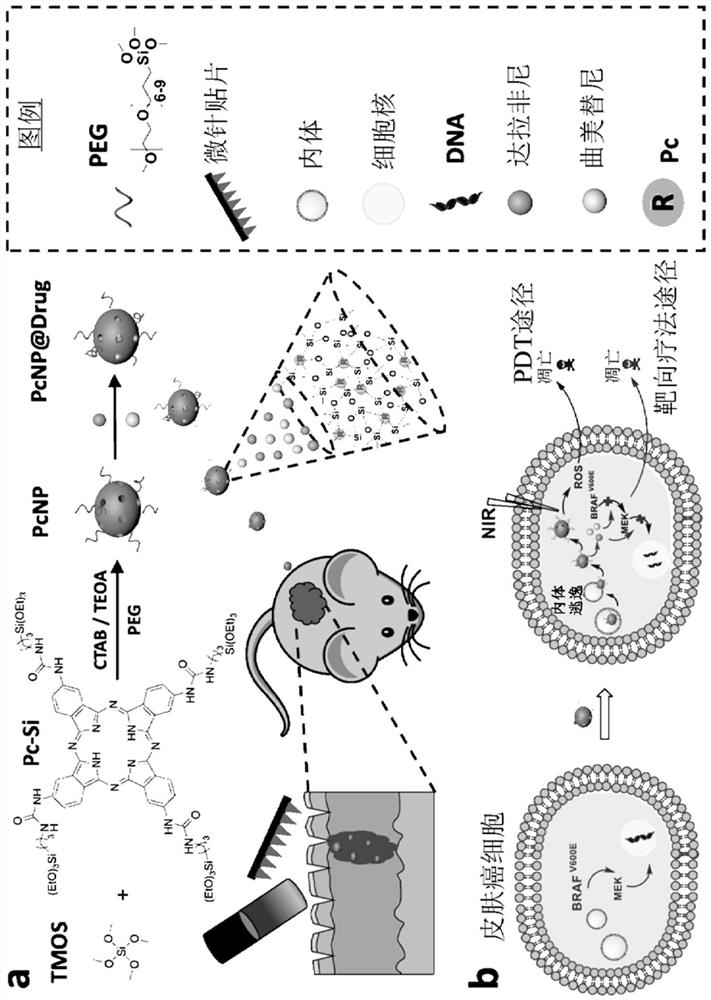
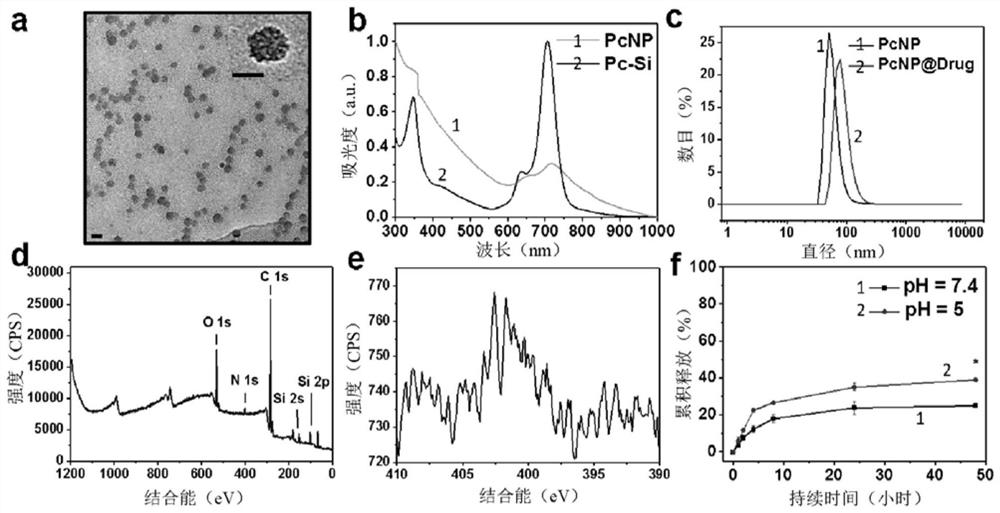
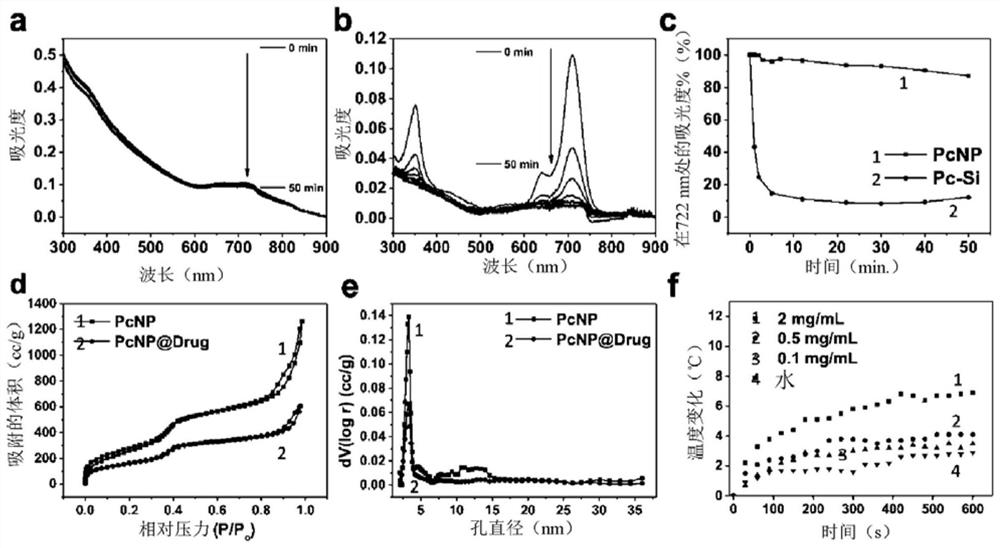
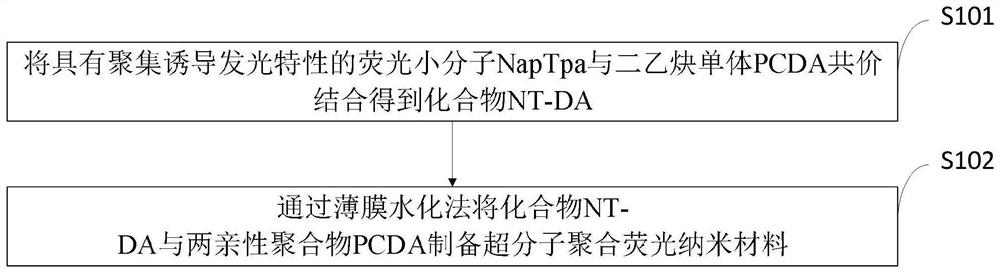
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Photo dynamic therapy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sono-Photo Dynamic Therapy. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a treatment that uses a drug, called a photosensitizer or photosensitizing agent, and a particular type of light.
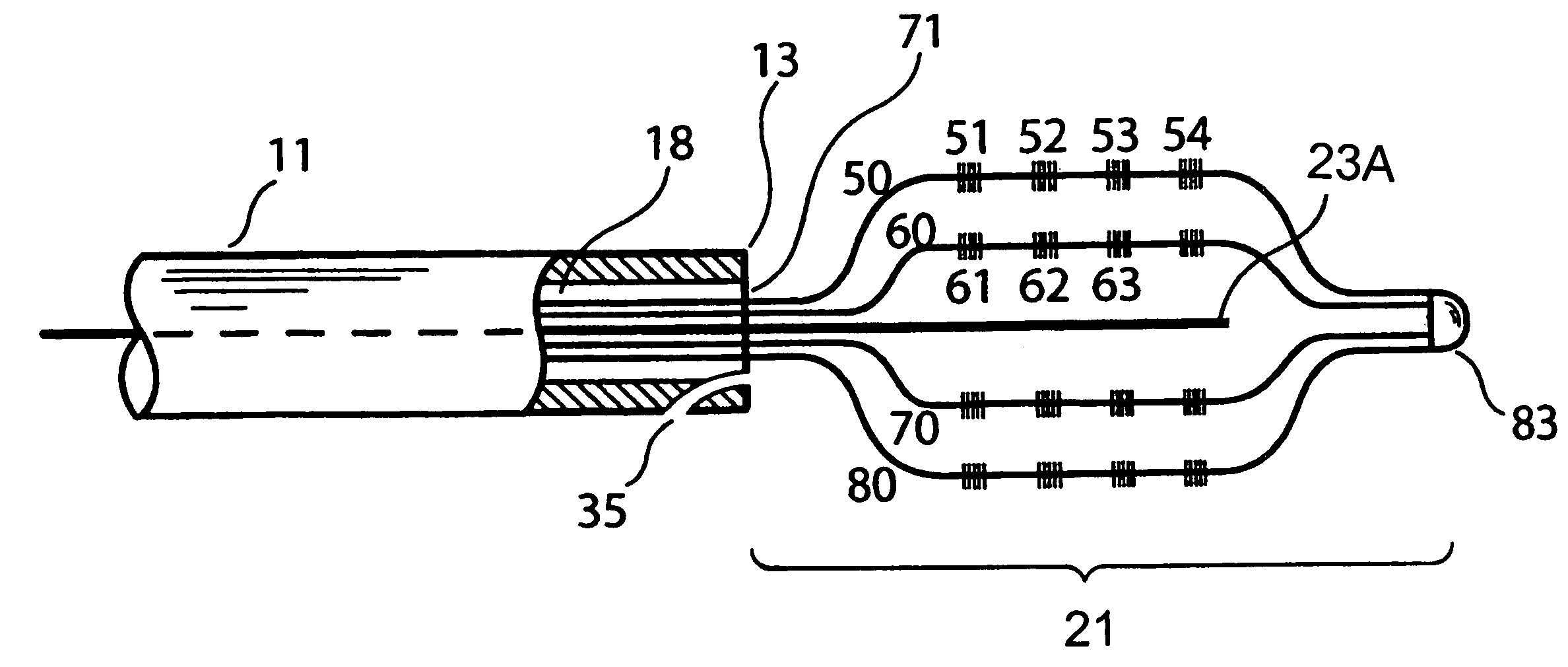
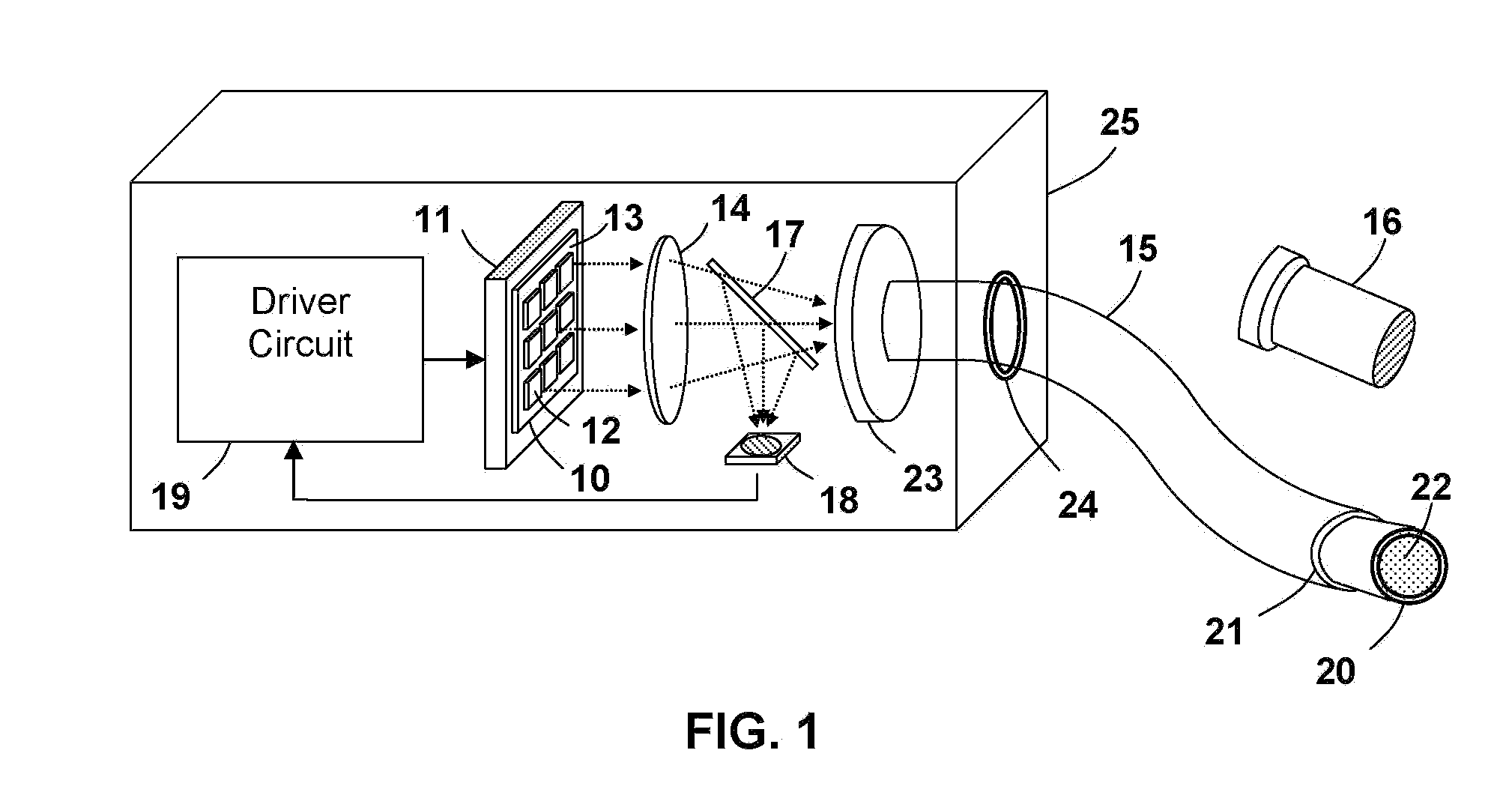
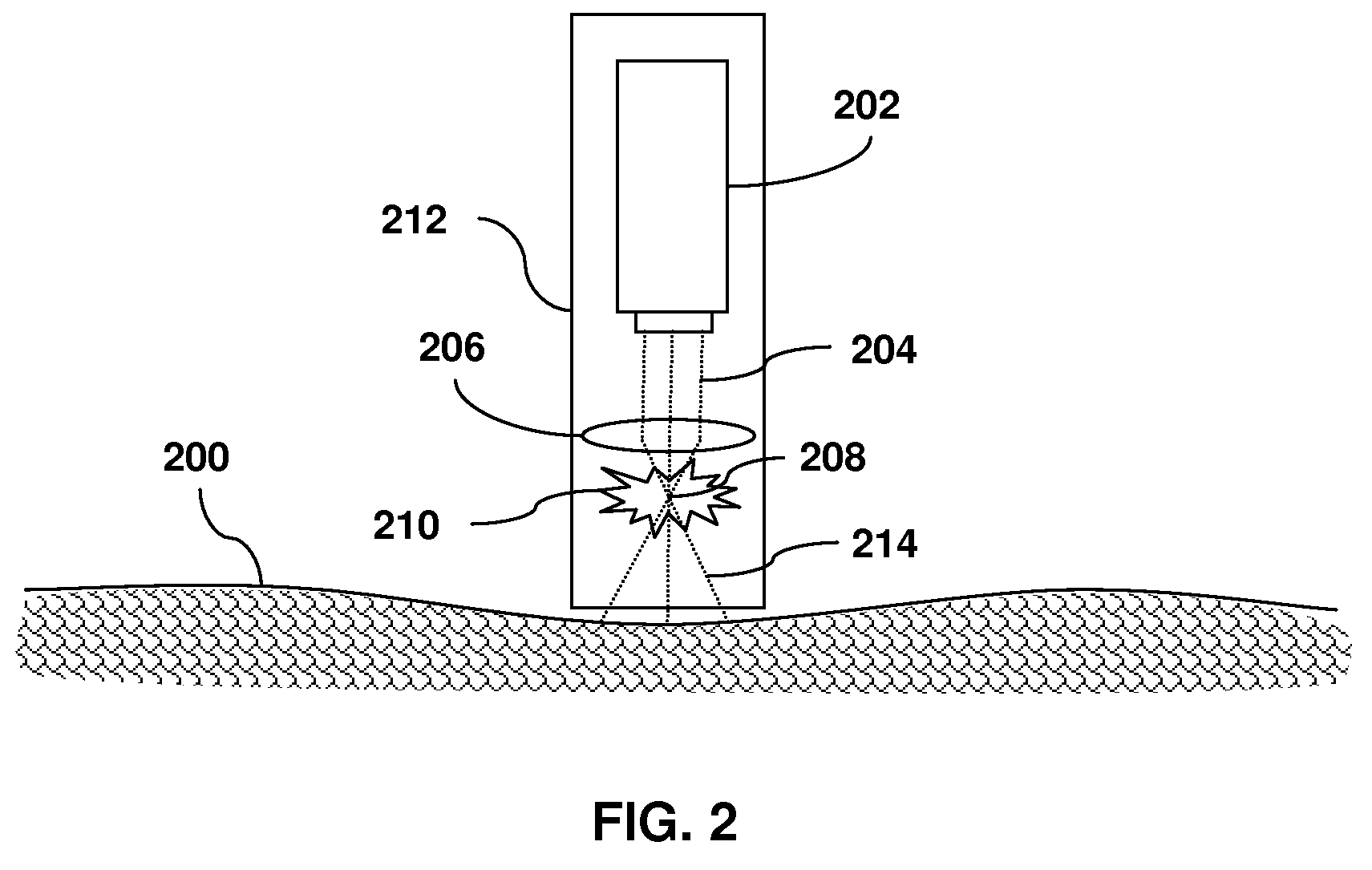
Optical apparatus for detecting and treating vulnerable plaque
InactiveUS7153299B1Easy to operateSimple, real-timeDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsFiberPhotodynamic therapy
An optical apparatus and methods for monitoring temperature enabling detection and treatment of a vulnerable plaque of a patient comprising an elongate catheter, a plurality of outer optical fibers deployably disposed within the lumen of the catheter and suitably expandable in an outwardly radial manner configured for forming a basket shape, the outer fibers having at least one optical grating along an axis of the fiber wherein the at least one optical grating reflects a certain wavelength or intensity of the light beam, the certain wavelength or intensity of the reflected light beam being correlated to known temperature, and a longitudinal middle optical fiber emitting a light energy suitable for photodynamic therapy.
Owner:MAXWELL SENSORS +1
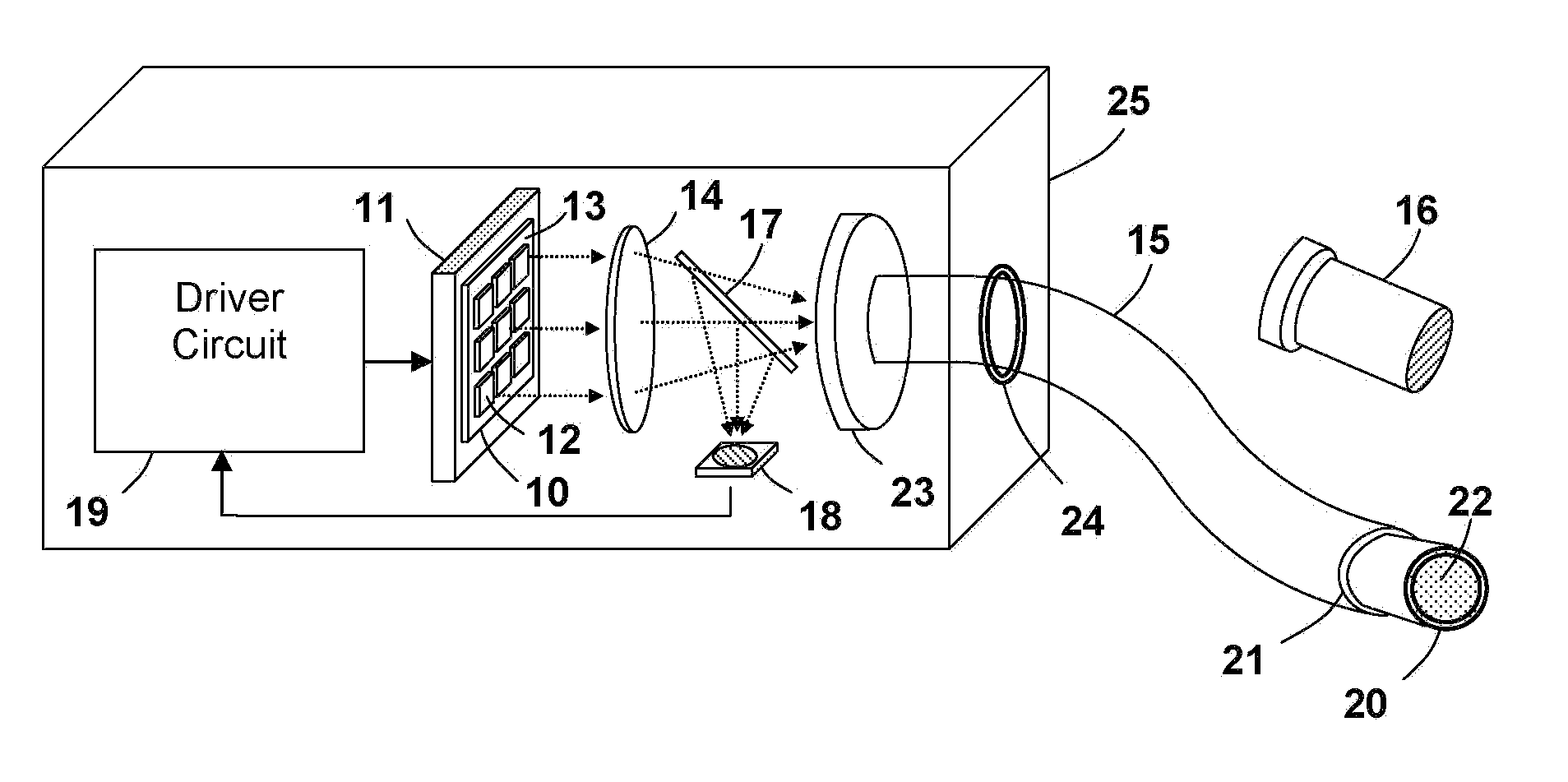
Multispectral therapeutic light source
ActiveUS20140288351A1High cost-effectiveHigh quantum-efficiencyElectrotherapySurgeryUltravioletPeak value
A light source apparatus including light spectrum-converting materials that emit light primarily over large portions of the 360 nm-480 nm and the 590-860 nm spectral range is provided. This apparatus provides a cooled, high-luminance, high-efficiency light source that can provide a broader spectrum of light within these spectral ranges than has been cost-practical by using many different dominant peak emission LEDs. Up to 15% of the output radiant power may be in the spectral range 350-480 nm in one embodiment of this device, unless a specific separate source and lamp operating mode is provided for the violet and UV. Control methods for light exposure dose based on monitoring and controlling reflected or backscattered light from the illuminated surface and new heat management methods are also provided. This flexible or rigid light source may be designed into a wide range of sizes or shapes that can be adjusted to fit over or around portions of the bodies of humans or animals being treated, or mounted in such a way as to provide the special spectrum light to other materials or biological processes. This new light source can be designed to provide a cost-effective therapeutic light source for photodynamic therapy, intense pulsed light, for low light level therapy, diagnostics, medical and other biological applications as well as certain non-organic applications.
