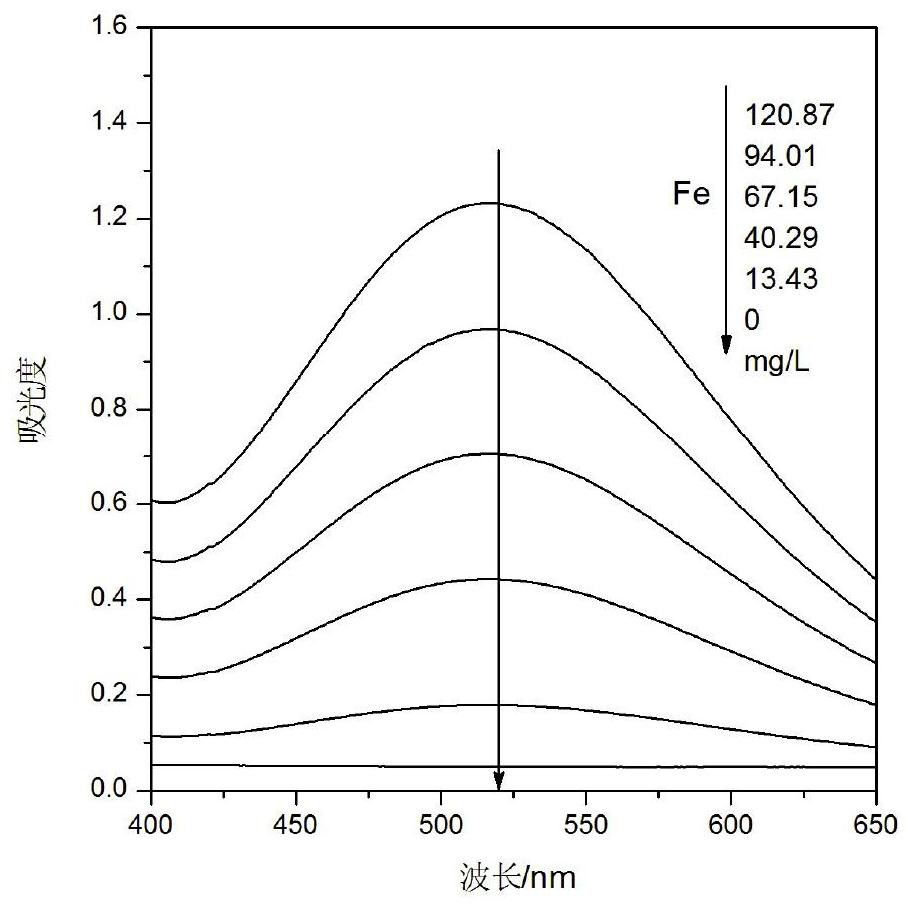
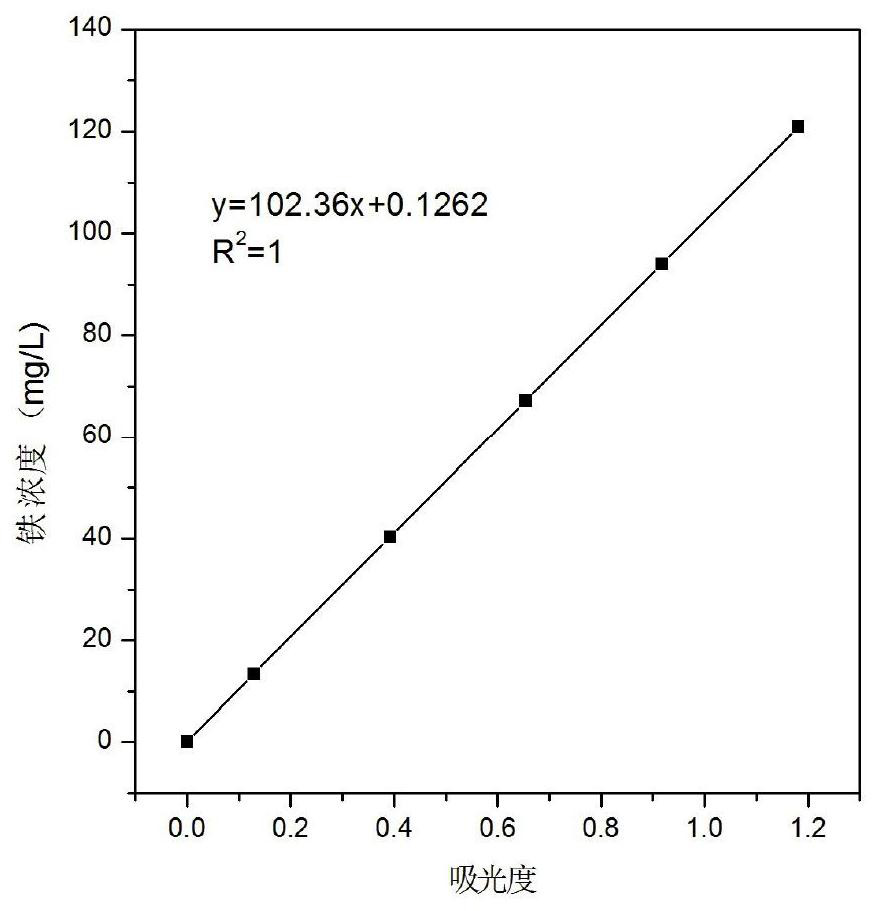
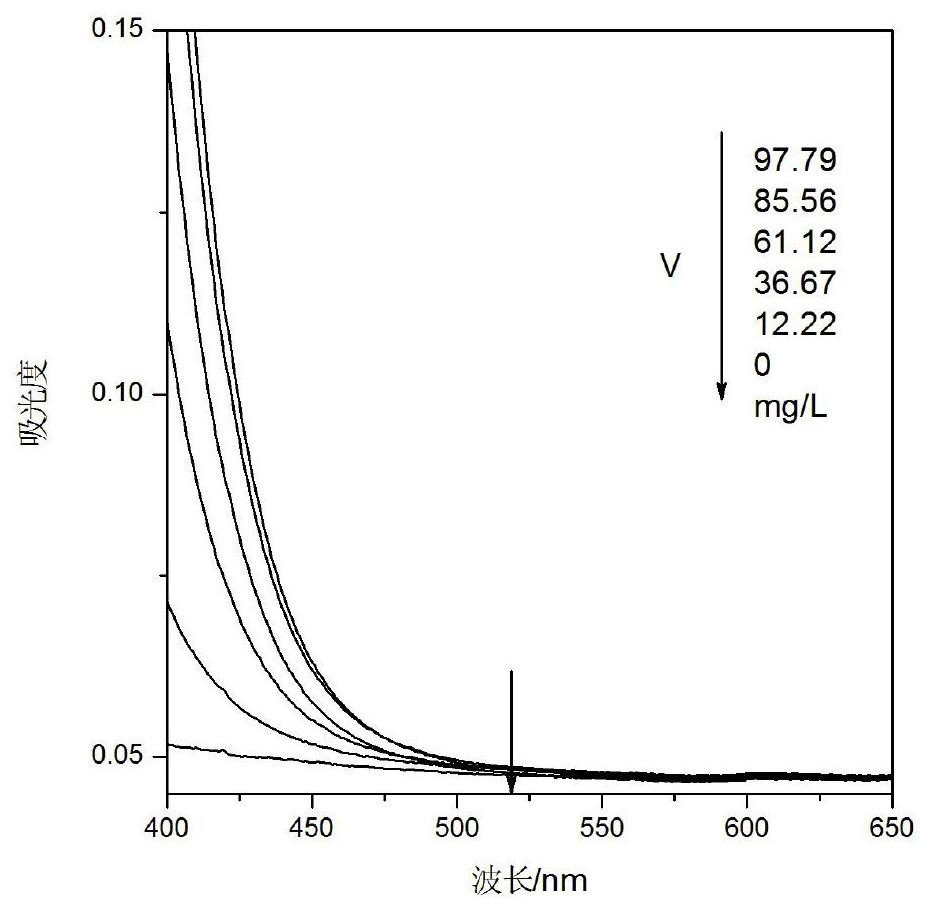
Method for determining iron content in ferrovanadium solution by EDTA complexing-hydrogen peroxide chromogenic matrix matching spectrophotometry
A hydrogen peroxide, matrix matching technology, used in the measurement of color/spectral properties, material analysis by observing the effect on chemical indicators, and analysis by chemically reacting materials, etc., to achieve high accuracy, improve sensitivity and Accurate, easy-to-use effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Concentration confirmation of vanadium content in matrix solution for detection of iron content in vanadium-containing solution
[0046] 1.1 Instrument
[0047] UV-visible spectrophotometer
[0048] 1.2 Reagents
[0049] Concentrated hydrochloric acid: ρ1.179g / mL, concentrated nitric acid: ρ1.4g / mL, potassium sodium tartrate: AR, EDTA solution: AR 100g / L, sodium hydroxide solution: AR 150g / L, ammonia water: AR, hydrogen peroxide: AR 30%, ferric oxide: spectrally pure;
[0050] Ammonium metavanadate: vanadium content 43.49%.
