Application method of aggregation-induced emission-based photosensitizer in cell imaging and photodynamic therapy
An aggregation-induced luminescent, multi-purpose technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems that cannot be applied in the biological field, fluorescent dyes are easy to leak, and do not have water solubility, etc., and achieve good water solubility, high fluorescence intensity, and prevent leakage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0044] The preparation method of the supramolecular polymerized fluorescent nanomaterial provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0045] The aggregation-induced luminescent compound is introduced into the polydiacetylene supramolecular system through covalent or non-covalent, and the nanoparticles are spontaneously assembled and polymerized by the intermolecular hydrophilic-hydrophobic interaction.
[0046]The chemical structural formula of the aggregation-induced luminescence compound provided by the embodiment of the present invention is:
[0047]
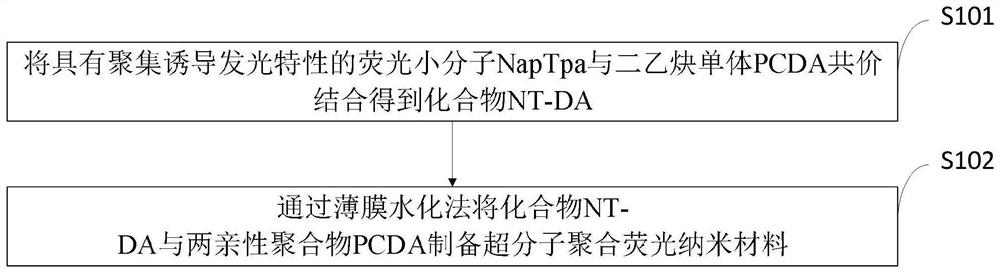
[0048] Such as figure 1 As shown, the preparation method of the supramolecular polymerized fluorescent nanomaterial provided in the embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0049] S101, the compound NT-DA is obtained by covalently combining the fluorescent small molecule NapTpa with aggregation-induced luminescent properties and the diacetylenic monomer PCDA;
[0050] S102, c...
Embodiment 1
[0061] Step 1. Synthesis of compound NT-DA: Accurately weigh NapTpa-OH (151 mg), DMAP (47.14 mg), and DCC (100 mg) on a balance and add them to a 25 ml reaction tube, add 5 ml of tetrahydrofuran, and stir to dissolve them; Then accurately weigh (106mg) PCDA in a small beaker, add 5ml of tetrahydrofuran to dissolve it, then slowly