Owner:JONES GARY W
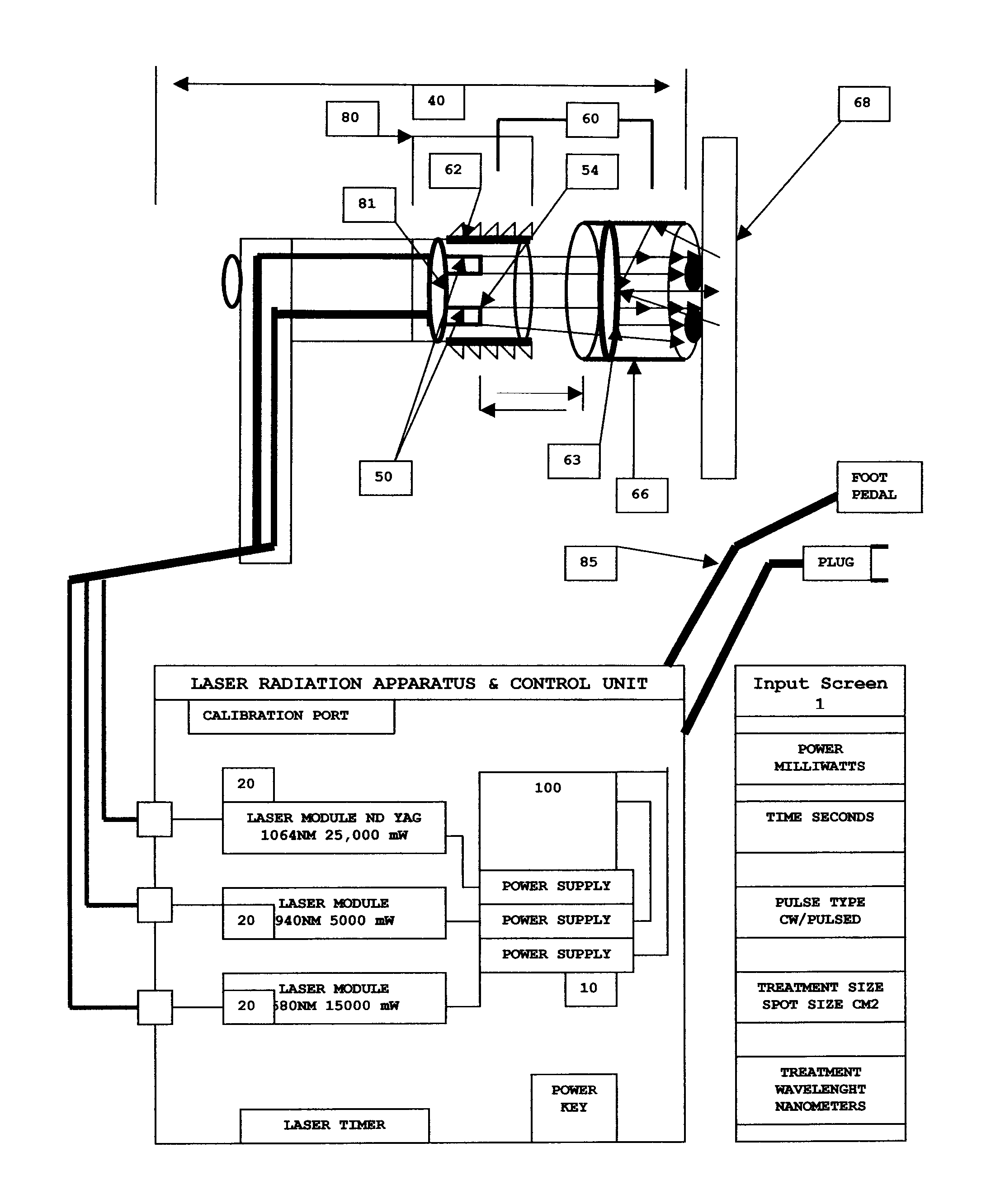
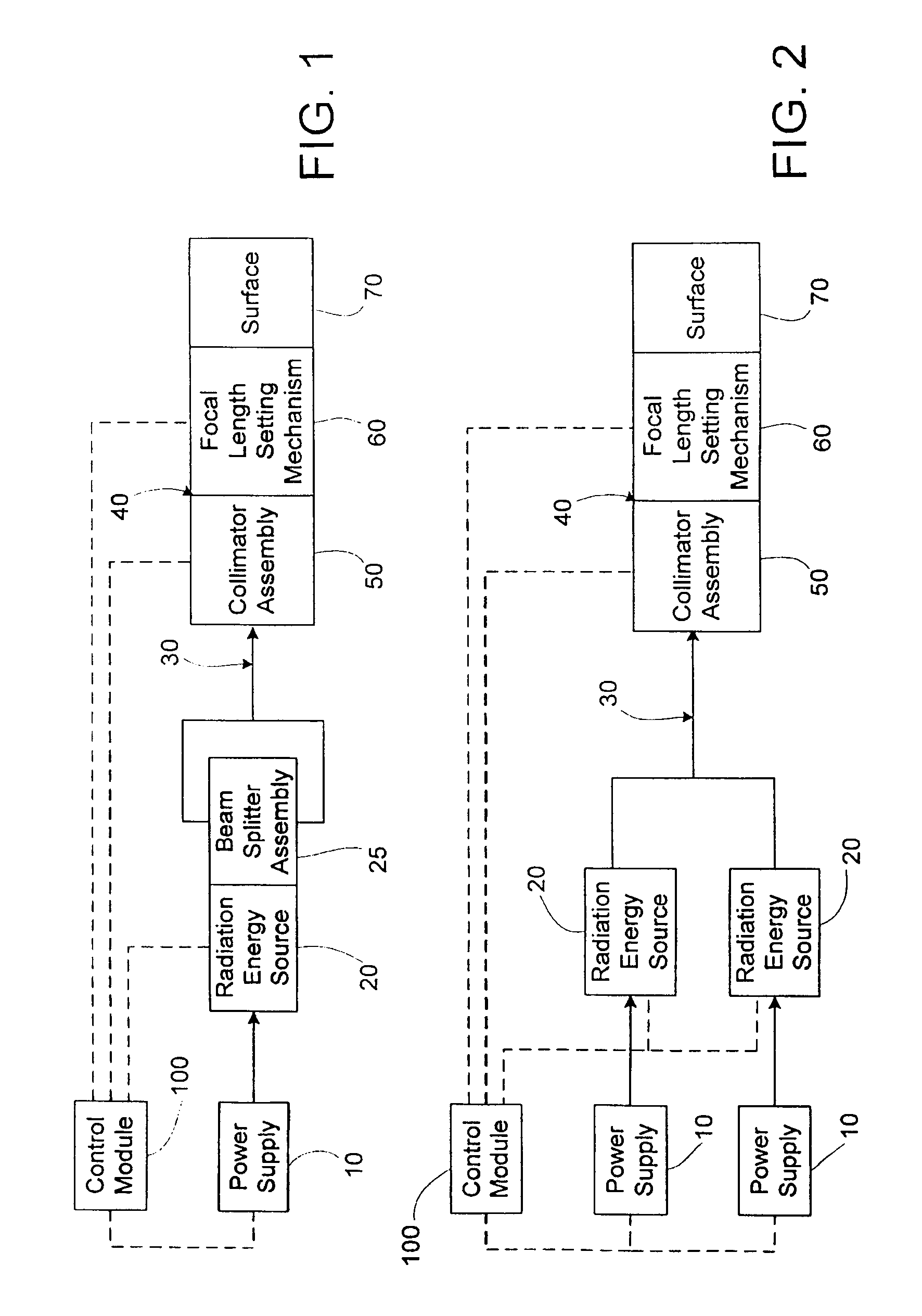
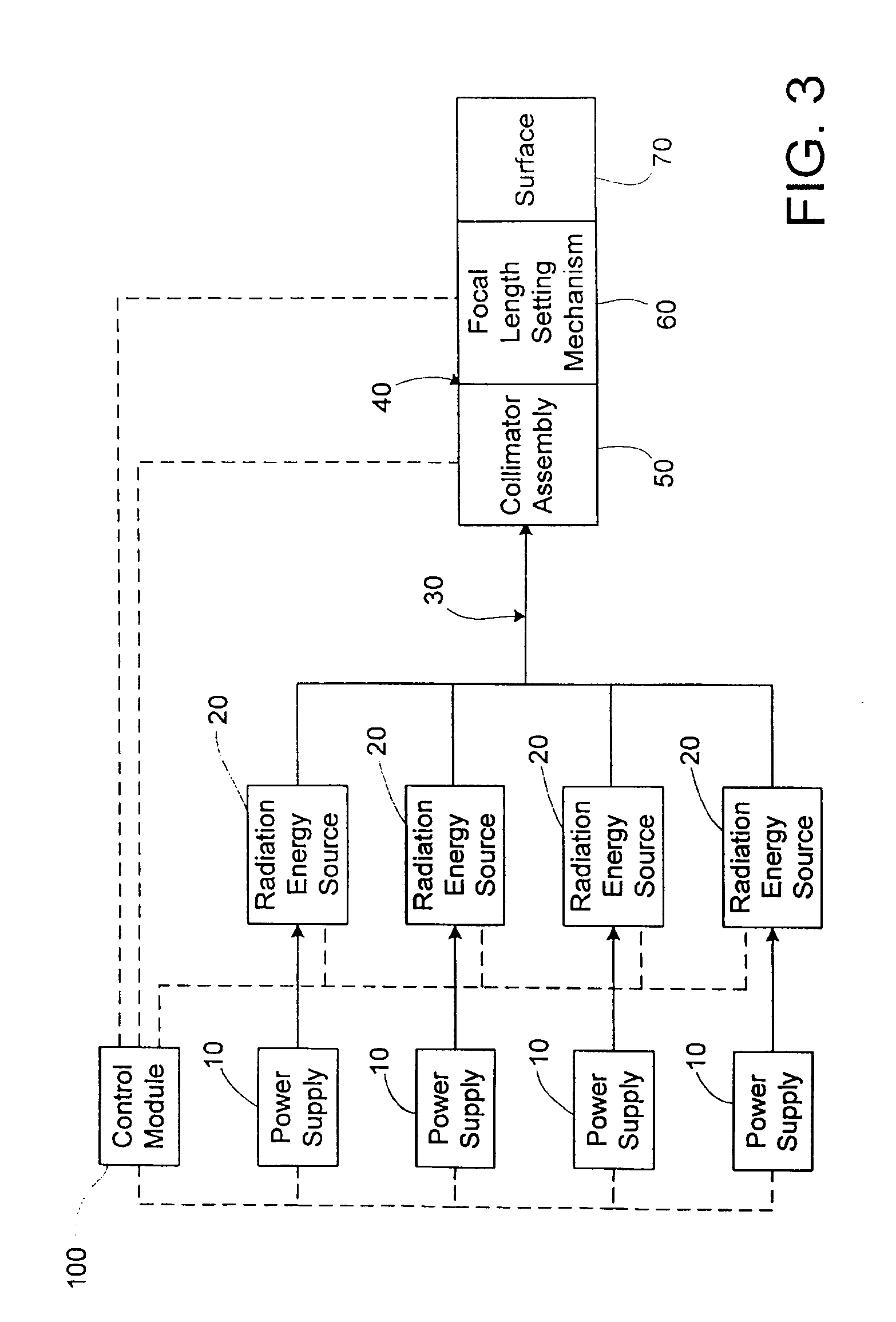
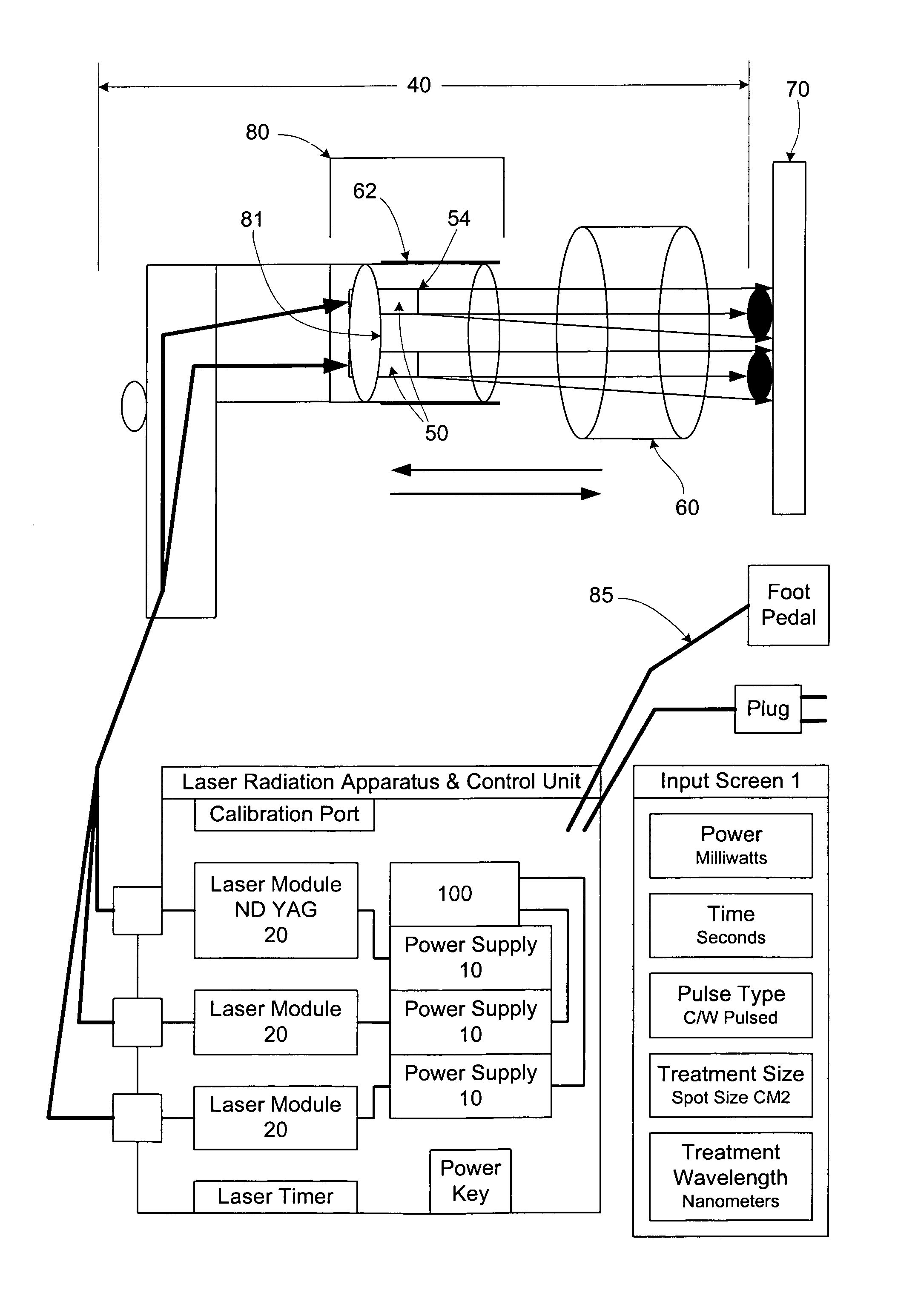
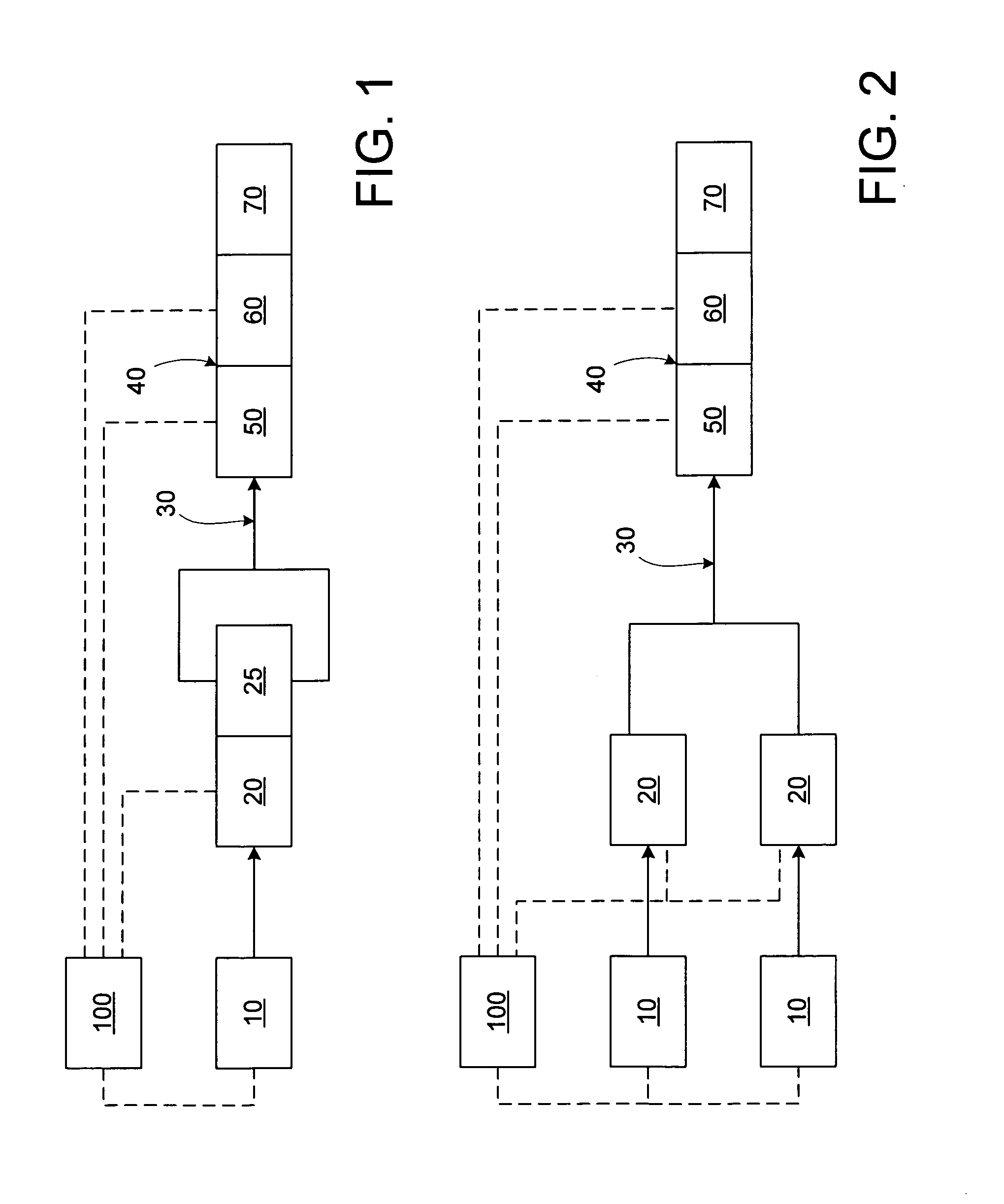
Apparatus and method for performing radiation energy treatments
InactiveUS8287524B2Improve efficiencyImprove securitySurgical instrument detailsLight therapyFiberTherapeutic effect
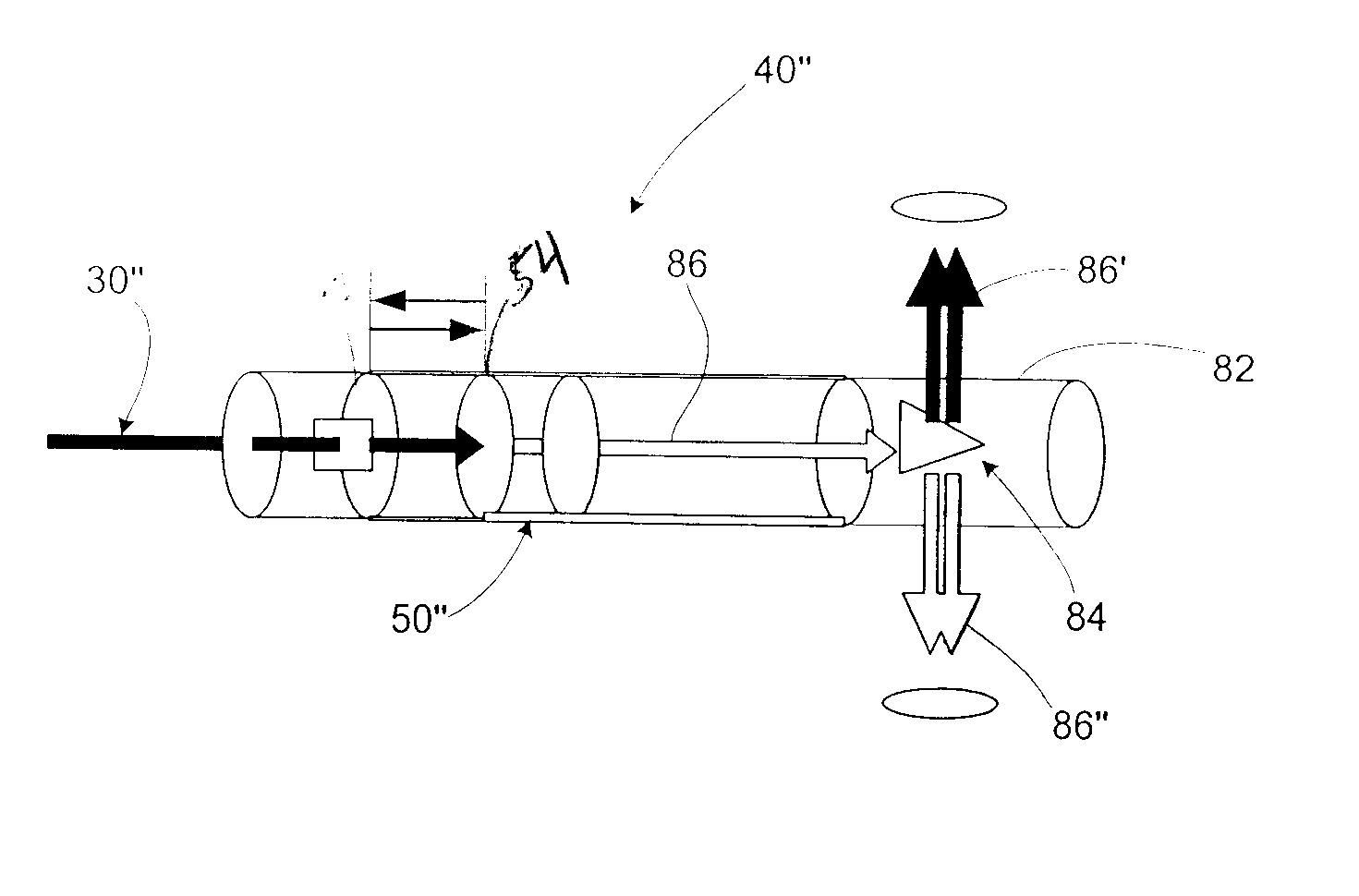
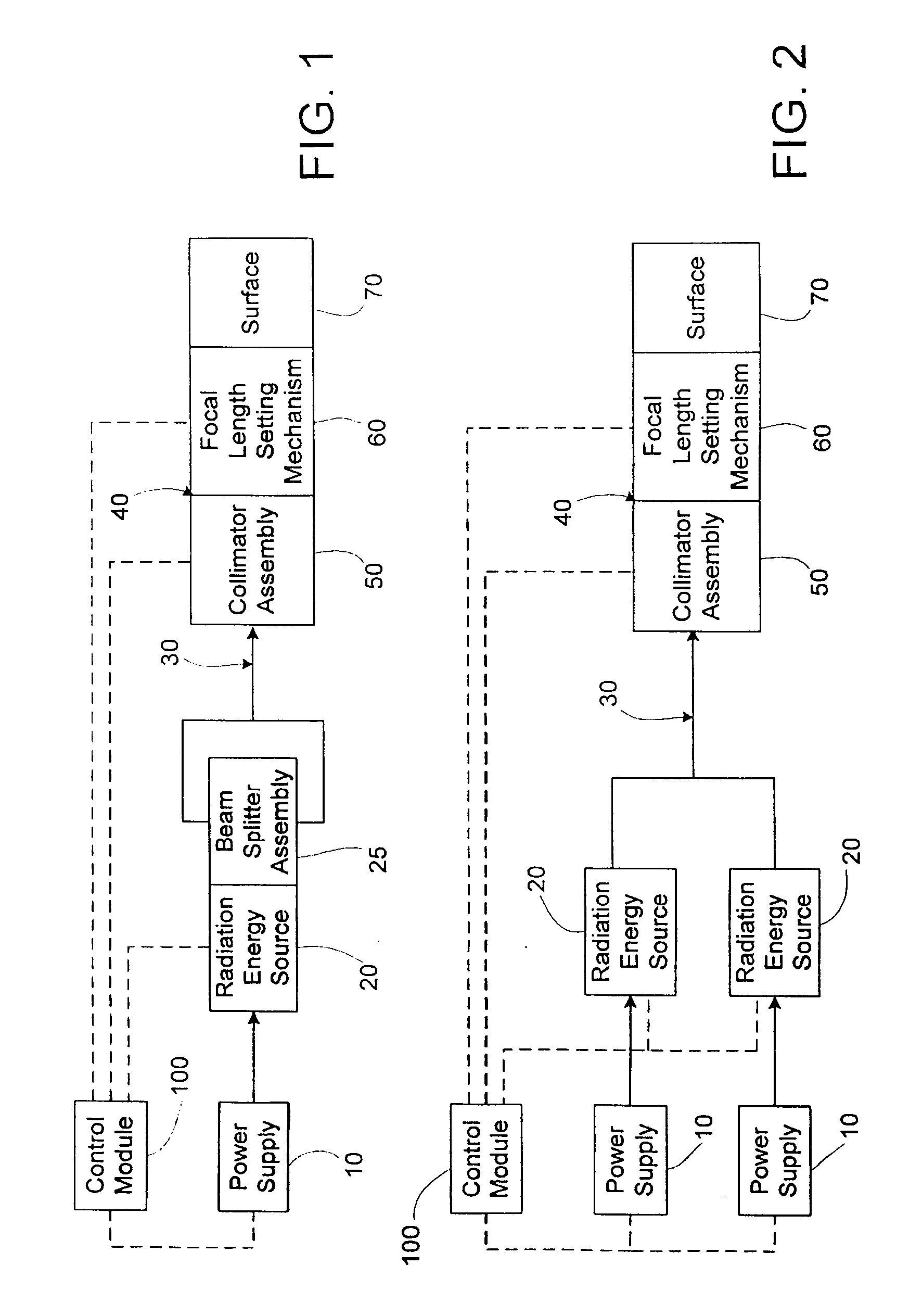
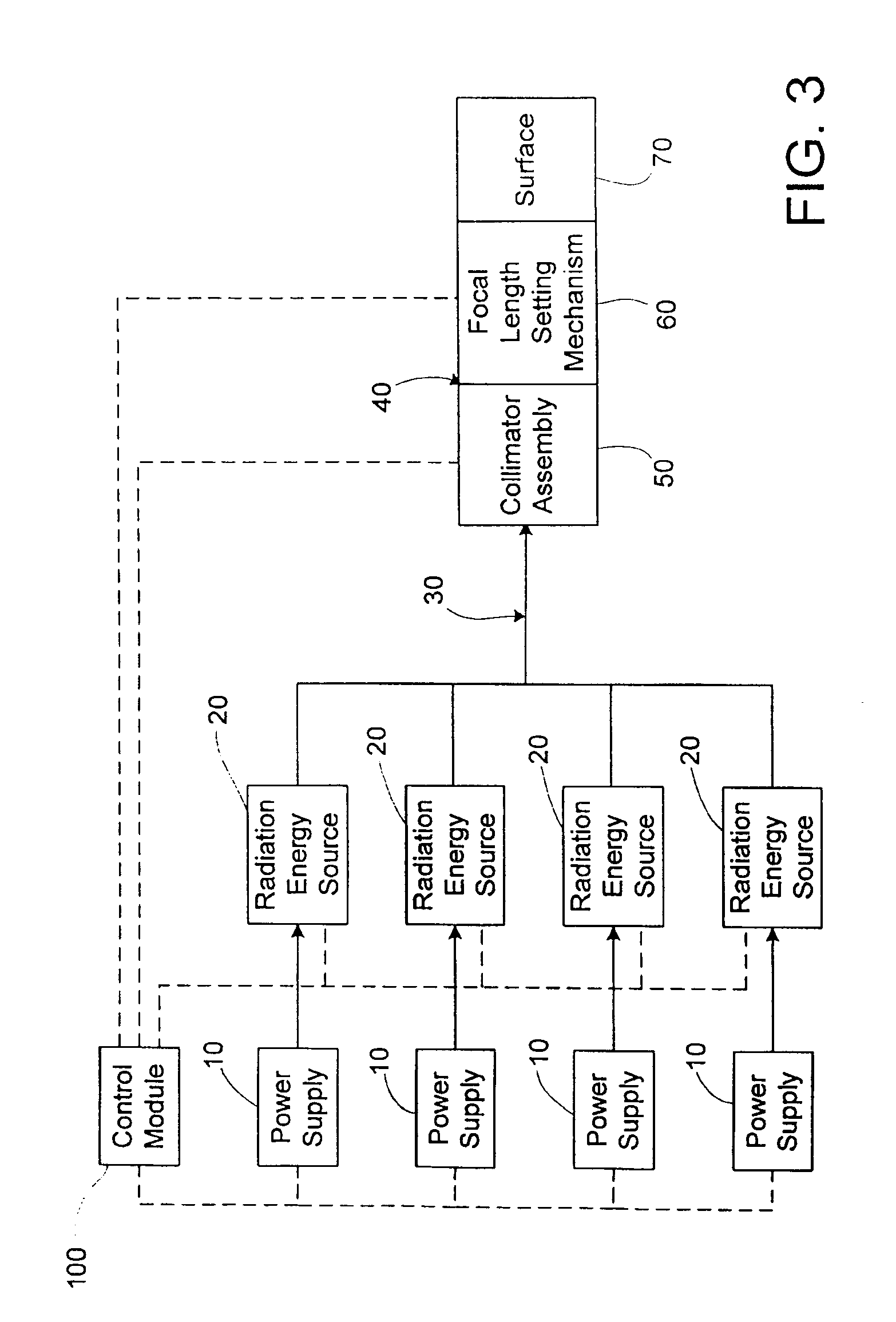
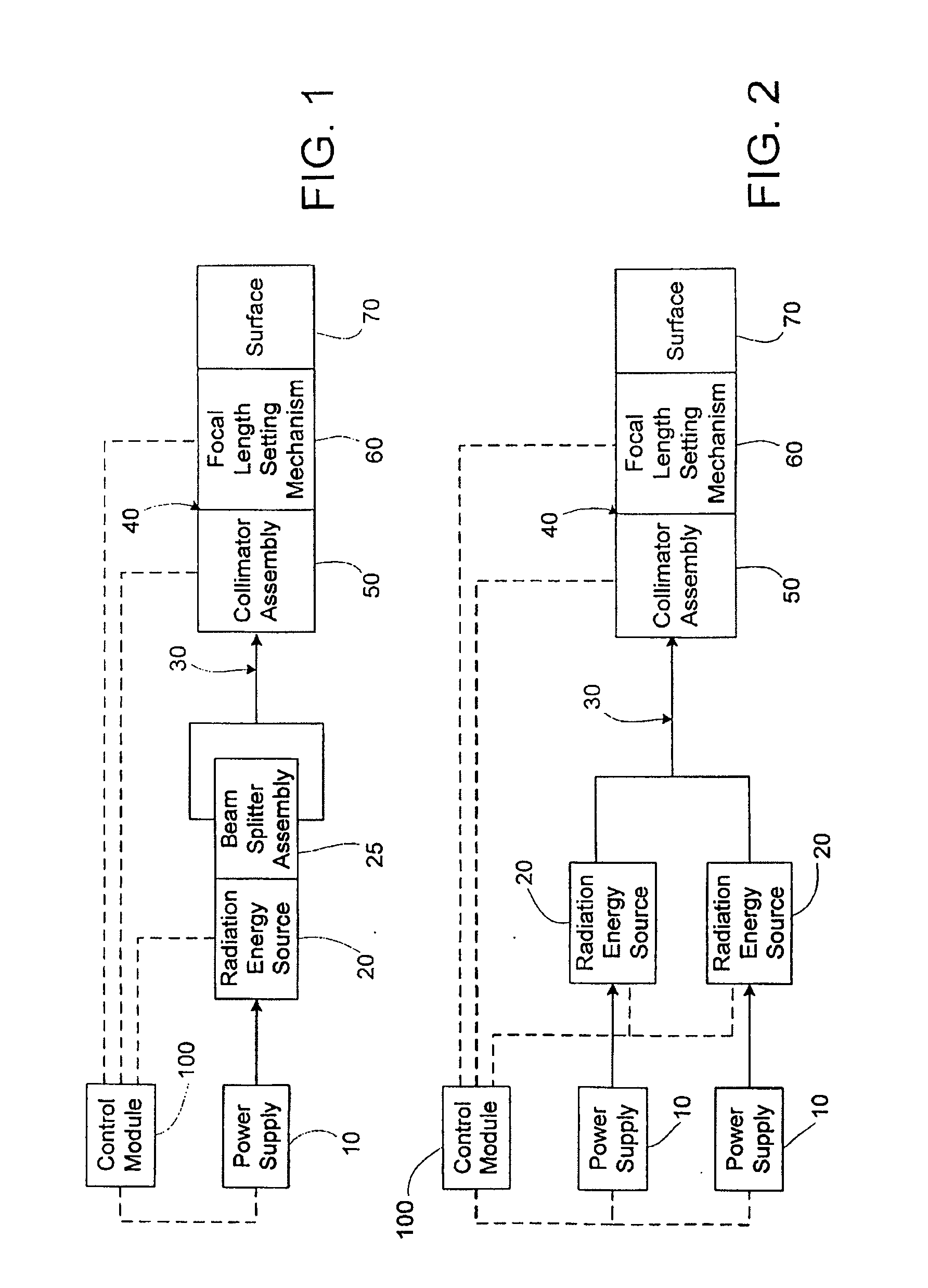
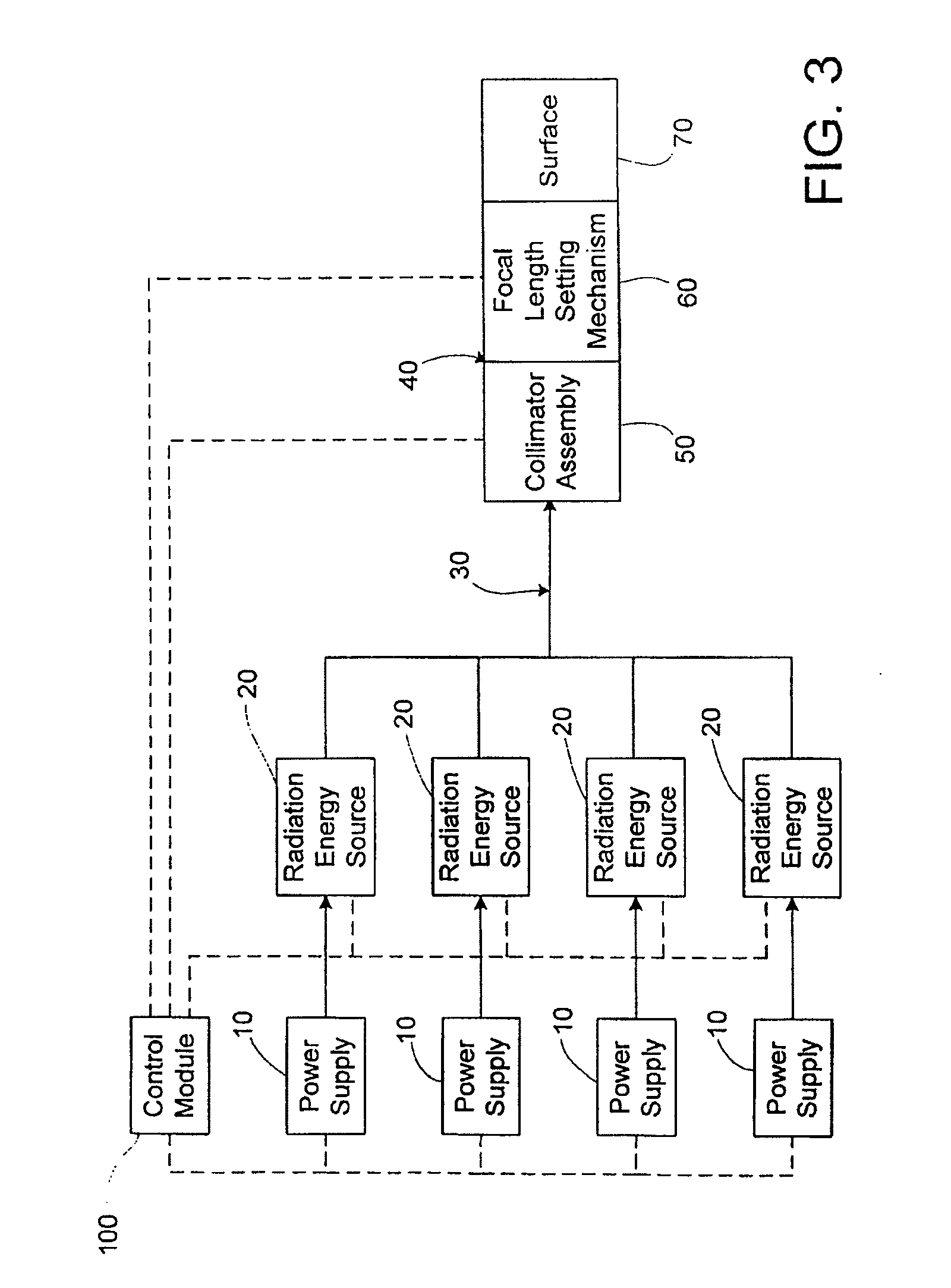
An apparatus and method to apply photo-stimulation, photo-dynamic therapy and / or ablation laser treatment to biological tissue. The apparatus includes a plurality of radiation energy sources, preferably laser beams. Additionally, the apparatus allows either a single wavelength or a combination of various wavelengths, either coincidentally or adjacently, to be utilized to achieve a desired treatment effect. Laser beams are transmitted to the treatment area by one or more fiber optic cables which terminate at an assembly structured to collimate the emitted radiation