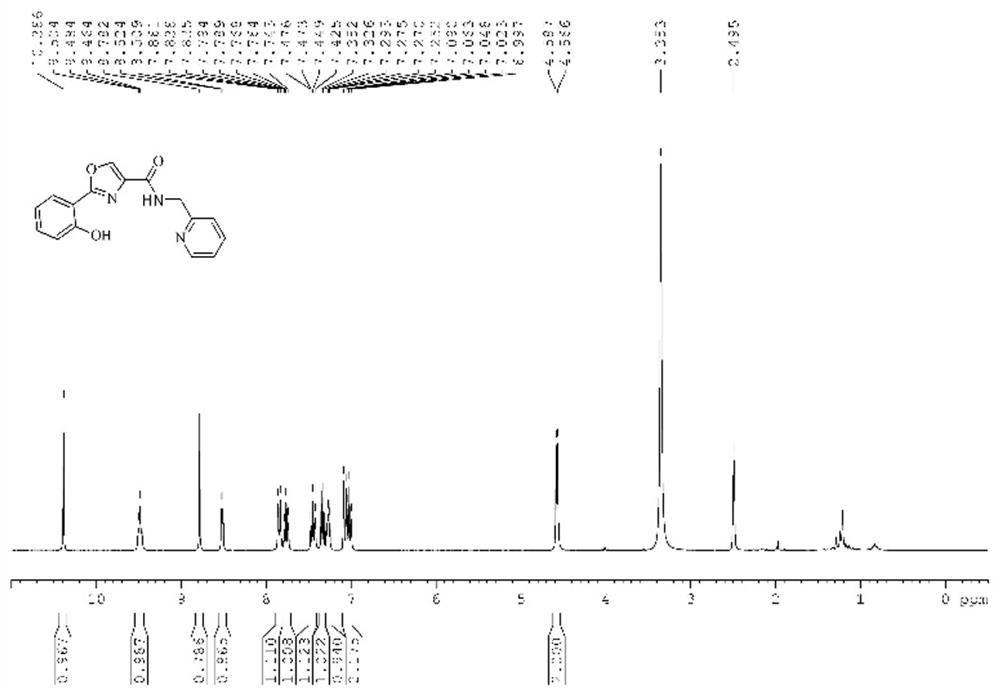
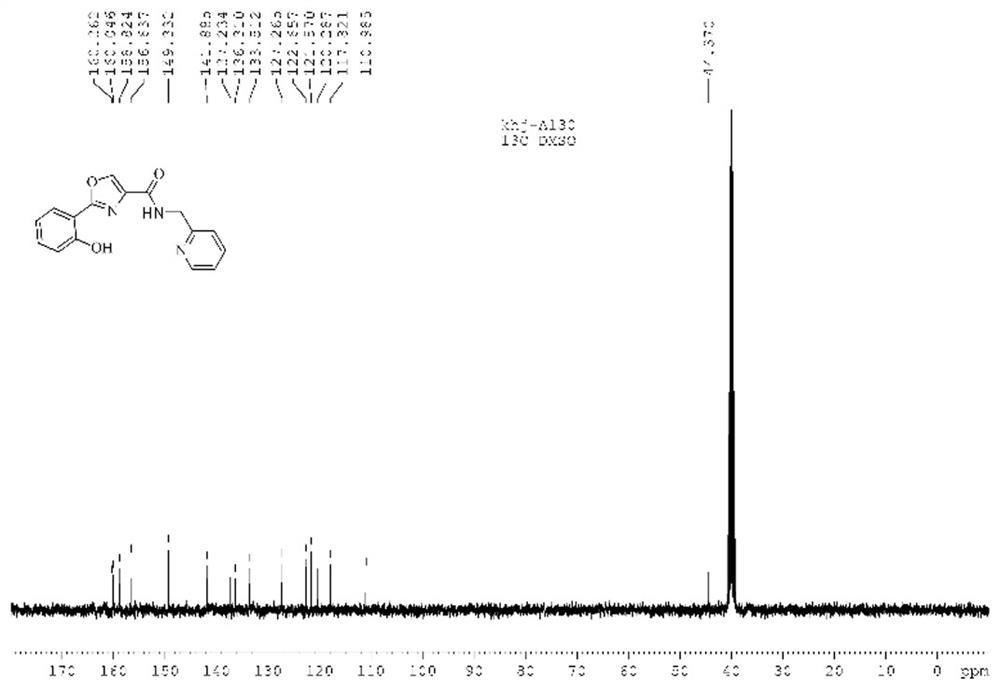
[0038] The characterization results of the oxazole-b...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A preparation method of an oxazole derivative fluorescent probe, the steps are as follows:
[0045] (1) Thionyl chloride (0.90 g, 7.50 mmol) was added to anhydrous dichloromethane (40 mL) containing 2-(2-hydroxybenzene)oxazole-4-carboxylic acid (0.51 g, 2.50 mmol) , heated to 45°C under magnetic stirring, and reacted under reflux for 6 hours. Cool to room temperature, remove the unreacted thionyl chloride and solvent dichloromethane to obtain the acid chloride of oxazoles;
[0046] (2) The acid chloride (3.00 mmol) of oxazoles prepared in step (1) was dissolved in anhydrous dichloromethane, and then 2-aminomethylpyridine (0.363 g, 3.30 mmol) was added, and heated to 45 °C to fully react After 6 hours, it was cooled to room temperature, and after the solvent was concentrated, column chromatography was performed to obtain 0.36 g of the oxazole-based copper ion detection reagent.
Embodiment 3
[0048] A preparation method of an oxazole derivative fluorescent probe, the steps are as follows:
[0049] (1) Add thionyl chloride (0.90 g, 7.50 mmol) to anhydrous benzene (40 mL) containing 2-(2-hydroxybenzene)oxazole-4-carboxylic acid (0.51 g, 2.50 mmol), and magnetically The mixture was heated to 80° C. with stirring, and the reaction was refluxed for 4 hours. Cool to room temperature, remove the unreacted thionyl chloride and solvent benzene to obtain the acid chloride of oxazoles;
[0050] (2) The acid chloride (2.75mmol) of the oxazoles prepared in step (1) was dissolved in anhydrous dichloromethane, and then 2-aminomethylpyridine (0.30 g, 2.75mmol) was added, and heated to 45°C to fully react After 5 hours, cooled to room temperature, the solvent was concentrated, and purified by column chromatography to obtain 0.31 g of oxazole derivative fluorescent probe.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com