add the dissolved PCDA solution dropwise to the above reaction tube; Stir on a stirrer at room temperature for 72 hours, point the plate to confirm the progress of the reaction; after the reaction is over, transfer the solution in the reaction tube to a round bottom flask, remove THF (35°C) by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure, and spin dry with an appropriate amount of Dichloromethane was dissolved; the resulting solution was washed with supersaturated NaHCO 3 Extraction, the purpose is to remove DCC; Add an appropriate amount of anhydrous sodium sulfate to remove water to obtain a crude product; Finally, add a small amount of silica gel to...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2: the test of NT-DA optical performance
[0065] Steps: At 25°C, the UV absorption and fluorescence emission spectra of NT-DA were measured, and the changes in the fluorescence emission spectra of 10uL NT-DA (1mM) in different volume ratios of DMSO / H2O mixed solvents (total volume 2mL) were investigated.
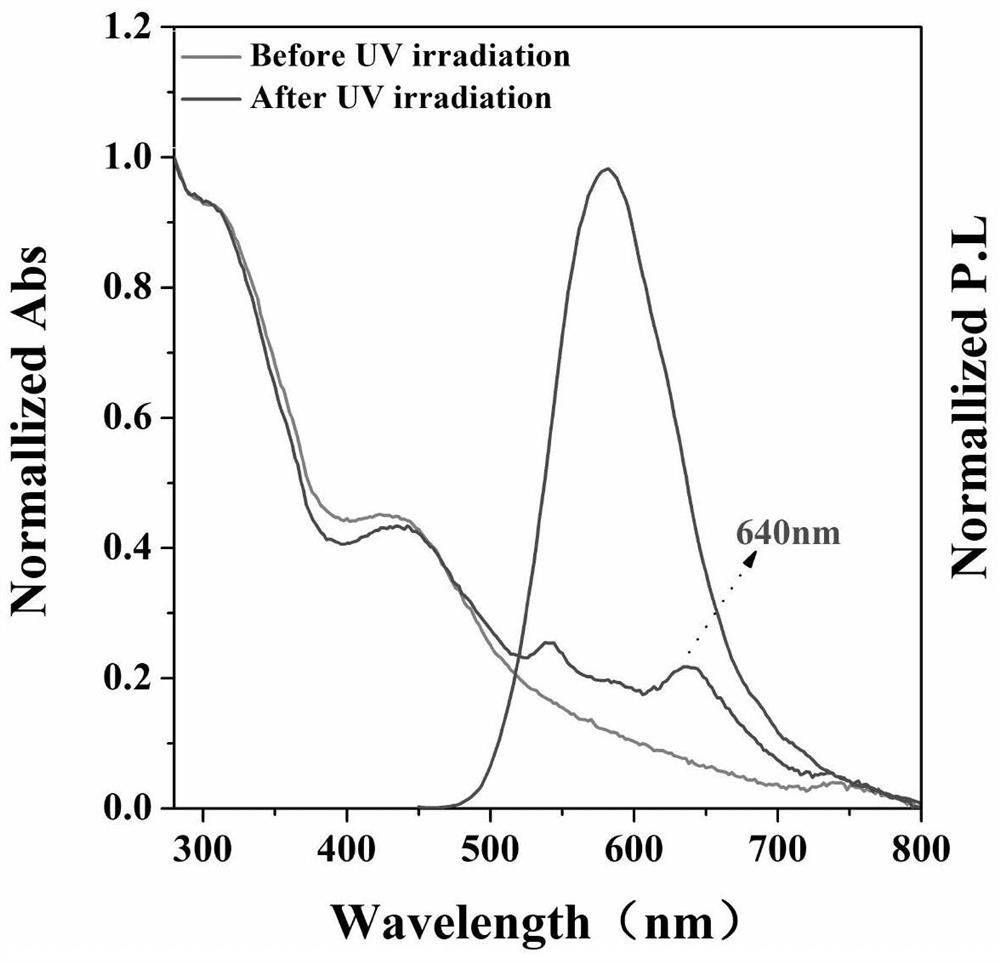
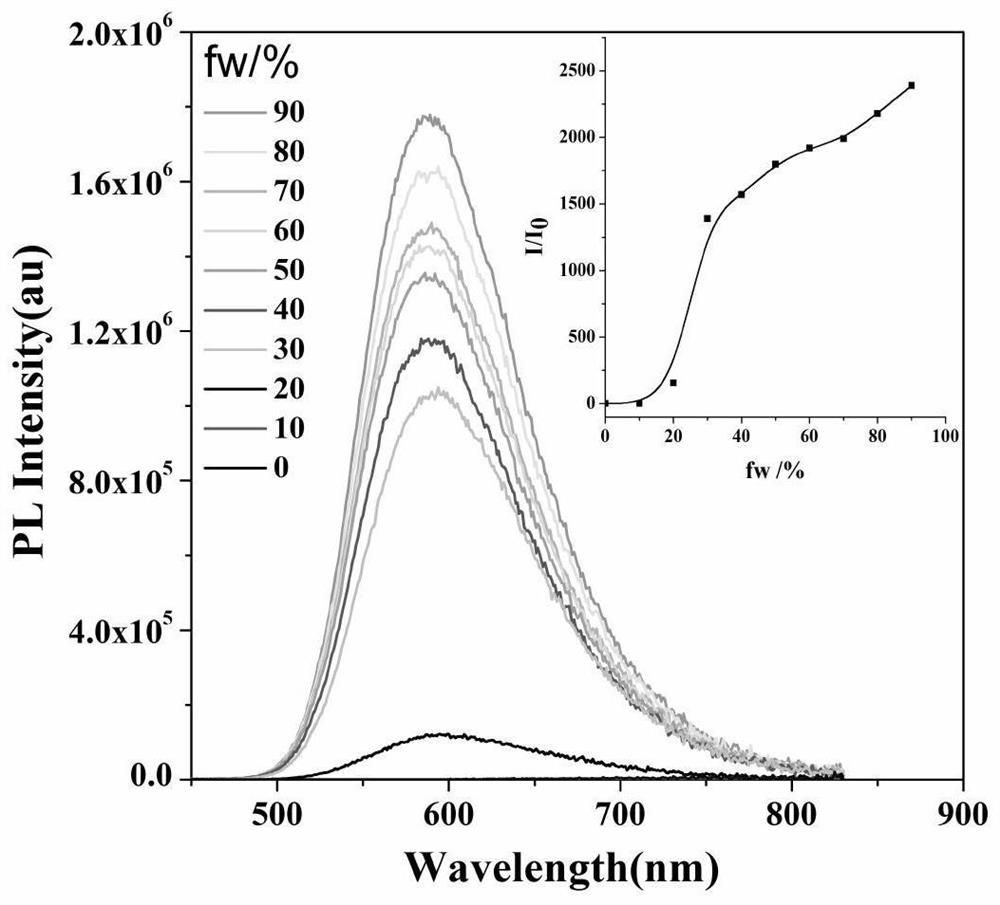
[0066] Result: if figure 2 The UV-Vis absorption spectrum of NT-DA shows that there are two maximum absorption peaks at 306nm and 418nm, image 3 The emission spectrum is arranged at 500-800nm, and the peak is around 590nm. It can be seen that the compound has a large Stokes shift (167nm), which avoids the light pollution of the excitation light and the self-absorption of the emission in the process of biomedical imaging. Such as Figure 4 , NT-DA has typical AIE effect characteristics, and it is almost weakly emitted in DMSO. When 0%-90% deionized water is gradually added, as the proportion of water increases, due to the limitation of intramolecular m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com