prior to application to the tissue. In addition, the apparatus includes a focal length setting mechanism which assures that a constant, fixed distance exists between the point of discharge of the laser beam and the biological tissue, thus assuring a constant energy density at the point of application. A method is presented for applying photo-stimulation, photocollagen stimulation and / or ablation laser treatment utilizing the above apparatus.
Owner:SIEGEL JERRY
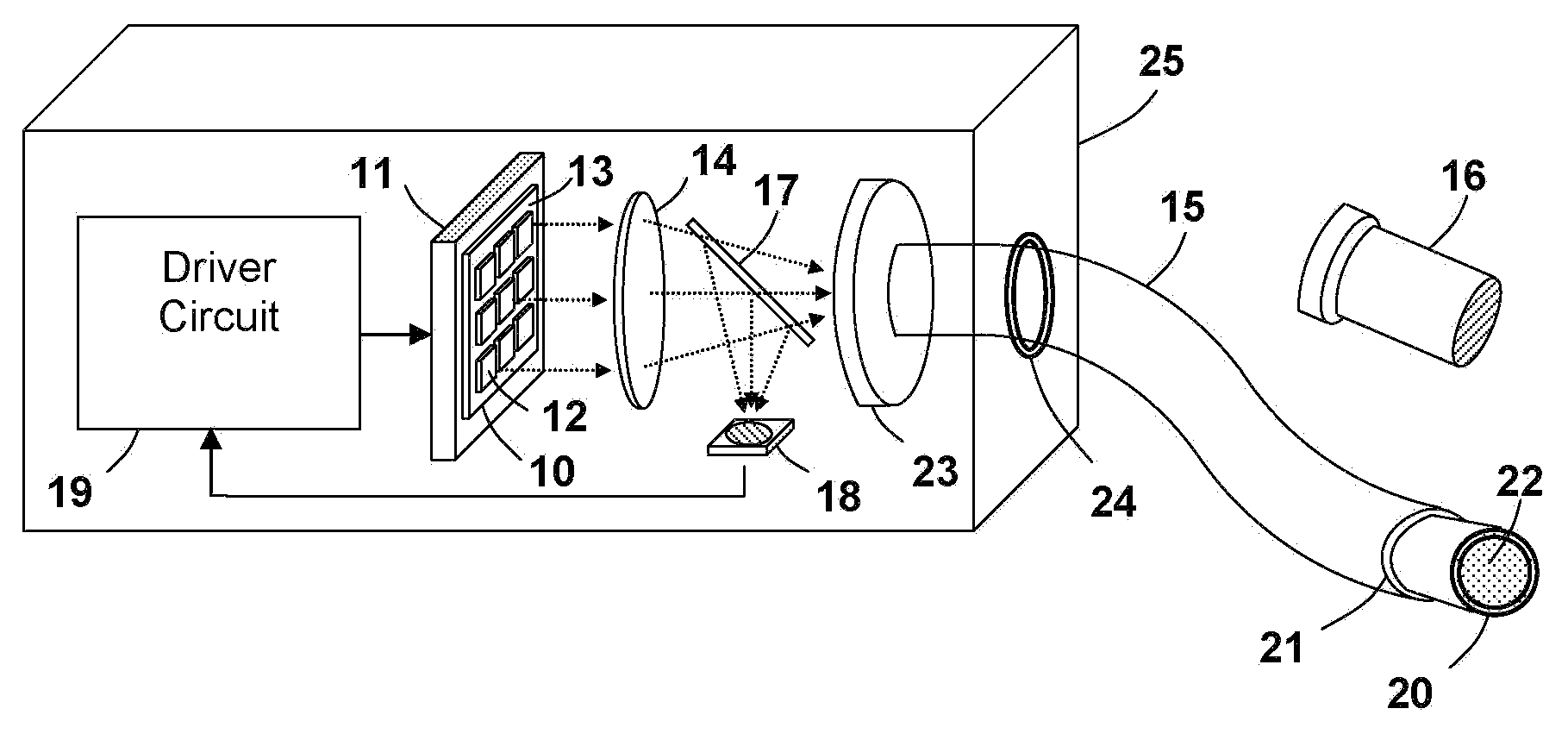
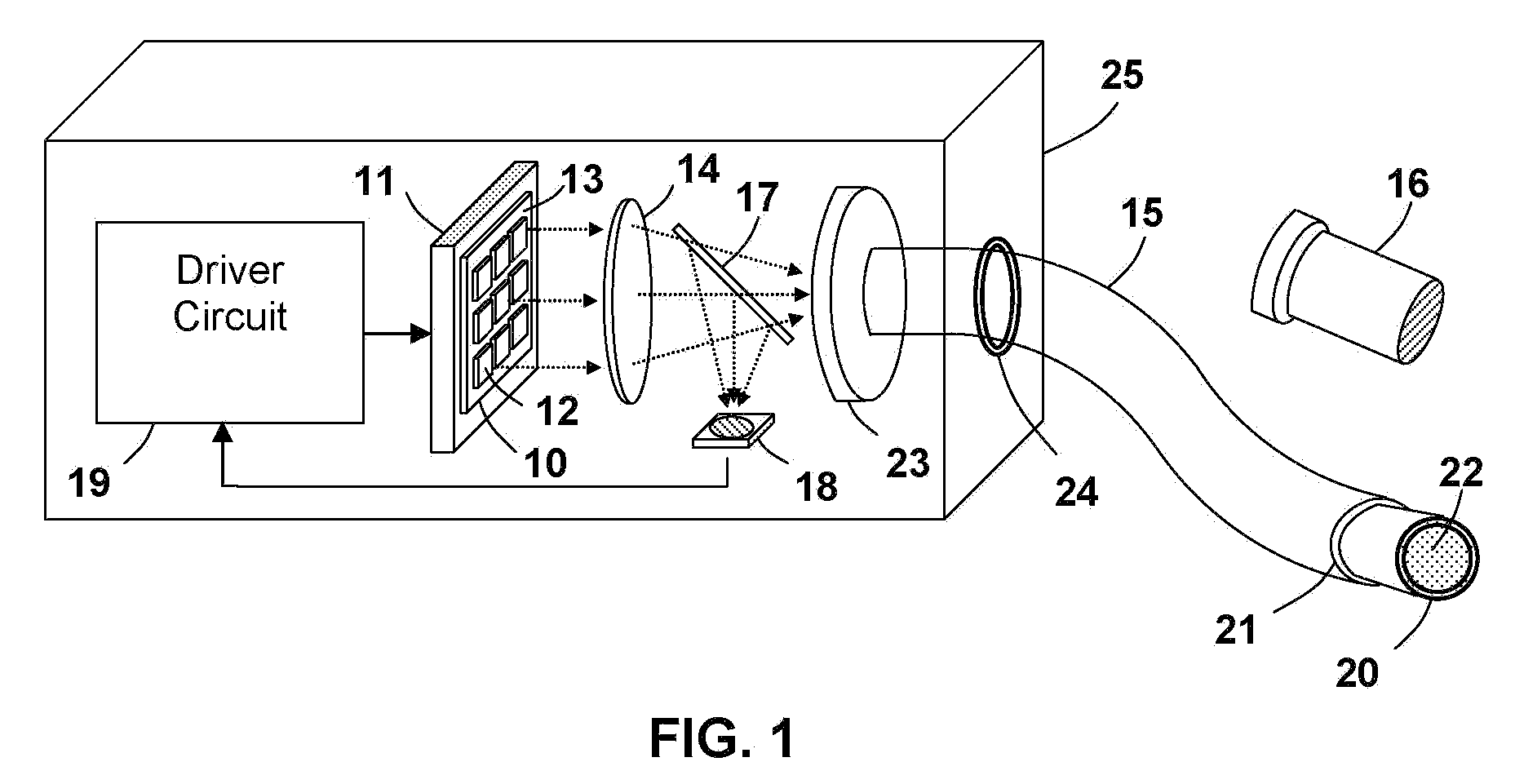
Light emitting apparatus for medical applications
ActiveUS7355155B2Efficient deliveryHigh strengthPhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryLight guideLight beam
A light emitting apparatus is disclosed for medical applications including photo-dynamic-therapy (PDT), photobiostimulation (photobiomodulation), photo-sterilization, and photo-curing. The light emitting apparatus comprises a plurality of semiconductor light emitting elements, preferably light emitting diodes (LEDs) to produce a high intensity light beam, and a liquid light guide for delivering the light beam from the light source to the treatment site.