[0051] 1.3 Working curve iron content range
[0052] 1.3.1 Series concentration iron standard solution preparation
[0053] Weigh the mass m 1 (0.1920g) (accurate to 0.0001g) of ferric oxide in a 250mL beaker, add 9mL concentrated hydrochloric acid and 3mL concentrated nitric acid (ie aqua regia), heat until completely dissolved, cool to room temperature, transfer to a 100mL volumetric flask ,Volume. Pipette the prepared iron standard solut...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Sulfuric acid-hydrochloric acid mixed acid iron vanadium electrolyte detection
[0077] 2.1 Instrument
[0078] UV-visible spectrophotometer
[0079] 2.2 Reagents
[0080] Concentrated hydrochloric acid: ρ1.179g / mL, concentrated nitric acid: ρ1.4g / mL, potassium sodium tartrate: AR, EDTA solution: AR 100g / L, sodium hydroxide solution: AR 150g / L, ammonia water: AR, hydrogen peroxide: AR 30%, ferric oxide: spectrally pure, ammonium metavanadate: vanadium content 43.49%.
[0081] 2.3 Drawing of standard curve
[0082] 2.3.1 Preparation of series concentration iron standard solution
[0083] Weigh the mass m 1 (0.1924g) (accurate to 0.0001g) of ferric oxide in a 250mL beaker, add an appropriate amount of 9mL concentrated hydrochloric acid and 3mL concentrated nitric acid, heat until completely dissolved, cool to room temperature, transfer to a 100mL volumetric flask, and constant volume.
[0084] Weigh the mass m 2 (0.3500g) of ammonium metavanadate in a 250mL beaker,...
Embodiment 3
[0114] Detection of Iron Content in VAlFe 69:19:12 Alloy Sample
[0115] 3.1 Instrument
[0116] UV-visible spectrophotometer
[0117] 3.2 Reagents and materials
[0118] Hydrochloric acid GR, nitric acid GR, potassium sodium tartrate AR, EDTA-2Na solution: 100g / L, sodium hydroxide solution: 120g / L, ammonia water AR, hydrogen peroxide AR, spectrally pure ferric oxide (baked at 105°C to constant weight);
[0119] Fe standard solution: 1000ug / mL, weigh 0.072g (accurate to 0.0001g) spectrally pure ferric oxide dried at 105°C for 1 hour in a 100mL beaker, add 6mL hydrochloric acid GR, 2mL nitric acid GR, heat to complete dissolve. After cooling, dissolve back to boiling, remove and cool, and dilute to 50mL;
[0120] Vanadium pentoxide: content ≥ 99.8%, iron content ≤ 0.01%, baked at 105°C to constant weight
[0121] Aluminum powder: content ≥ 99.7%, iron content ≤ 0.01%
[0122] 3.3 Preparation of standard curve
[0123] Weigh vanadium pentoxide (m V2O5 )0.617g (accurate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com