Processing technology of mildew-proof and heat-insulating plate
A processing technology and board technology, which is applied in the field of heat insulation materials, can solve the problems of mildew of plastic-wood composite materials, the loss resistance and stability of boards can not be effectively solved, and the treatment cycle is long, etc., to achieve a good mildew-proof effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
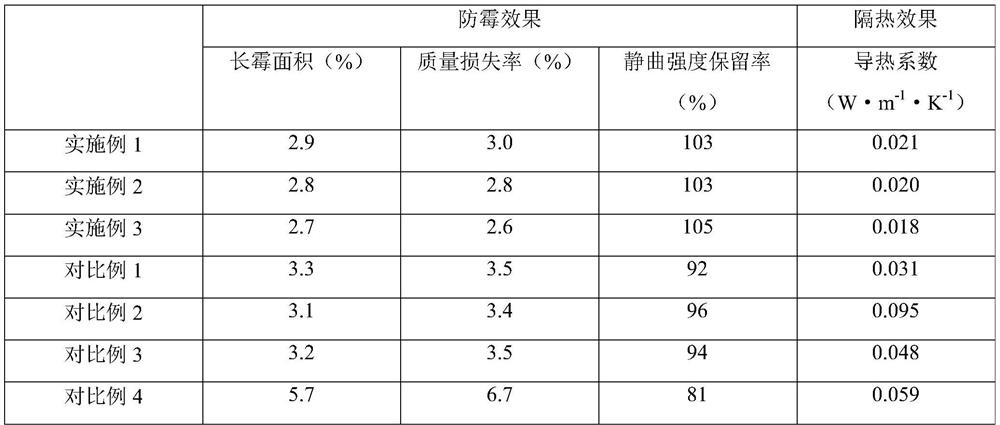
[0037] A process for processing a mildew-proof and heat-insulating board. First, 100 g of fiber particles are mixed with 35 g of hydroxymethyl polystyrene resin, 15 g of polyvinylidene fluoride, and 5 g of maleic anhydride-grafted polystyrene to obtain a premix; then The premix is extruded by blending and molded to obtain the described mildew-proof and heat-insulating board; wherein, the preparation method of the fiber particles is as follows:
[0038] (A) first carry out benzylation modification to the pretreated plant fiber powder to obtain benzylated plant fiber powder;
[0039](B) mixing the benzylated vegetable fiber powder with N-β(aminoethyl)-γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane modified rock wool powder again to obtain mixed powder;
[0040] (C) then take ethyl orthosilicate and trimethyl borate as raw materials and mix to make sol, ultrasonically disperse the mixed powder in absolute ethanol to make prefabricated slurry, and then ultrasonically disperse the sol in absolute ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] A process for processing a mildew-proof and heat-insulating board. First, 100 g of fiber particles are mixed with 45 g of hydroxymethyl polystyrene resin, 12 g of polyvinylidene fluoride, and 7 g of maleic anhydride-grafted polystyrene to obtain a premix; then The premix is extruded by blending and molded to obtain the described mildew-proof and heat-insulating board; wherein, the preparation method of the fiber particles is as follows:
[0060] (A) first carry out benzylation modification to the pretreated plant fiber powder to obtain benzylated plant fiber powder;
[0061] (B) mixing the benzylated vegetable fiber powder with N-β(aminoethyl)-γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane modified rock wool powder again to obtain mixed powder;
[0062] (C) then take ethyl orthosilicate and trimethyl borate as raw materials and mix to make sol, ultrasonically disperse the mixed powder in absolute ethanol to make prefabricated slurry, and then ultrasonically disperse the sol in absolute...
Embodiment 3
[0081] A process for processing a mildew-proof and heat-insulating board, firstly mixing 100g of fiber particles with 40g of hydroxymethyl polystyrene resin, 13g of polyvinylidene fluoride and 6g of maleic anhydride grafted polystyrene to obtain a premix; then The premix is extruded by blending and molded to obtain the described mildew-proof and heat-insulating board; wherein, the preparation method of the fiber particles is as follows:
[0082] (A) first carry out benzylation modification to the pretreated plant fiber powder to obtain benzylated plant fiber powder;
[0083] (B) mixing the benzylated vegetable fiber powder with N-β(aminoethyl)-γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane modified rock wool powder again to obtain mixed powder;
[0084] (C) then take tetraethyl orthosilicate and trimethyl borate as raw materials and mix to make sol, ultrasonically disperse the mixed powder in absolute ethanol to make a prefabricated slurry, and then ultrasonically disperse the sol in absolute...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com