Owner:BWT PROPERTY
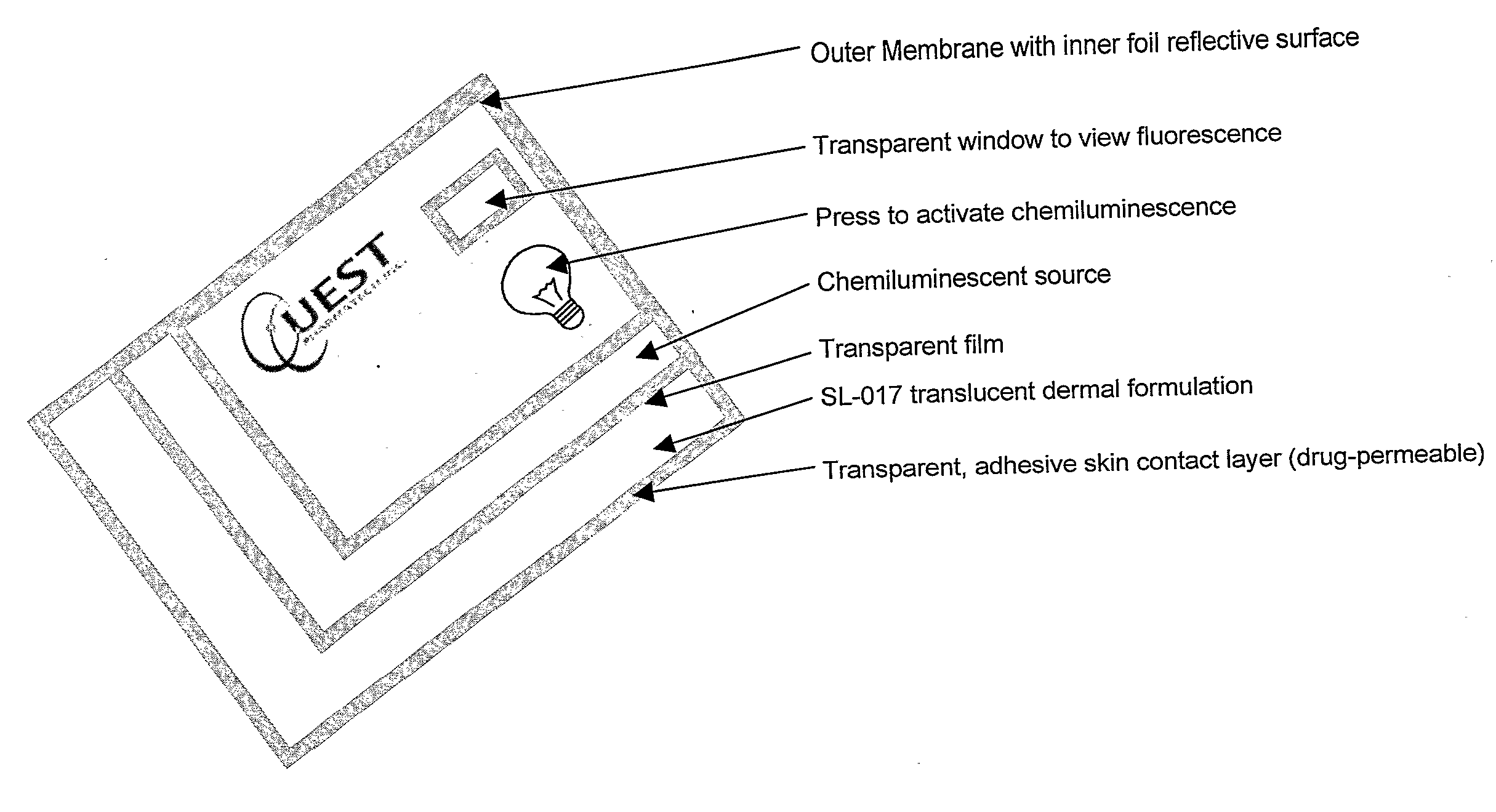
Method and device for photodynamic therapy
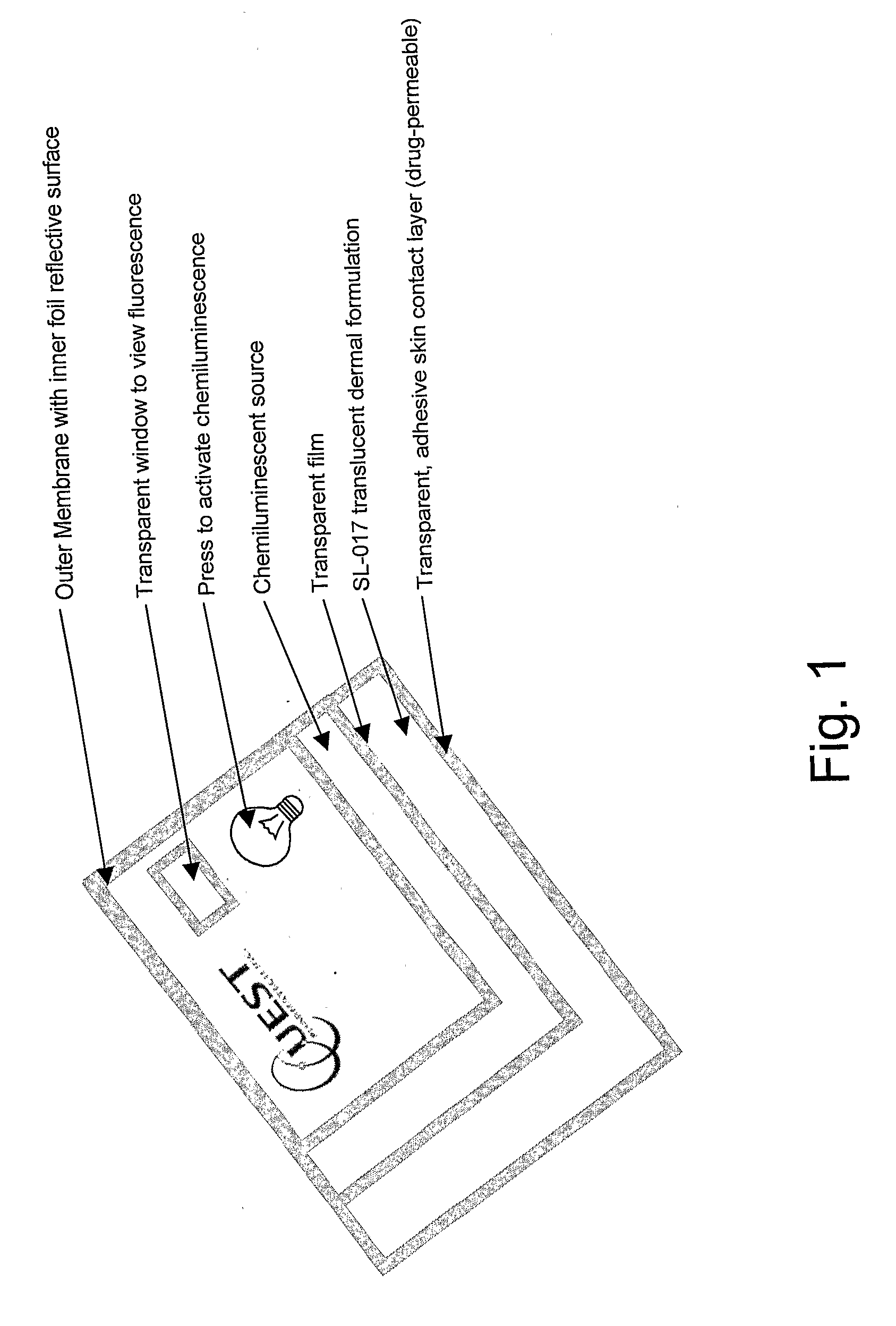
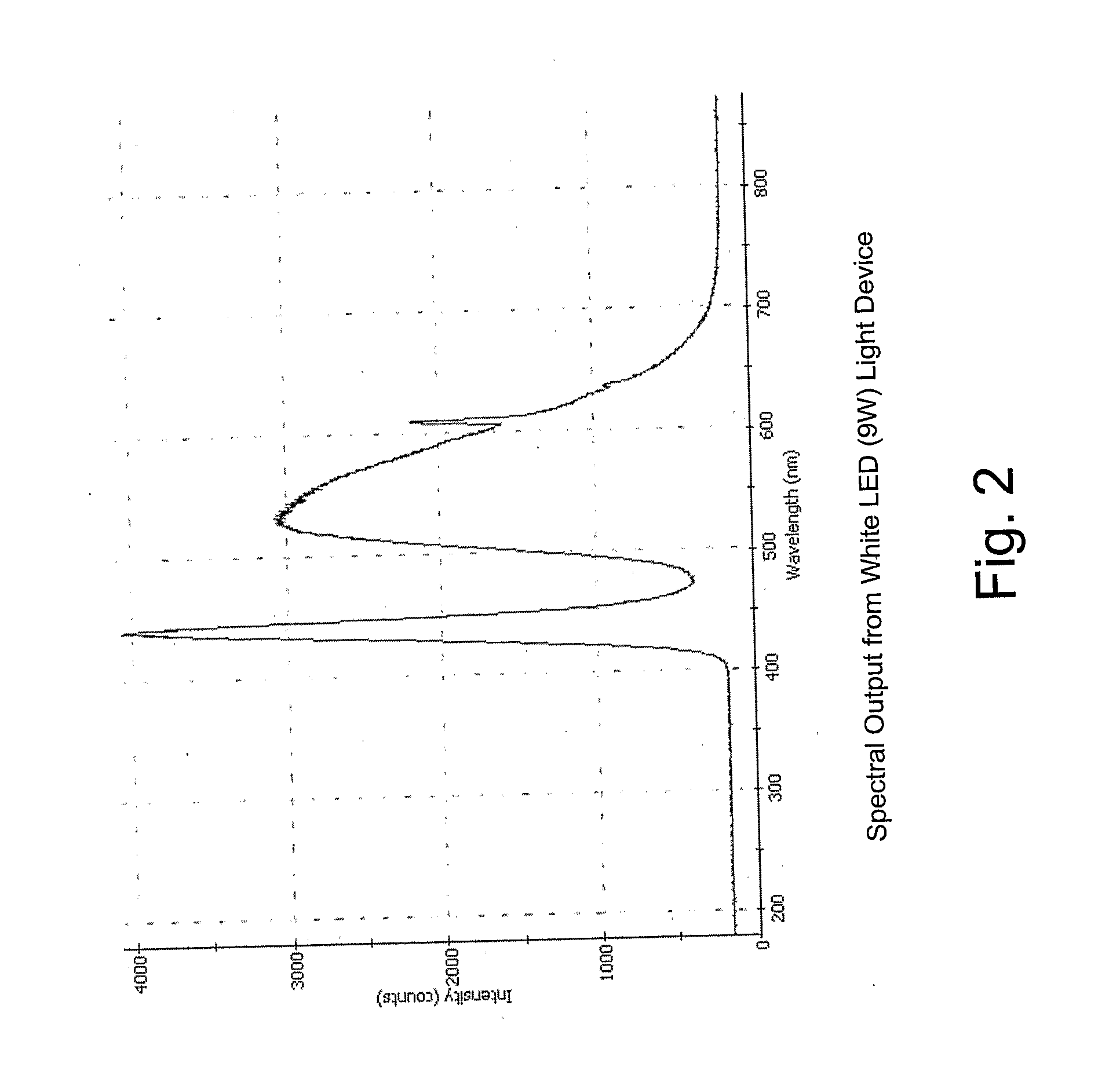
ActiveUS20090204057A1Improve skinImprove nail conditionCosmetic preparationsElectrotherapyPhotosensMedicine
The present invention relates to a photodynamic therapy method and uses thereof for treating an individual in need thereof, comprising administering a photosensitizer to an individual and activating the photosensitizer with a chemiluminescent light source, and / or a light-emitting diode light source, wherein the light source is in dermal contact with the individual. The present invention also relates to a device for photodynamic therapy comprising a permeable reservoir, for containing a photosensitizer formulation for skin application, the device is adapted to deliver the photosensitizer to the individual. The present invention also relates to a device for photodynamic therapy, comprising a permeable reservoir for containing a photosensitizer formulation for skin application and a light source. The light source is a chemiluminescent light source or a light-emitting diode light source and the device is adapted to deliver the photosensitizer to the individual and to irradiate a part of an individual to activate the photosensitizer.
Owner:QUEST PHARMATECH INC
Apparatus and method for performing radiation energy treatments
InactiveUS7160287B1Great treatment area coverageIncrease coverageSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyFiberTreatment effect
An apparatus and method to apply photo-stimulation, photo-dynamic therapy and / or ablation laser treatment to biological tissue. The apparatus includes a plurality of radiation energy sources, preferably laser beams. Additionally, the apparatus allows either a single wavelength or a combination of various wavelengths, either coincidentally or adjacently, to be utilized to achieve a desired treatment effect. Laser beams are transmitted to the treatment area by one or more fiber optic cables which terminate at an assembly structured to collimate the emitted radiation prior to application to the tissue. In addition, the apparatus includes a focal length setting mechanism which assures that a constant, fixed distance exists between the point of discharge of the laser beam and the biological tissue, thus assuring a constant energy density at the point of application. A method is presented for applying photo-stimulation, photocollagen stimulation and / or ablation laser treatment utilizing the above apparatus.
Owner:SIEGEL JERRY
Photodynamic therapy with spatially resolved dual spectroscopic monitoring
ActiveUS20090043296A1Accurate representationDiagnostics using lightSurgical instrument detailsUltraviolet fluorescenceSpectrometer
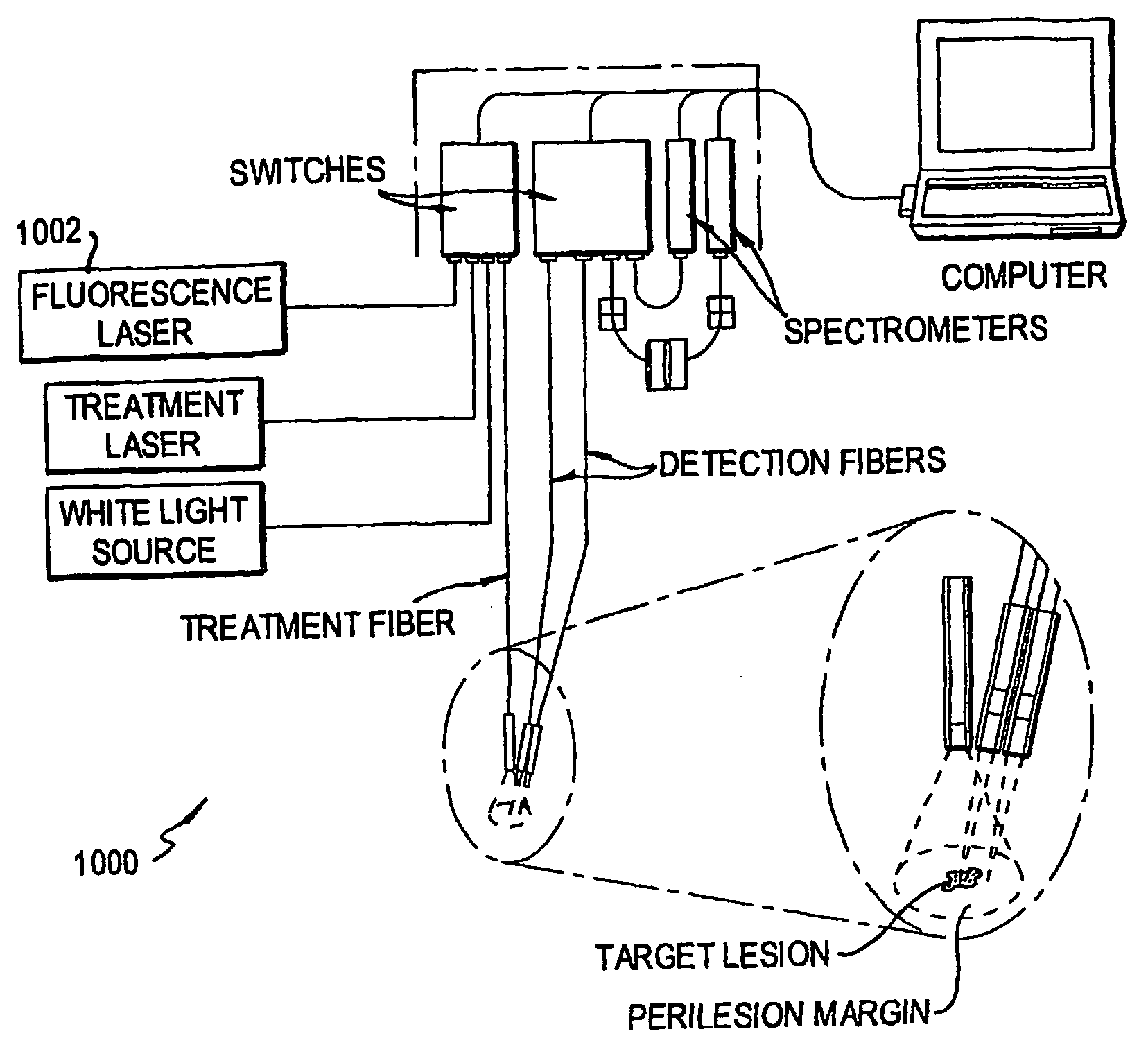
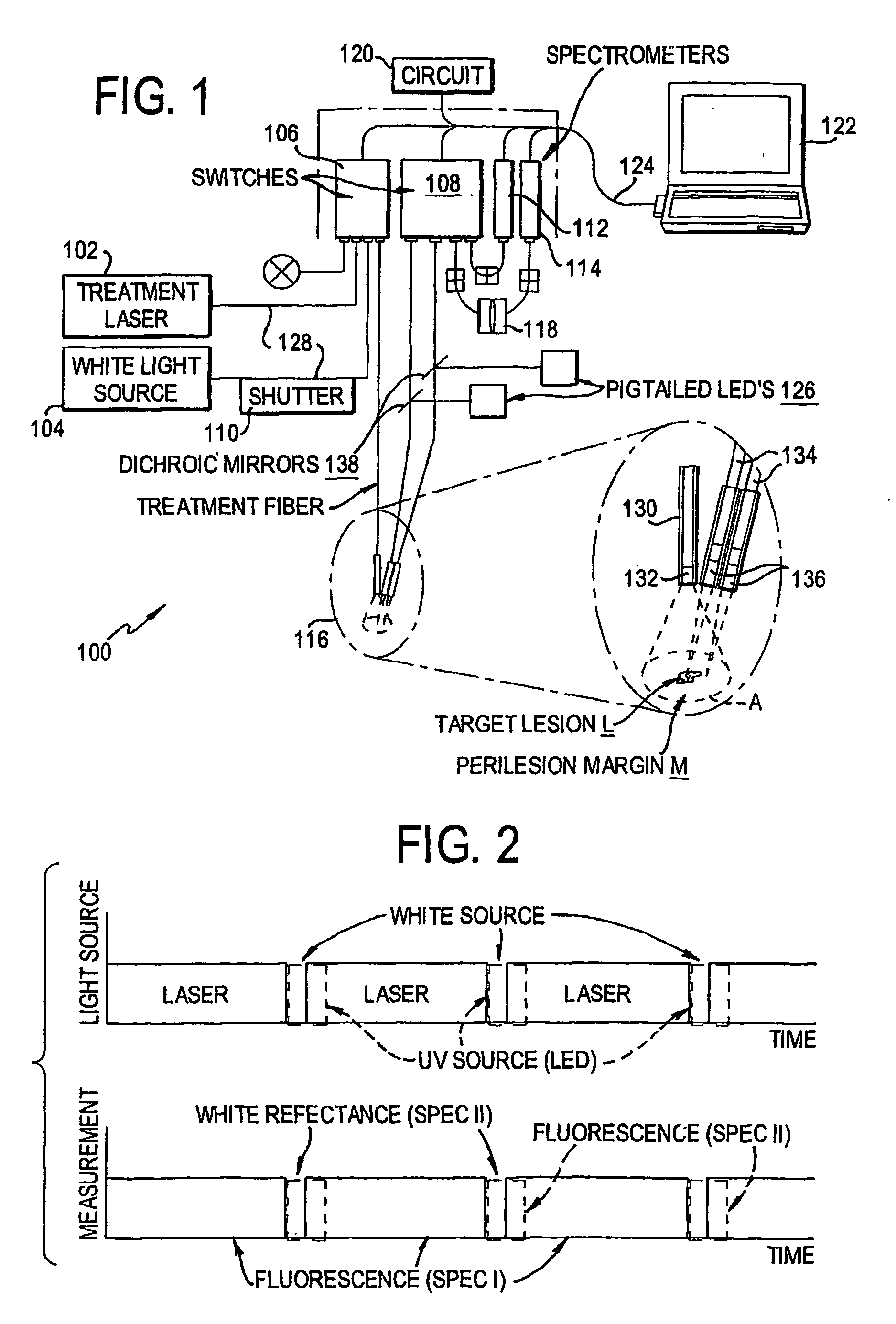
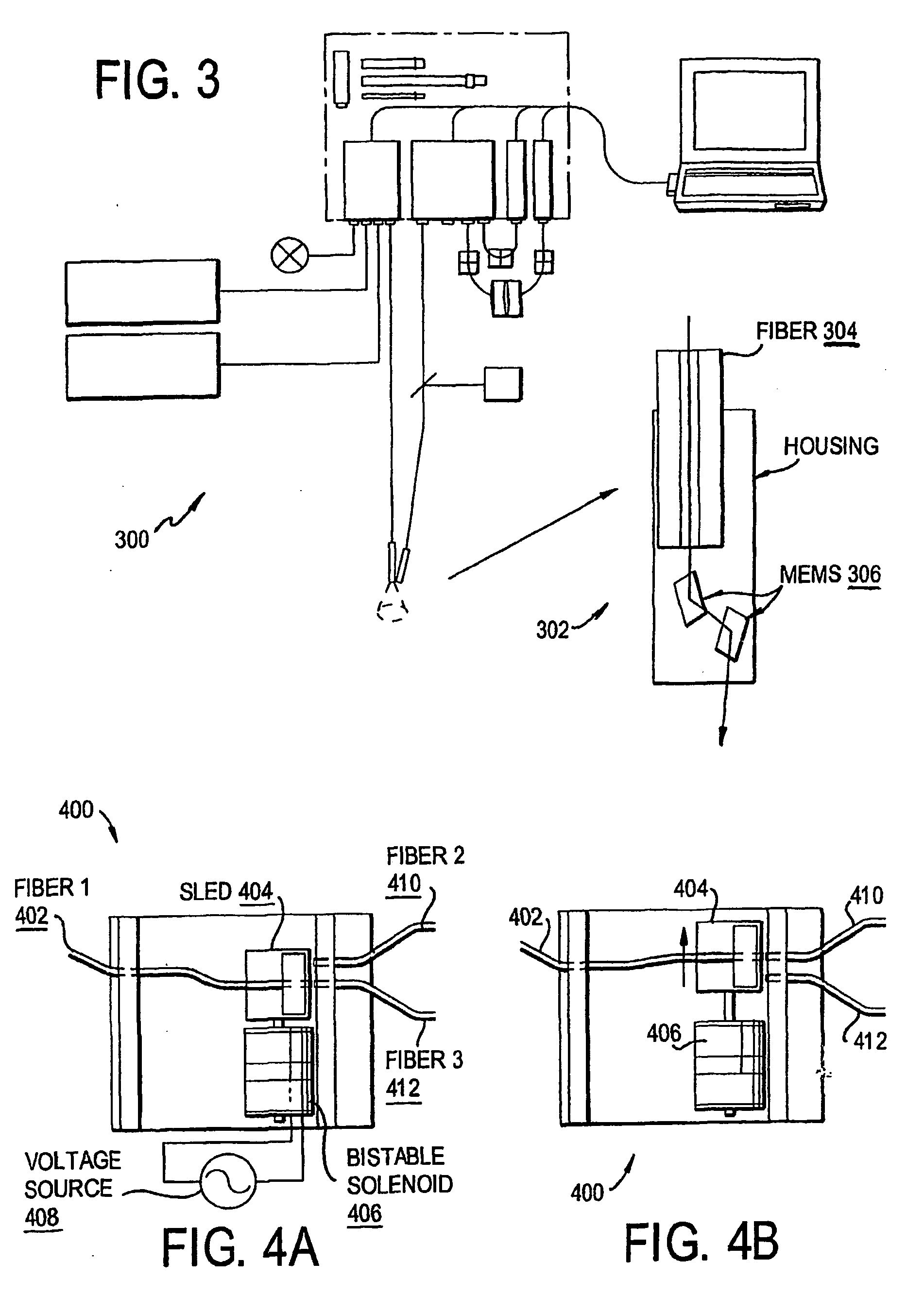
An instrument for photodynamic therapy applies treatment light from a dye laser, white light, and ultraviolet fluorescence excitation light from an LED onto a lesion and surrounding areas in a time-multiplexed manner. The reflected white light is analyzed in a spectrometer to determine a correction for the dynamic optical spectral properties of the patient's tissue. Light emitted by fluorescence from the lesion and the surrounding areas is analyzed in another spectrometer, and the results are corrected in a computer, using the correction. An optical switch has been developed for the instrument, using a bistable solenoid and a sled.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +1
Apparatus and method for performing radiation energy treatments
InactiveUS20070106284A1Improve efficiencyImprove securitySurgical instrument detailsLight therapyFiberTreatment effect
An apparatus and method to apply photo-stimulation, photo-dynamic therapy and / or ablation laser treatment to biological tissue. The apparatus includes a plurality of radiation energy sources, preferably laser beams. Additionally, the apparatus allows either a single wavelength or a combination of various wavelengths, either coincidentally or adjacently, to be utilized to achieve a desired treatment effect. Laser beams are transmitted to the treatment area by one or more fiber optic cables which terminate at an assembly structured to collimate the emitted radiation prior to application to the tissue. In addition, the apparatus includes a focal length setting mechanism which assures that a constant, fixed distance exists between the point of discharge of the laser beam and the biological tissue, thus assuring a constant energy density at the point of application. A method is presented for applying photo-stimulation, photocollagen stimulation and / or ablation laser treatment utilizing the above apparatus.
Owner:SIEGEL JERRY
Light Emitting Apparatus for Medical Applications
ActiveUS20070090272A1Efficient delivery meanHigh strengthPhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryLight guideLight beam
A light emitting apparatus is disclosed for medical applications including photo-dynamic-therapy (PDT), photobiostimulation (photobiomodulation), photo-sterilization, and photo-curing. The light emitting apparatus comprises a plurality of semiconductor light emitting elements, preferably light emitting diodes (LEDs) to produce a high intensity light beam, and a liquid light guide for delivering the light beam from the light source to the treatment site.
Owner:BWT PROPERTY
Induction driven light module and use thereof
The present invention relates to an induction driven light module. In particular, the present invention is directed to an induction driven LED or LD module for photodynamic therapy, entertainment or decoration. The present invention also relates to a method for treating cancer, tumor or other ailments.
Owner:NATIONAL YANG MING UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and method for performing radiation energy treatments
InactiveUS20130041309A1Improve efficiencyImprove securityElectrotherapyMedical devicesMedicineDirect radiation
Method to apply photo-stimulation, photo-dynamic therapy and / or ablation laser treatment to biological tissue including directing radiation from at least one radiation energy source for supplying a treatment radiation; adjusting a collimator assembly for directing radiation from the at least one radiation energy source to the treatment site; collecting radiation not absorbed at the treatment site and reflecting the radiation back to the treatment site, while a contact surface of the collector is engaged with the surface of the biomass; maintaining a set distance between the adjustable collimator assembly and the contact surface; and moving a lens relative to an outlet aperture of the adjustable collimator assembly when the collector is adjusted to thereby produce a given spot size, shape or energy density of the treatment radiation emitted from the adjustable head assembly.
Owner:SIEGEL JERRY
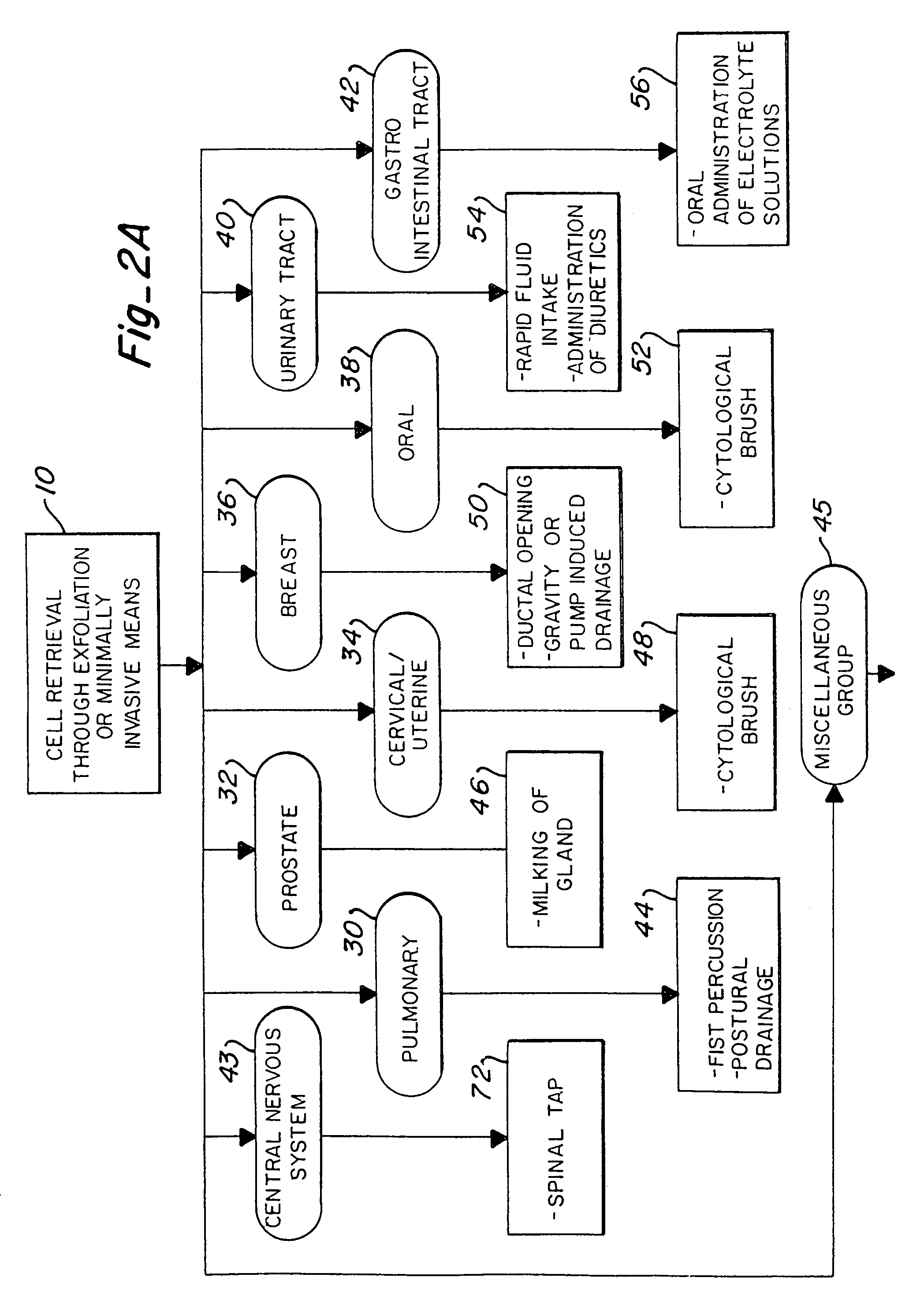
Method of cancer screening primarily utilizing non-invasive cell collection, fluorescence detection techniques, and radio tracing detection techniques
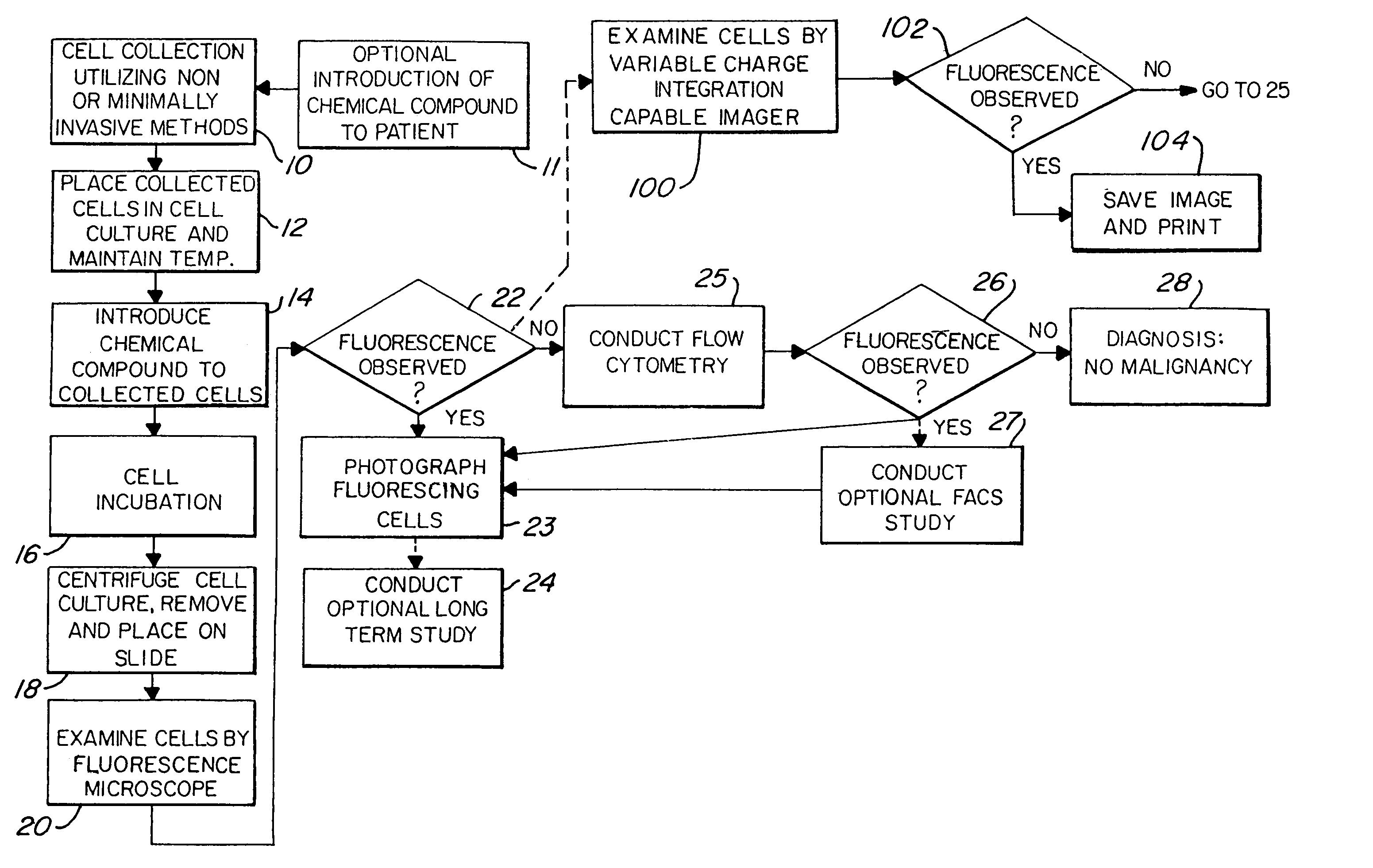
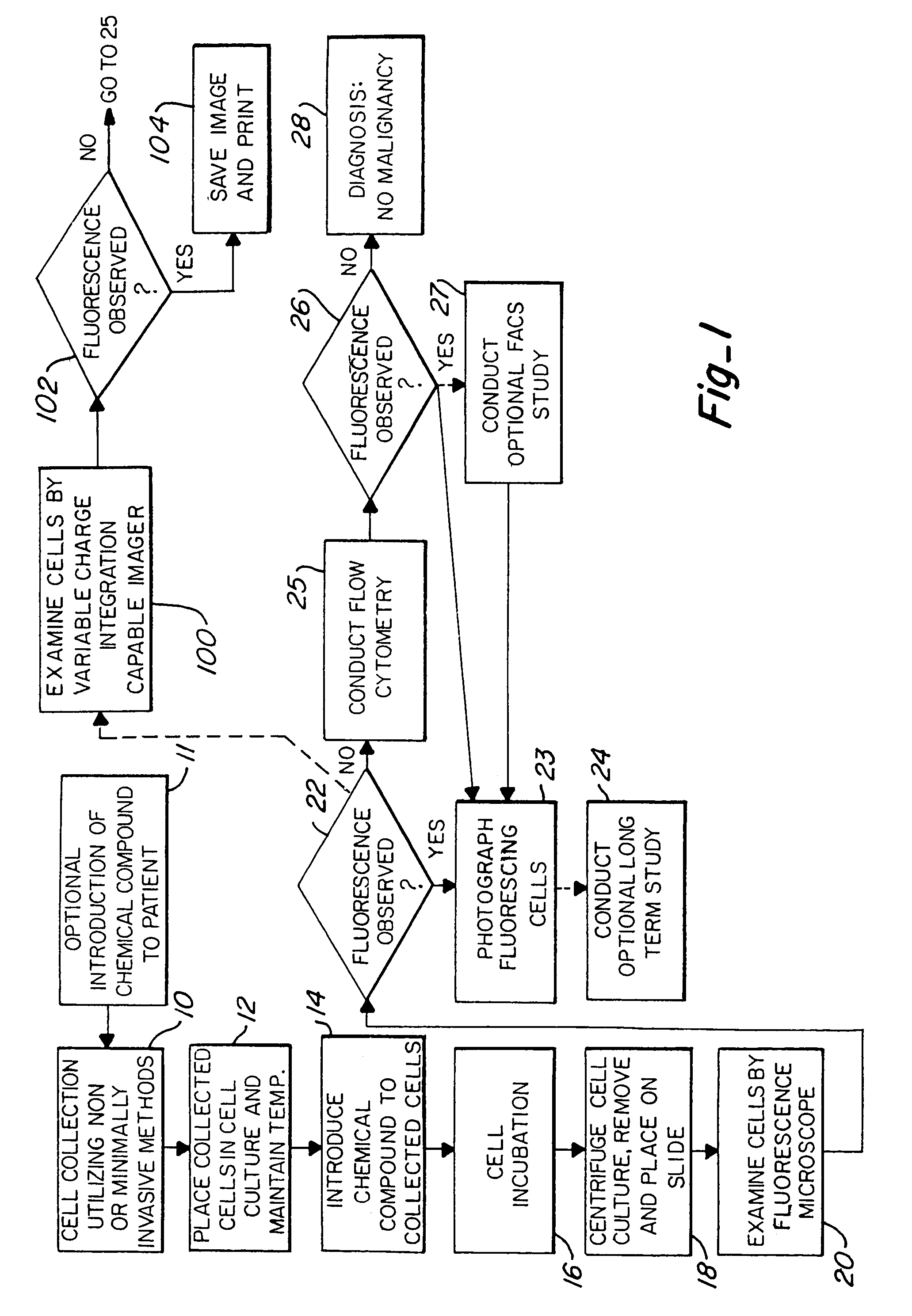
InactiveUS6984498B2Accurate mappingQuick and reliableUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryFluorescenceTomography
A cancer screening method is provided, wherein the method is characterized by administering a compound to a patient, the compound being a complex of a fluorescent marker and a radioactive marker, in a dose emitting between 5 Gy and 20 Gy radiation. Cells are then collected preferably through non-invasive or minimally invasive means. If fluorescence is observed in the exfoliated cells, tomographic scanning is conducted to further locate and / or confirm suspected malignant areas or metastatic areas. Further observation or treatment may be conducted either through fluorescence guided endoscopy, photo-dynamic therapy, and / or radiation treatment.
Owner:ADAIR EDWIN L
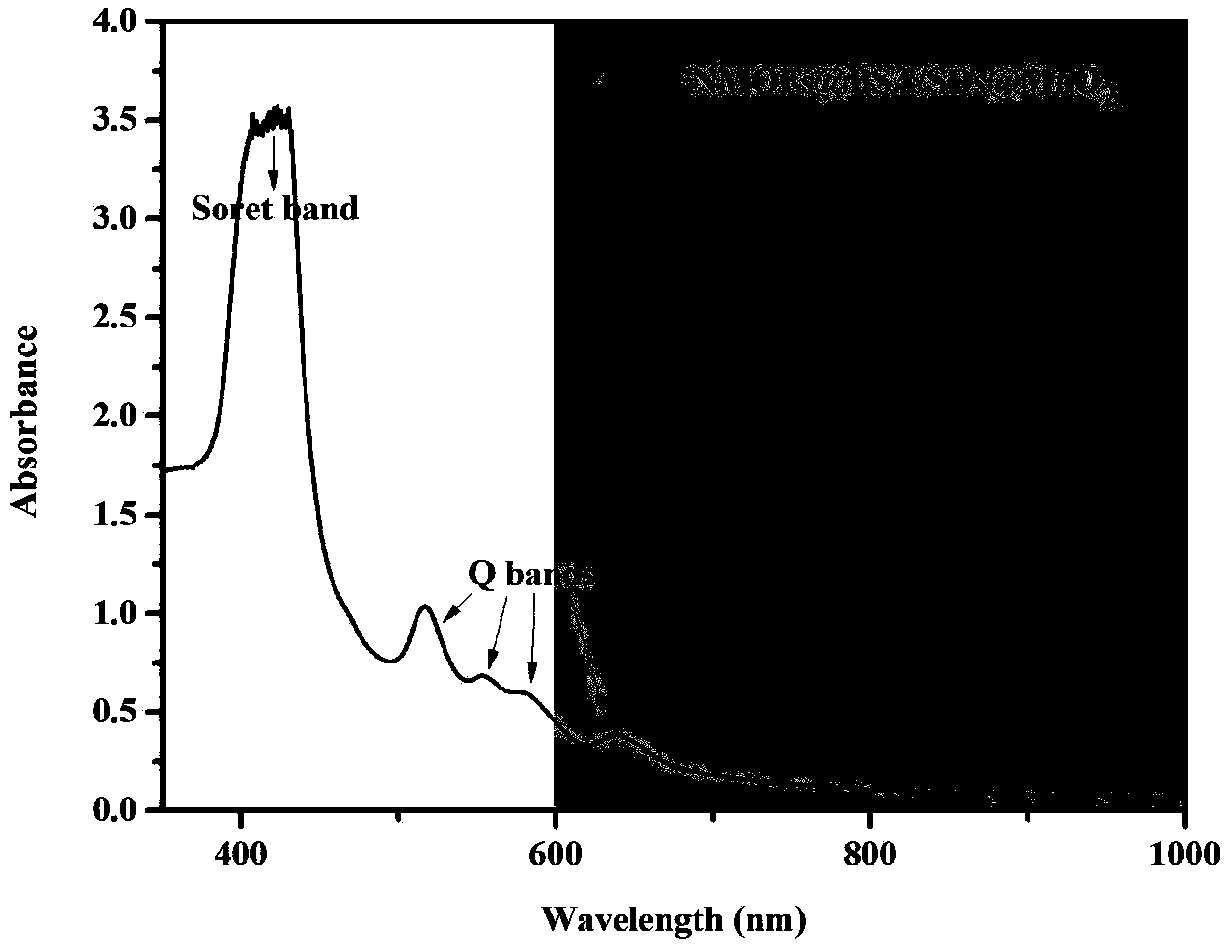
Nano carrier for tumor photo-dynamics therapy (PDT) and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108939072AGood biocompatibilityIncrease oxygen contentOrganic active ingredientsPhotodynamic therapyAbnormal tissue growthDecomposition
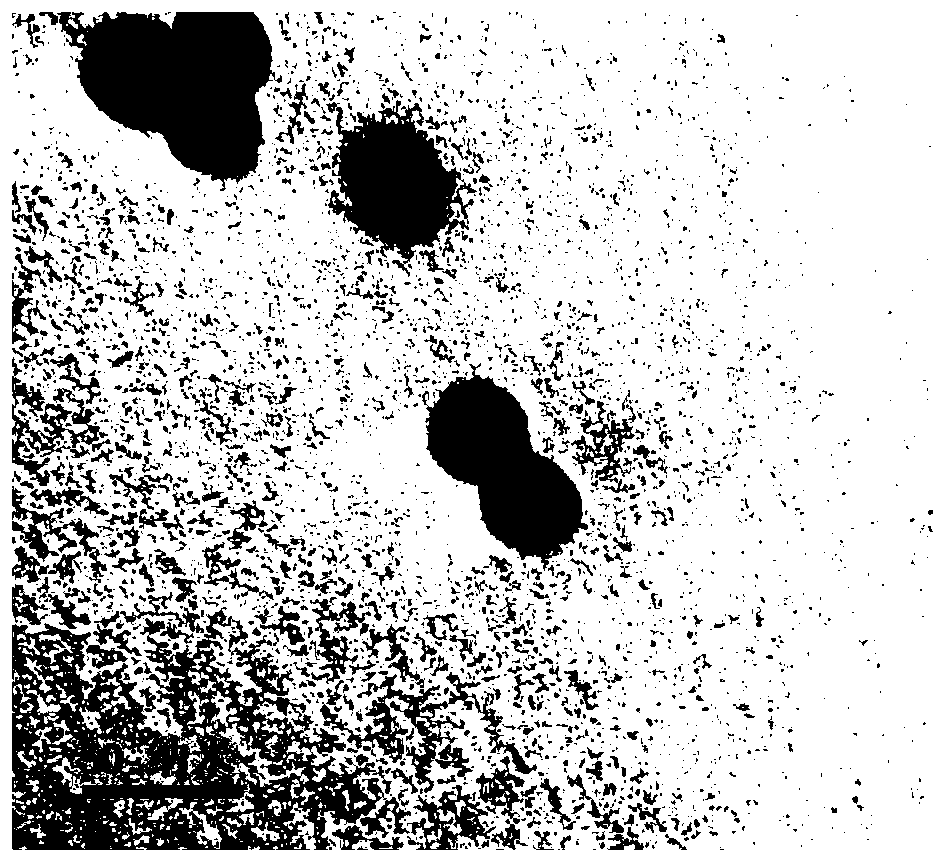
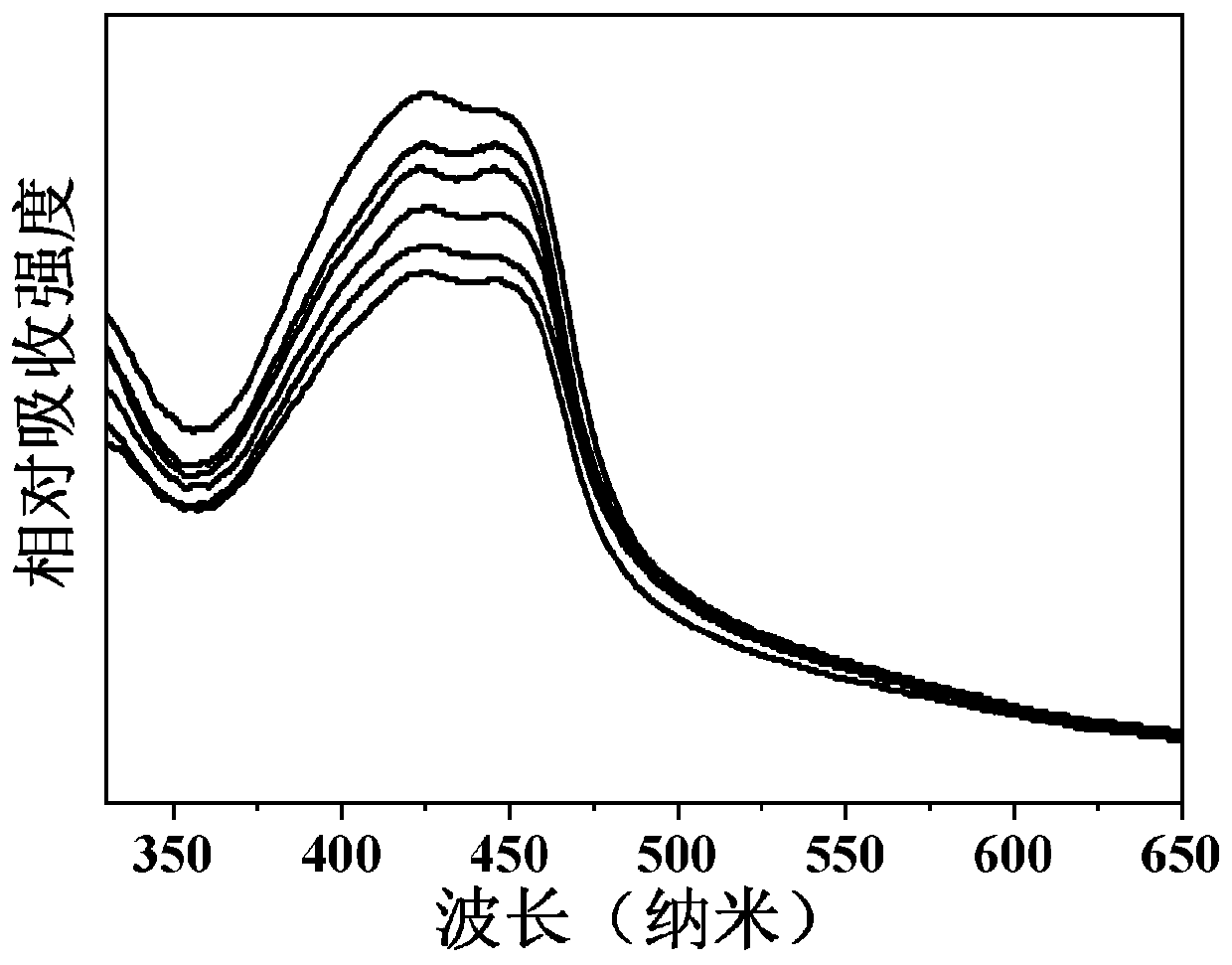
The invention provides a preparation method of a nano carrier for tumor photo-dynamics therapy (PDT). According to the preparation method, Fe<3+> salts are dissolved in DMF, then a photo-sensitizer (TCPP) is added to obtain particles (NMOFs); then the particles are dispersed in water under the assistance of ultrasonic waves; crosslinking agents (EDC and NHS) are added; after the reactions betweenBSA and sulfadiazine (SDs) finish completely, dialysis is performed to obtain particles (NMOFs@BSA / SDs); then the particles are dispersed in distilled water, then Mn<2+> salts are added, the pH is adjusted, and finally dialysis is performed to obtain a carrier (NMOFs@BSA / SDs@MnO2). Nano metal organic framework particles are taken as the basis and coated by protein (BSA) and sulfadiazine (SDs); finally the particles are in-situ mineralized to obtain required particles; SDs can specifically recognize carbonic anhydrase of tumors and is capable of actively targeting the oxygen-deficient parts oftumors; MnO2 generated in mineralization can catalyze the H2O2 decomposition to increase the oxygen content of tumors; and the PDT efficiency is improved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV +1
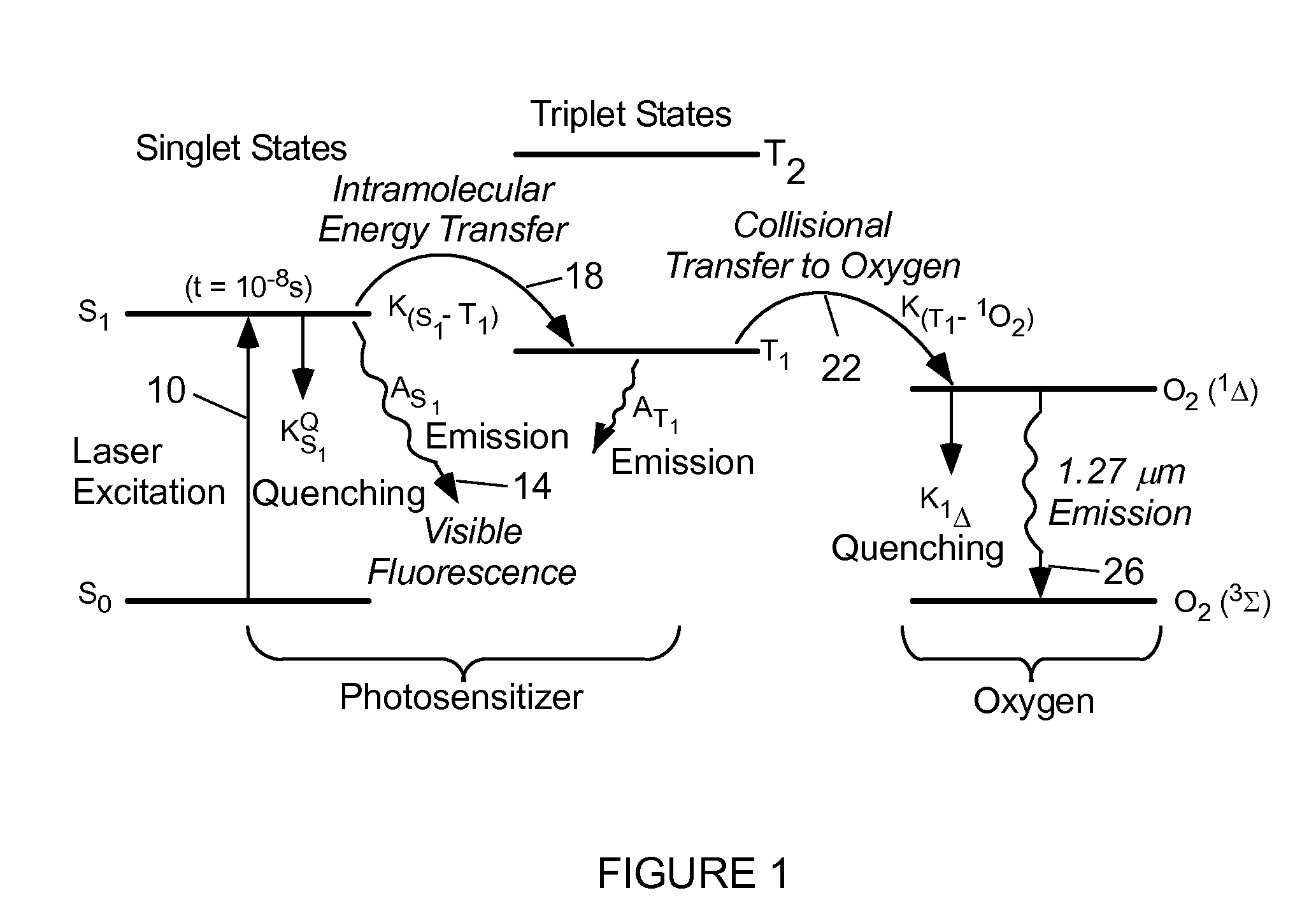
Singlet Oxygen Production and Dosimetry for Photodynamic Therapy
InactiveUS20120209125A1Good curative effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhotodynamic therapyDosimetry radiation
An apparatus for photodynamic therapy (PDT) includes a light source configured to provide excitation light for a photosensitizer, an optical system configured to direct the excitation light to a target region and receive light emitted by the photosensitizer and / or singlet oxygen generated in the target region, and a detection system configured to receive the light emitted by the photosensitizer and / or the singlet oxygen. The apparatus also includes a filter system configured to spectrally discriminate between emission from the photosensitizer and the singlet oxygen and a processor configured to determine concentrations of the singlet oxygen and / or the photosensitizer based on an emission signal measured by the detection system.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
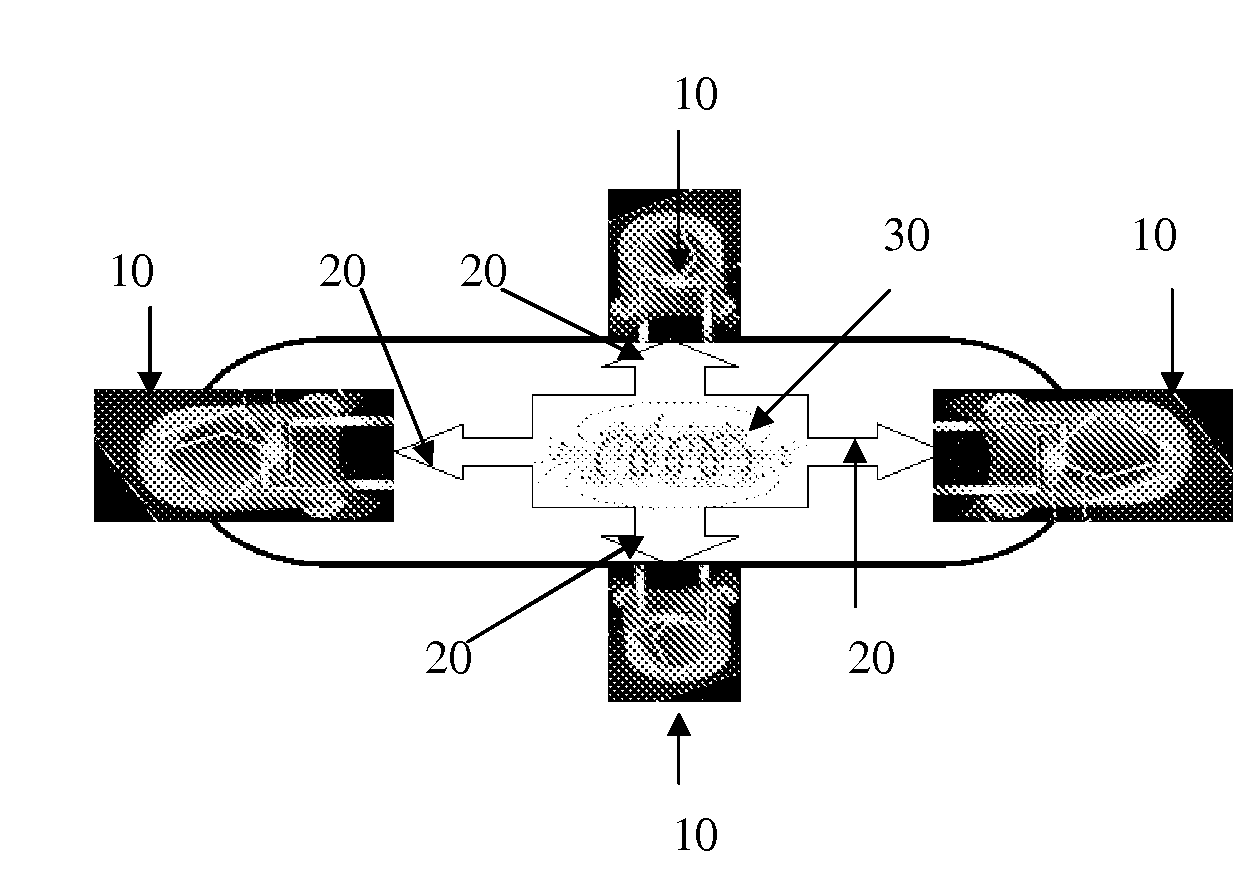
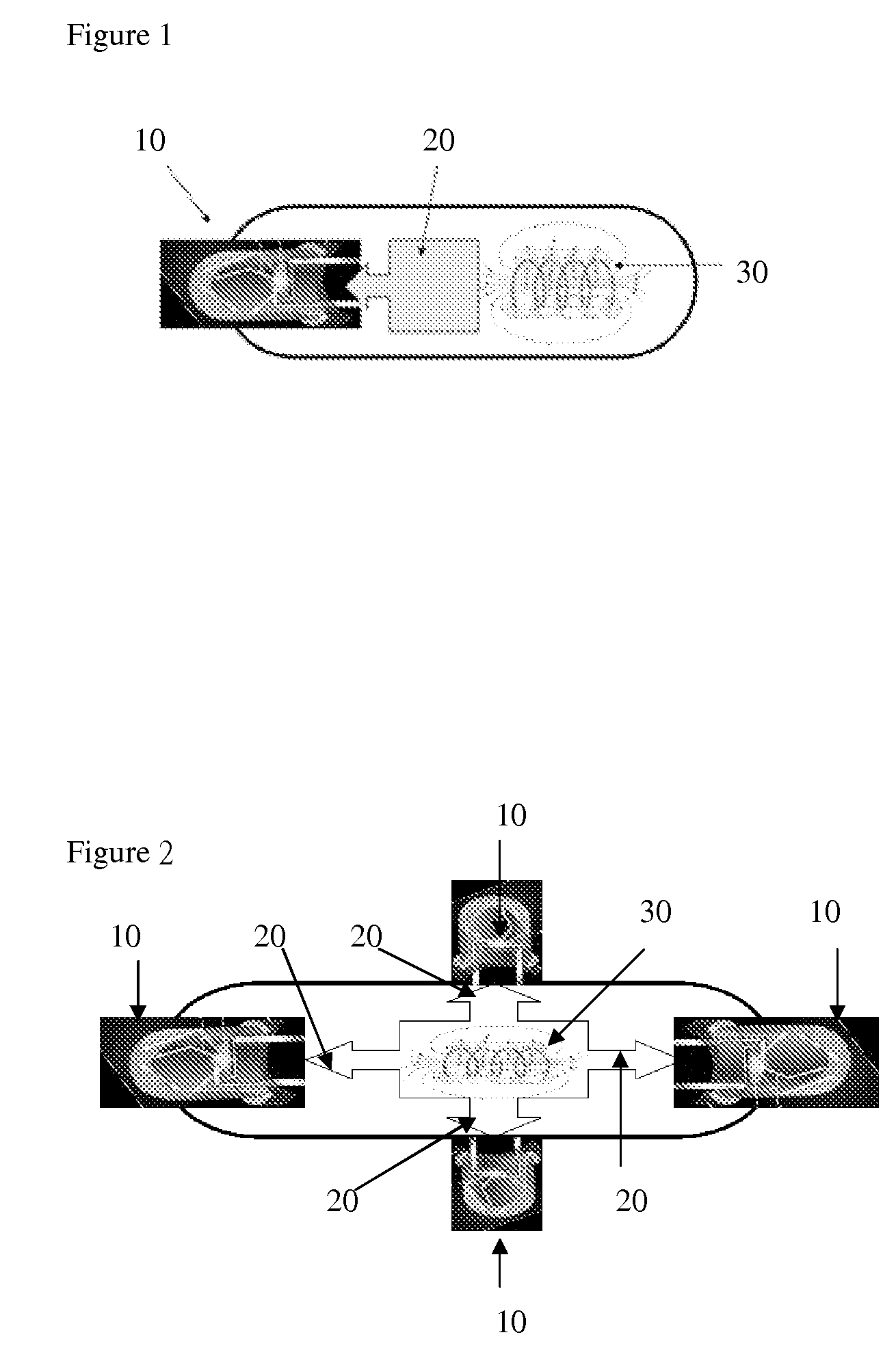
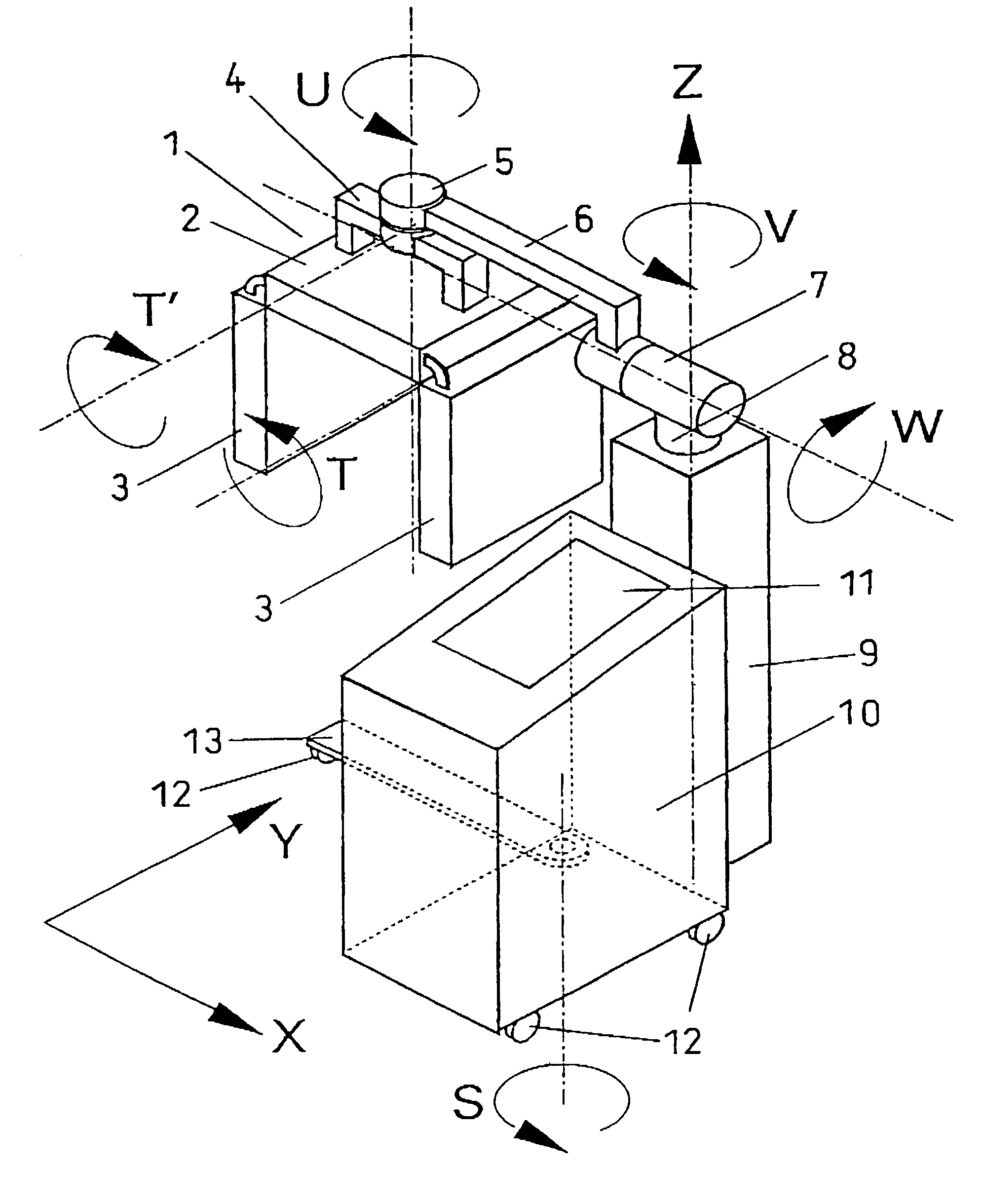
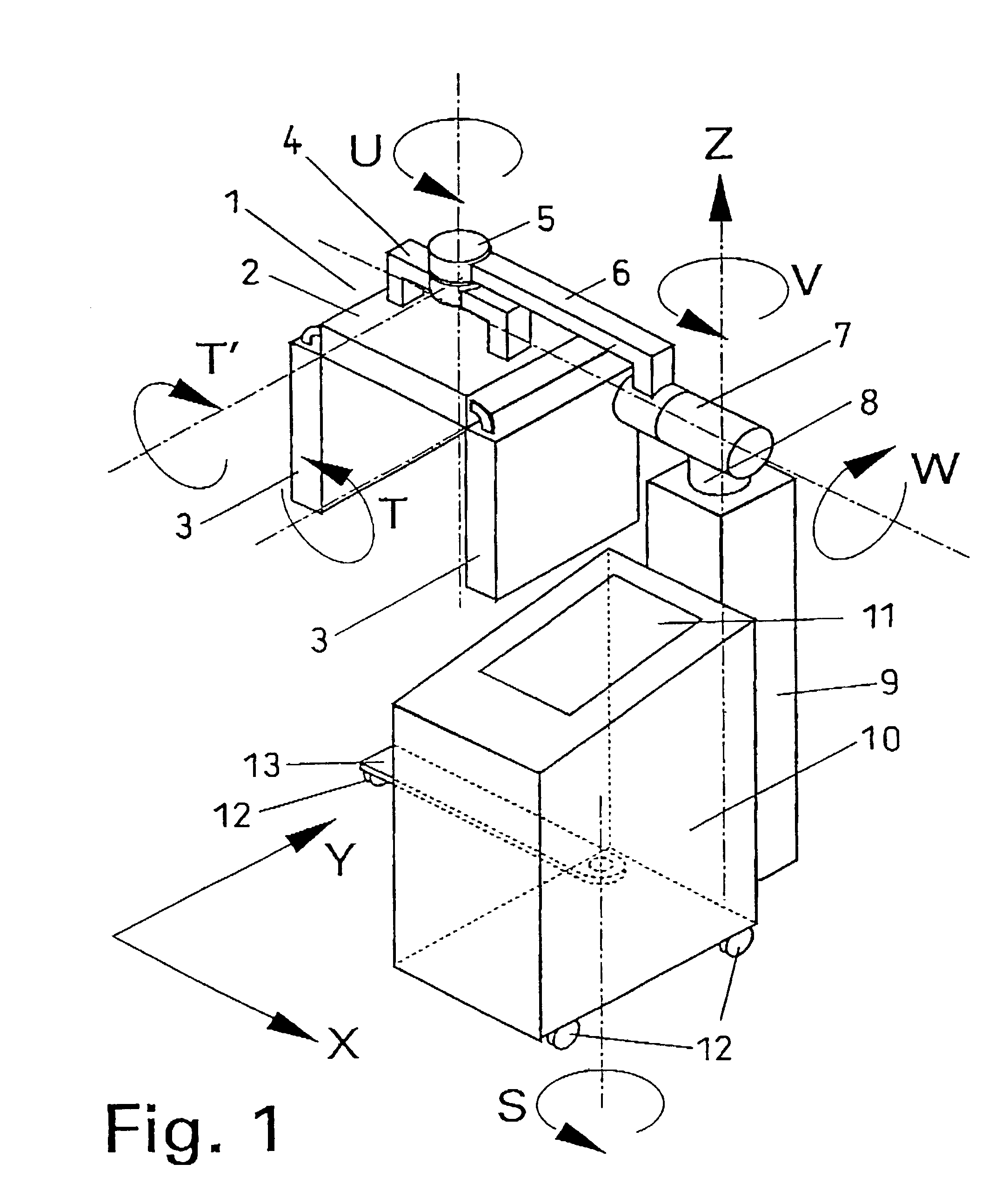
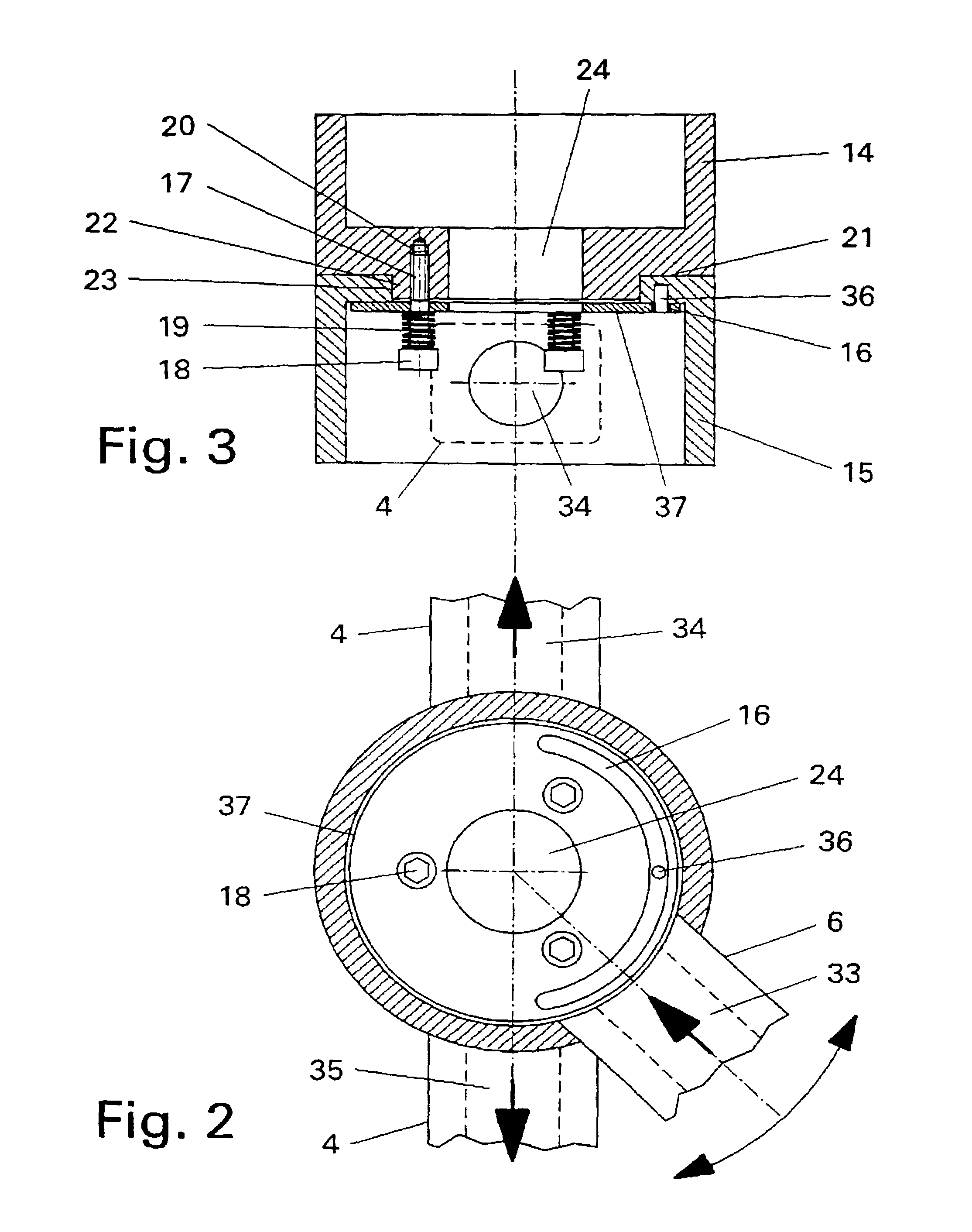
Irradiation apparatus and system, especially for photodynamic therapy
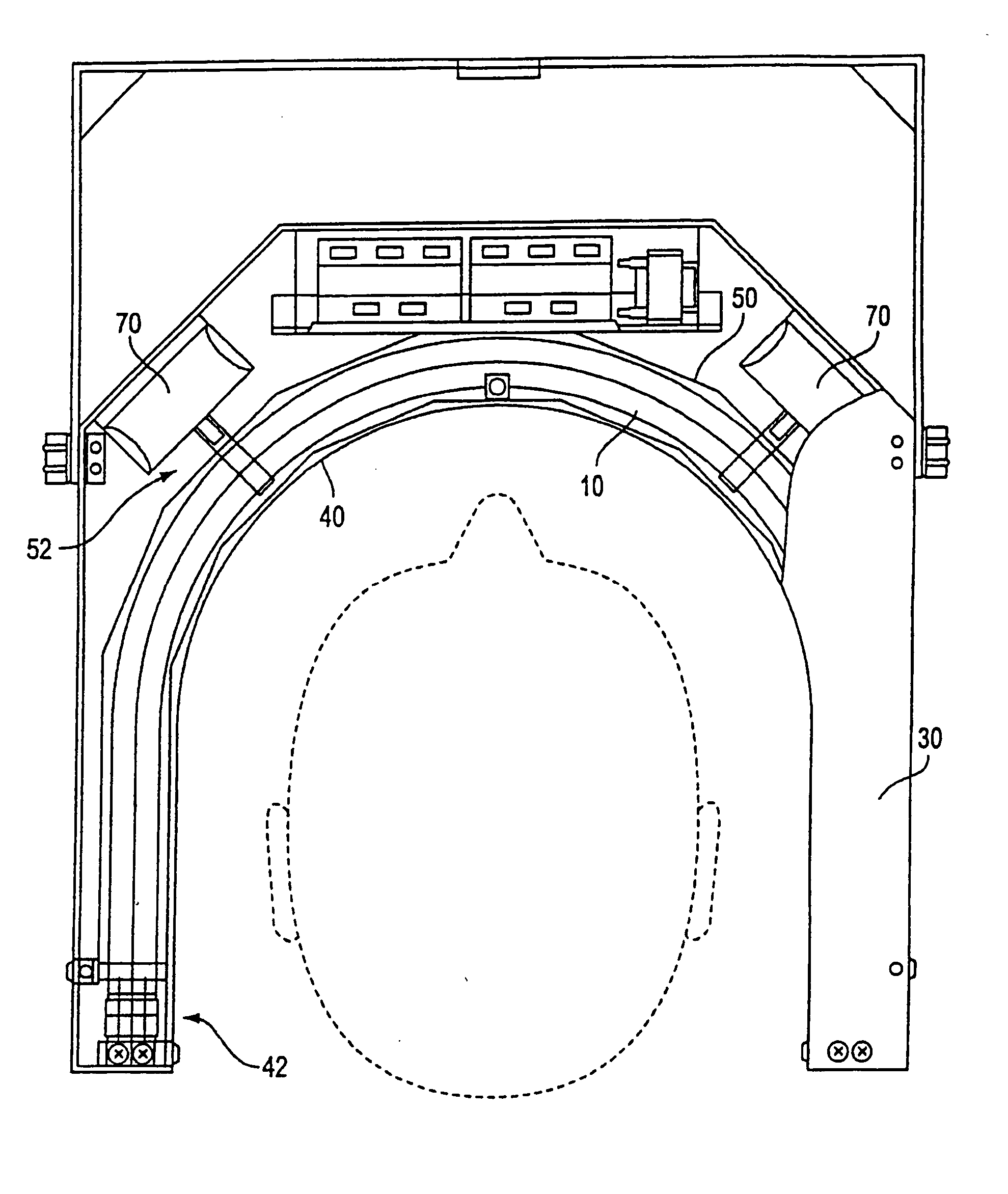
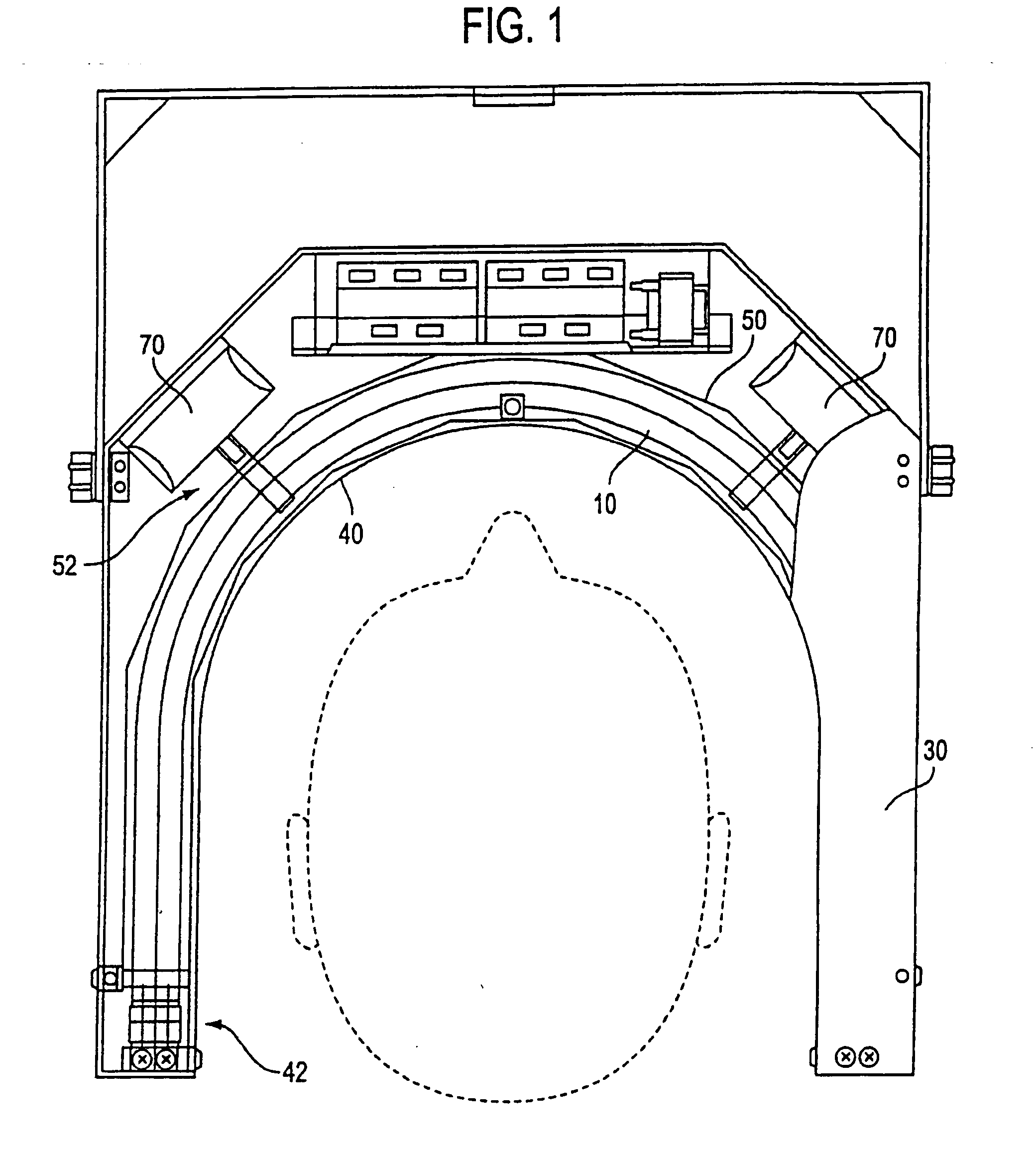
To allow optimum adaptation of irradiation equipment, especially irradiation equipment for photodynamic therapy, to the individual anatomy of a patient, an irradiation head (1) is provided with a plate-shaped middle section (2) and plate-shaped lateral leaves (3), mounted on the middle section (2) in such a way that they can swivel. The irradiation head can be rotated about two perpendicular axes (U, W), and its height can be adjusted. With its lateral leaves (3) extended, the irradiation head (1) has a plane configuration formed by the middle section (2) and the extended lateral leaves (3). The configuration is suitable for areal irradiation of the trunk or extremities of a patient. It can also be configured to a rectangular U shape suitable for three-sided irradiation, when the lateral leaves (3) are swivelled 90°. Radiation sources, e.g., cylindrical or compact light fixtures, which have a spectrum from UV, through visible light, to IR and are preferably interchangeable, are provided in or on the undersides of the middle section (2) and the lateral leaves (3). The middle section (2) is mounted at one end of a preferably telescoping swivel arm (6) by means of a first swivel joint (5). A second swivel joint (7) is provided for mounting the other end of the swivel arm (6) on the upper end of a column (8), which is supported in a column support (9) in such a way that it can be moved along its longitudinal axis (Z) and rotated about its longitudinal axis (Z). The column support (9) is mounted, for example, on a control console (10).
Owner:HERBERT WALDMANN GMBH & CO KG
Ruthenium-anthraquinone conjugates, preparation method thereof and application for optical power therapeutic photosensitizer
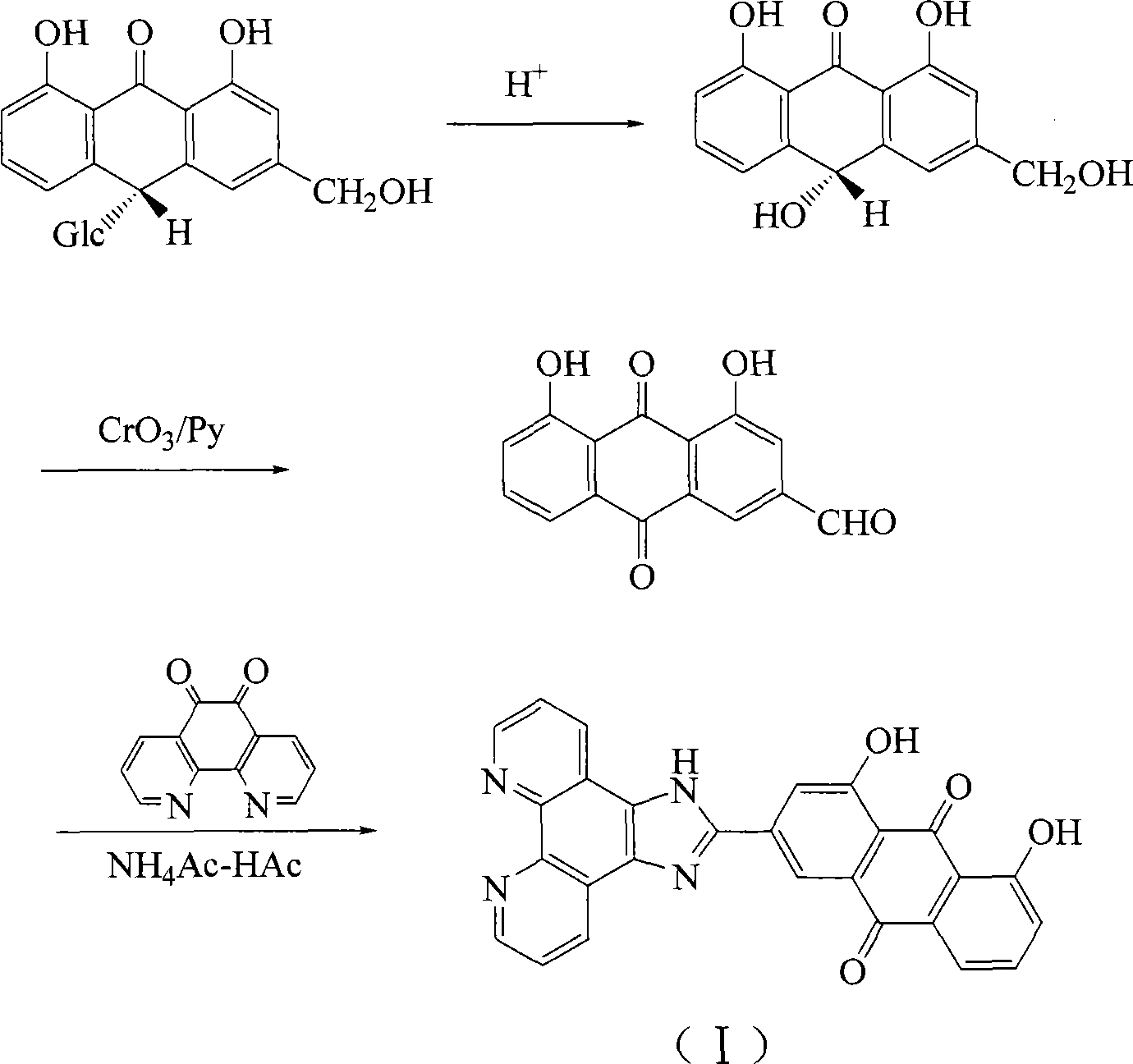
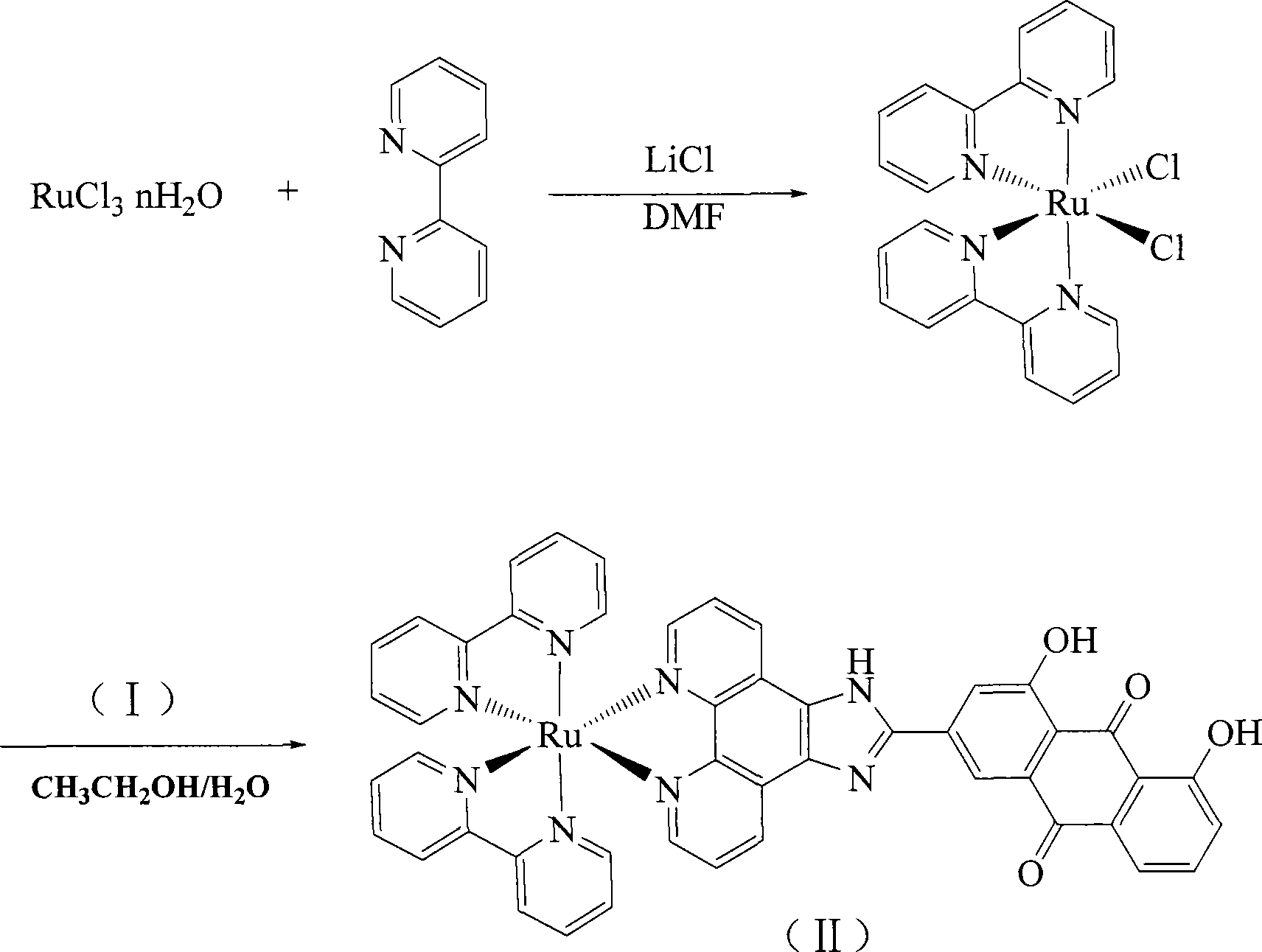
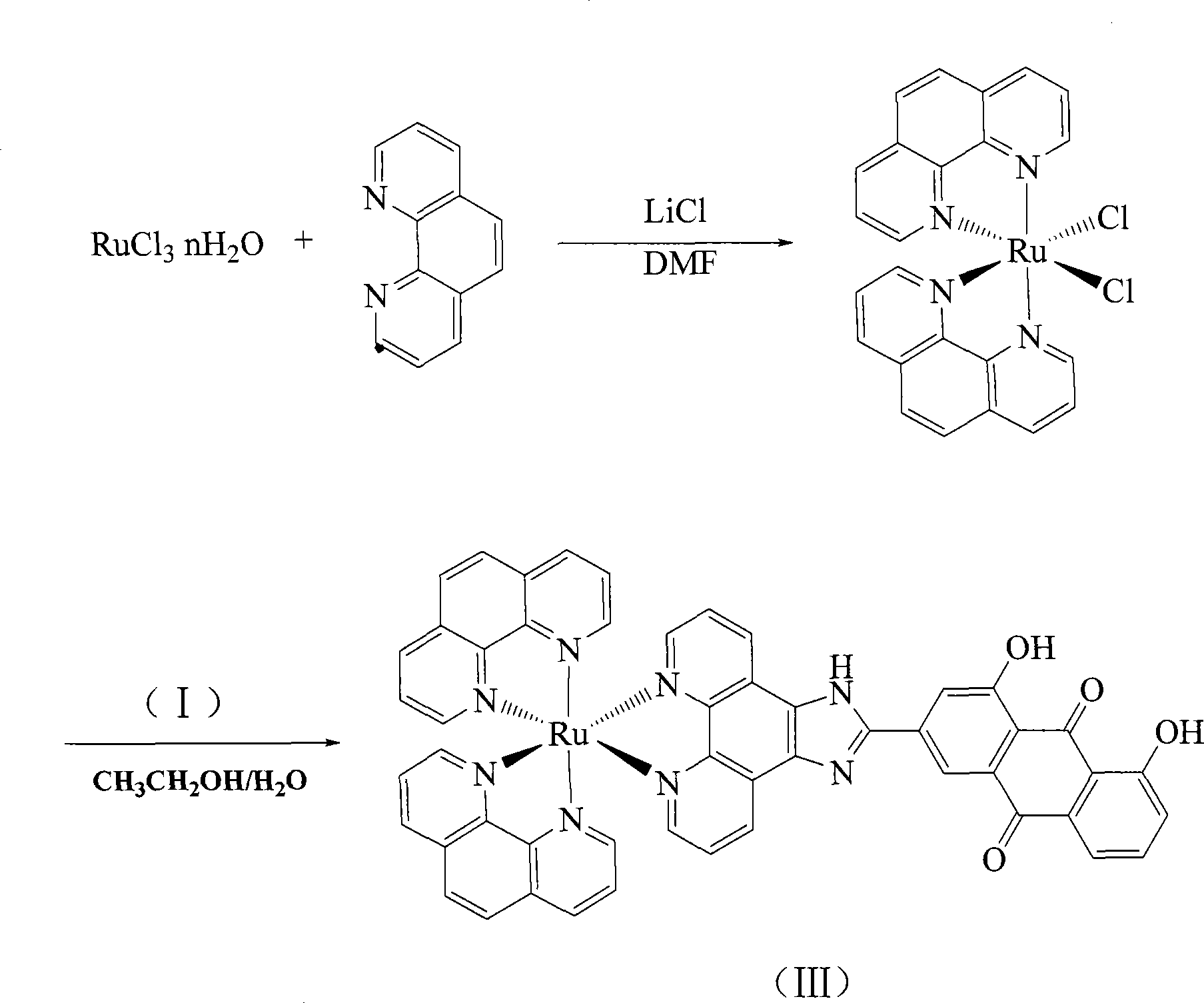
InactiveCN101117340AHigh inhibition rateThe synthetic route is simpleOrganic active ingredientsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCancer cellPhenanthroline
The invention discloses a ruthenium-anthraquinone conjugate, the preparation process thereof and the application as a photo-dynamic therapy photosensitizer. The general formula of the ruthenium-anthraquinone conjugate of the invention is [Ru(L)2HAIP].(PF6)2, the general formula of the HAIP is 1,8- dihydroxy -9,10- anthraquinoneimidazole [4,5-f][1,10] phenanthroline, the general of the L is bpy or phen. The preparation process for the ruthenium-anthraquinone conjugate comprises the following procedures: 1. the synthesis of the HAIP: 1,8- dihydroxy -9,10- anthraquinone-3-aldehyde is reacted with the phenanthroline5,6-diketone to produce the HAIP; 2. Ru(L)2Cl2 is reacted with HAIP and NH4PF6 to produce the [Ru(L)2HAIP].(PF6)2. The invention takes the aloe-emodin as the raw material and the ruthenium polypyridyl complex has single chemical composition; the synthesis route is simple and the yields are higher; during the experiment, the compound shows the light suppression to the growth of cancer cells.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Bone treatment instrument and method
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is used in the case of bone. A photosensitizing drug is administered to a mammal. A bone insertion member is secured into bone. A fiber optic cable sheath extends from within the bone insertion member and is accessible. A fiber optic cable is inserted in the fiber optic cable sheath to deliver light to the bone. A locking member is then attached to the insertion member. Non-thermal light at a specific wavelength is then delivered to activate the drug. The insertion member and the fiber optic cable sheath may remain inside the mammal for further photodynamic therapy.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
Medical laser apparatus with enhanced disinfection function
InactiveUS20090012587A1Efficient oxygen generationSurgical instrument detailsLight therapySinglet oxygenPower intensity
Owner:BWT PROPERTY
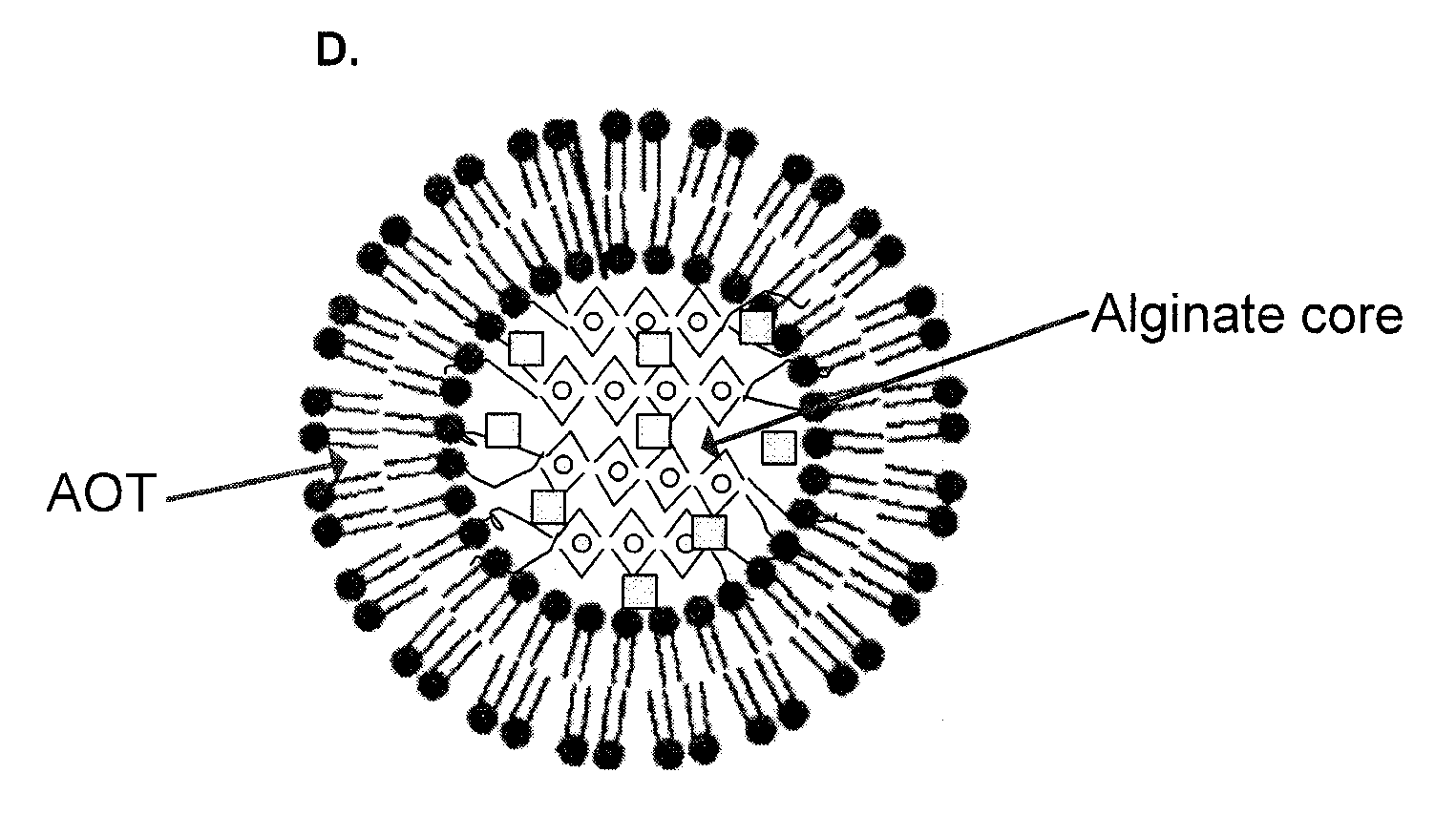
Polymer-surfactant nanoparticles for sustained release of compounds
A polymer-surfactant nanoparticle formulation, using the anionic surfactant aerosol OT (AOT) and polysaccharide polymer alginate, is used for sustained release of water-soluble drugs. The AOT-alginate nanoparticles are suitable for encapsulating doxorubicin, verapamil and clonidine, as well as therapeutic agents effective against dermal conditions such as psoriasis. The nanoparticles are also suitable for encapsulating photo-activated compounds such as methylene blue for use in photo-dynamic therapy of cancer and other diseases, and for treating tumor cells that exhibit resistance to at least one chemotherapeutic drug.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Ring-fused structural near-infrared photosensitizer and preparation method thereof
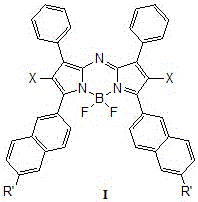
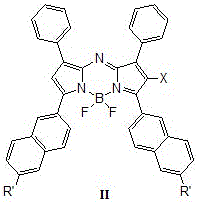
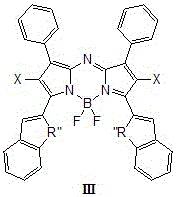
InactiveCN105085556AGood light stabilityHigh molar absorptivityEnergy modified materialsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsSinglet oxygenBODIPY
The invention relates to a kind of ring-fused structural near-infrared photosensitizer and a preparation method thereof, especially relates to a kind of a photosensitizer treating malignant tumor through photodynamic therapy and a preparation method thereof, and concretely provides a kind of a heavy-atom-substituted near-infrared aza-BODIPY-like (aza-boron dipyrromethene-like) photosensitizer, a preparation method thereof, and efficiency of the photosensitizer generating singlet oxygen. The photosensitizer is a series of novel photosensitizers taking heavy-atom-substituted near-infrared fluorescent dye aza-BODIPY developed from azodipyrromethane boron trifluoride as a mother nucleus. The general formula of the phoosensitizer is shown as formulas I / II / III / IV. The aza-BODIPY-like photosensitizer possesses a ring-fused structure, and also possesses advantages of classic traditional dye BODIPY / aza-BODIPOY spectrum performances. The ring-fused structural aza-BODIPY-like photosensitizer has the absorption wavelength more than 700 nm, is capable of deeply penetrating biological issue under irradiation of a long-wavelength monochromatic light source, possesses low toxicity and low side effect, and is high in singlet oxygen generation efficiency, and electron of the photosensitizer is easy for intersystem crossing.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Rare earth upconversion diagnosis-and-treatment-integrated nanocomposite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
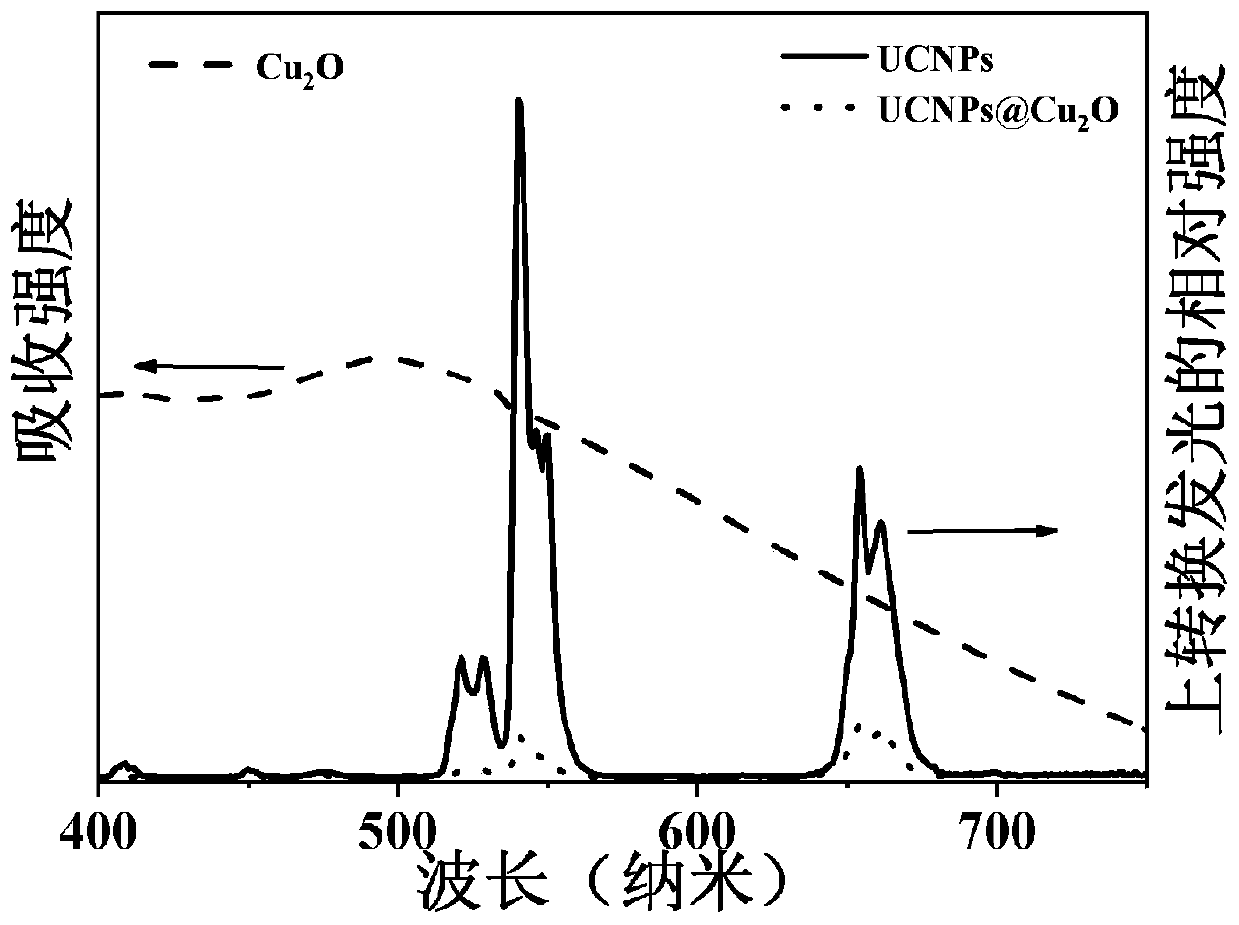
ActiveCN110947007AUnique structureEasy to degradePowder deliveryPhotodynamic therapyFluorescenceBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a rare earth upconversion diagnosis-and-treatment-integrated nanocomposite material. The rare earth upconversion diagnosis-and-treatment-integrated nanocomposite material is acuprous oxide modified rare earth upconversion nanocomposite prepared by the following steps: using oil-soluble upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) as cores; and then, allowing epitaxial growth of cuprous oxide (Cu(2)O) on surfaces of the UCNPs so as to form shells, thereby obtaining the cuprous oxide modified rare earth upconversion nanocomposite grown by interface nucleation. The Cu(2)O can transfer fluorescence resonance energy with upconversion emission of the UCNPs excited by near-infrared light so as to produce sufficient active oxygen, thereby meeting needs of photodynamic therapy; and moreover, the Cu(2)O can synchronously cooperate with the oil-soluble UCNPs so as to realize integrated diagnosis and treatment. The invention further provides a preparation method of the rare earth upconversion diagnosis-and-treatment-integrated nanocomposite material. The preparation method of the rare earth upconversion diagnosis-and-treatment-integrated nanocomposite material comprises the following steps: using the oil-soluble UCNPs as cores; and then, allowing interface nucleation growth of the (Cu(2)O) on the surfaces of the UCNPs. The rare earth upconversion diagnosis-and-treatment-integrated nanocomposite material prepared by the preparation method is uniform in size, good in stability, and excellent in biocompatibility; and thus, the nanocomposite material can be used in imaging diagnosis guided photodynamic therapy so as to meet needs of clinical diagnosis and treatment integration.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
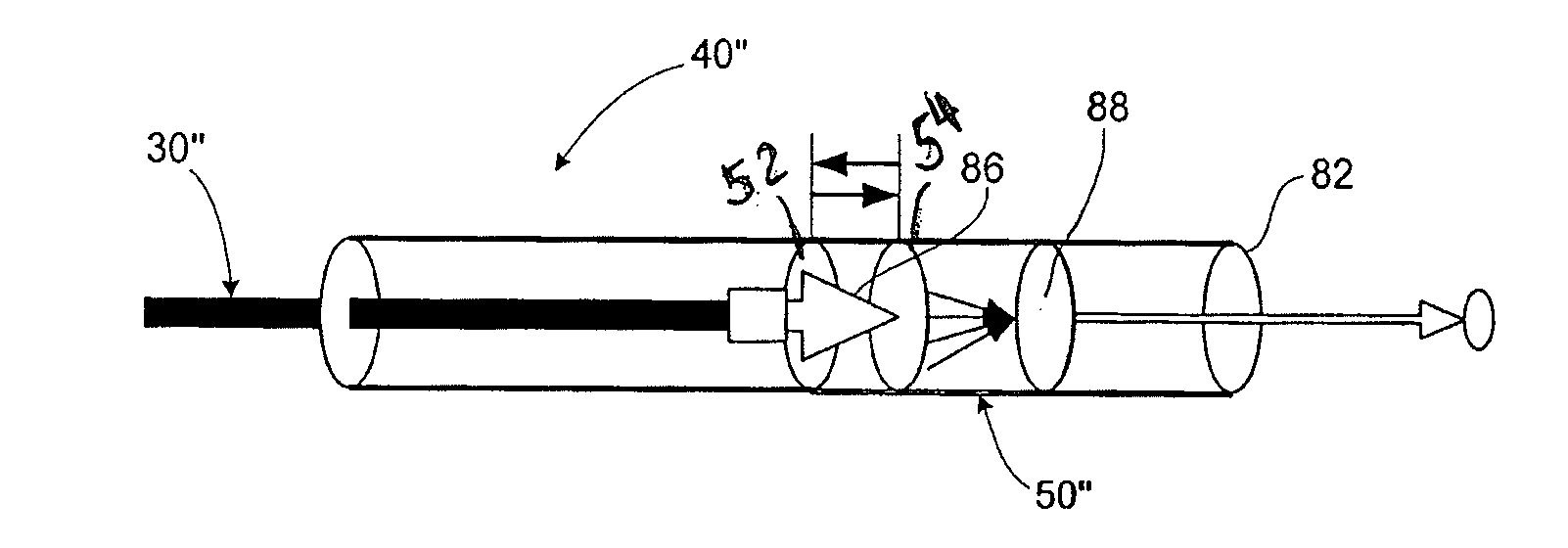
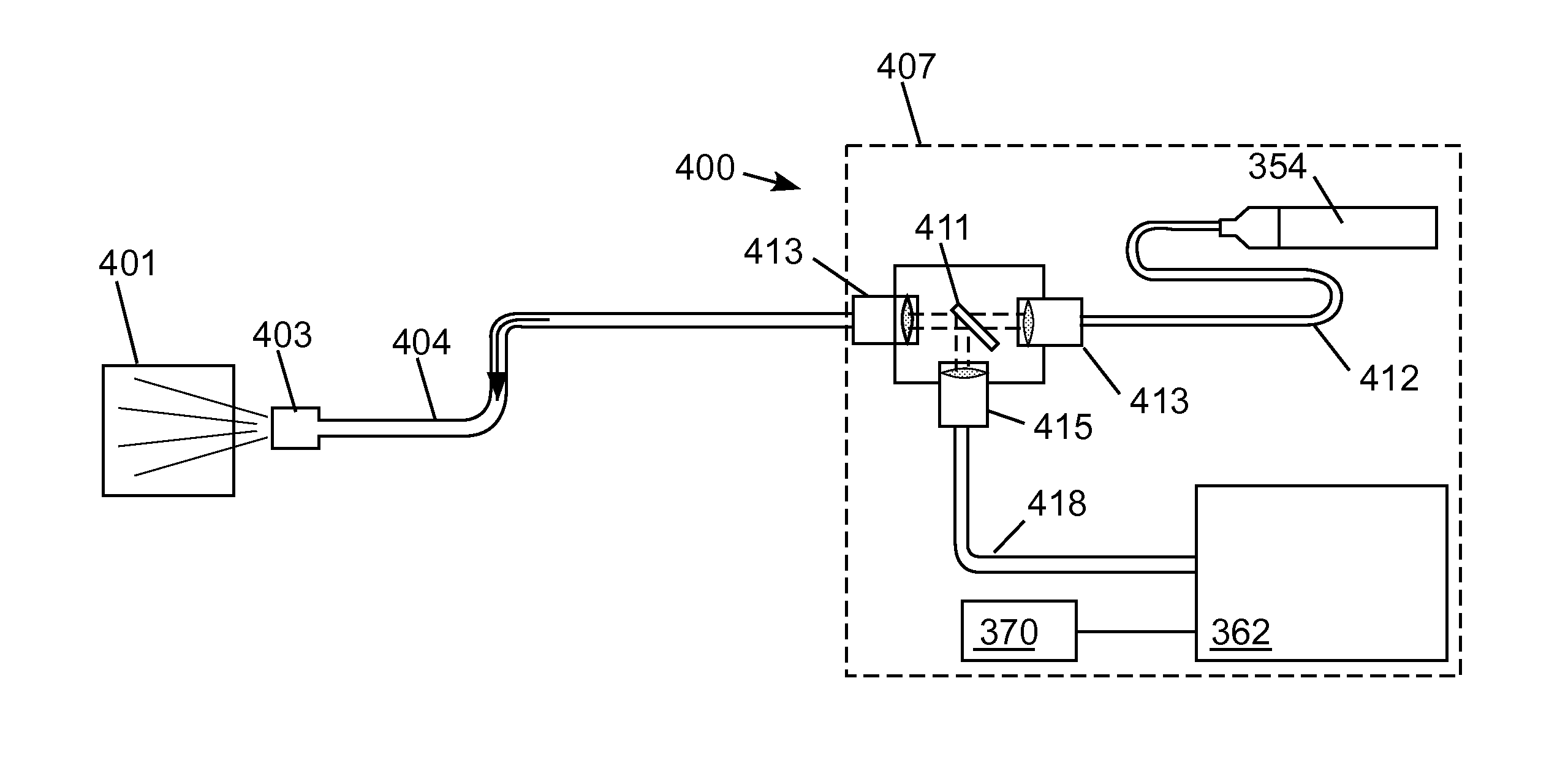
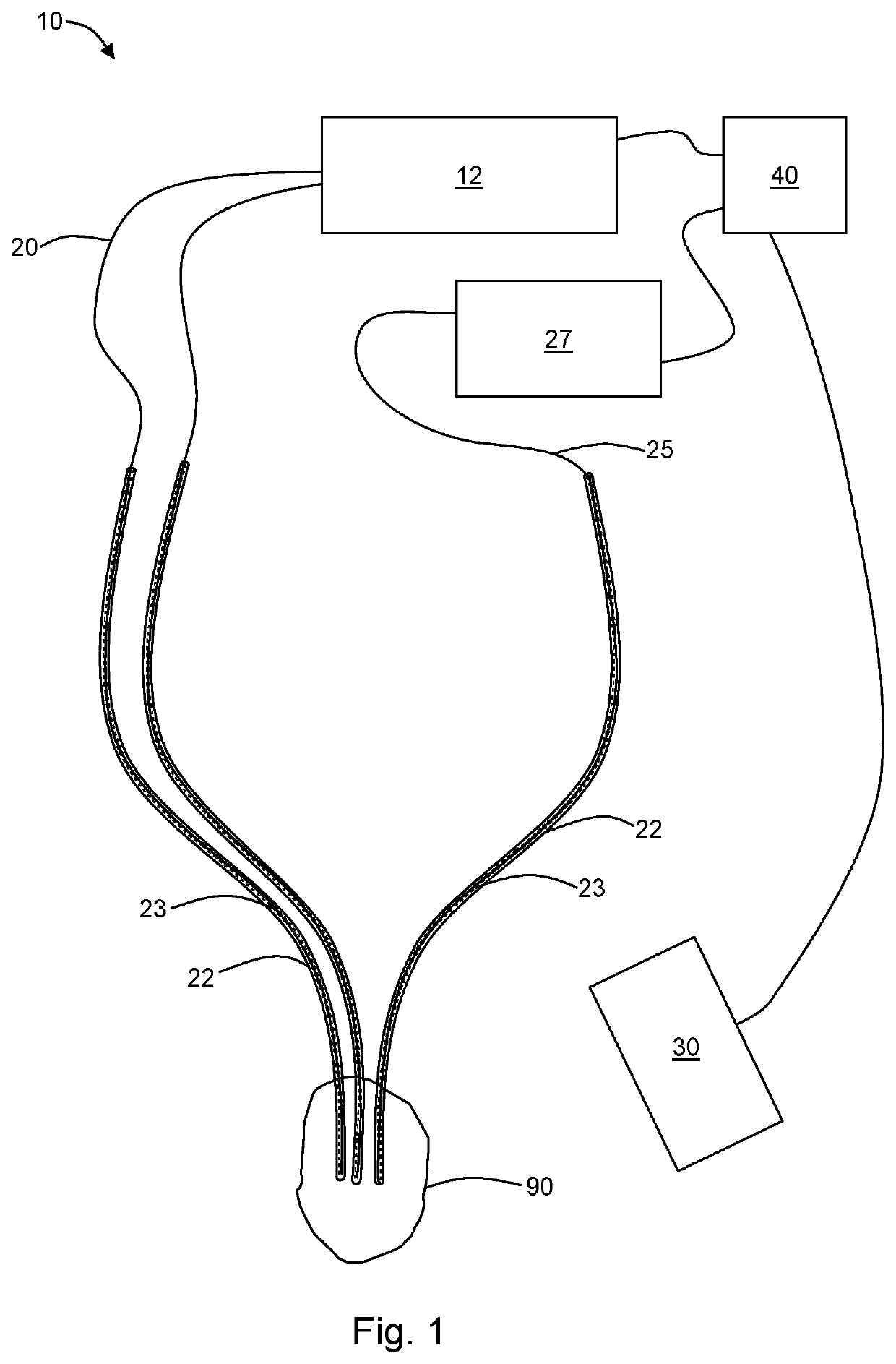
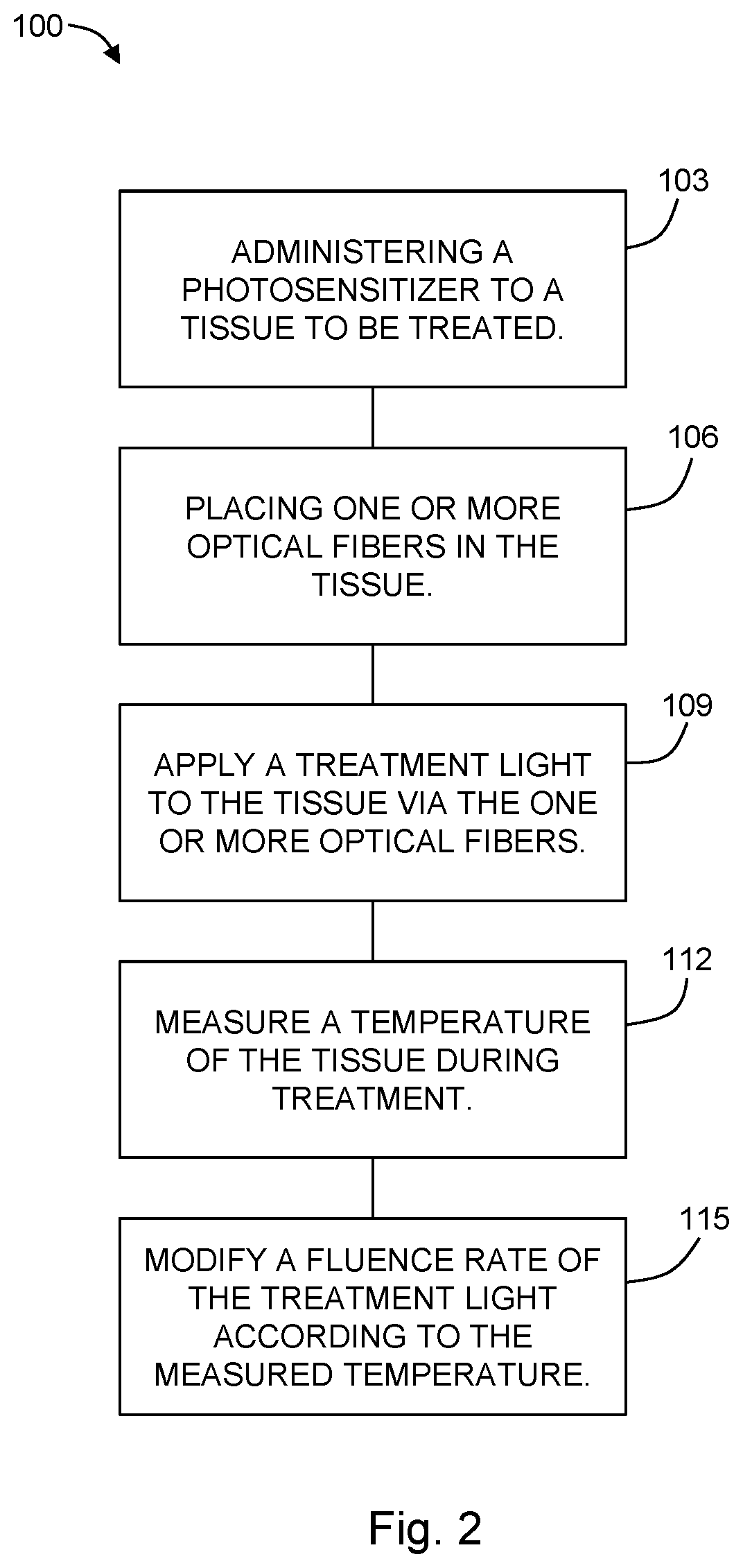
Method and system for concurrent photothermal ablation and interstitial photodynamic therapy
InactiveUS20200046997A1Thermometers using electric/magnetic elementsSurgical instrument detailsPhotosensPhotothermal ablation
The present disclosure provides a method and a system for treating a tissue using photodynamic therapy (PDT). A photosensitizer is administered to the tissue and one or more optical fibers are placed in the tissue. A treatment light is applied to the tissue by way of the one or more optical fibers. A temperature of the tissue is measured during application of the treatment light, and a fluence rate of the treatment light is modified based on the temperature of the tissue. For example, the fluence rate may be modified to be lower if the temperature of the tissue is higher than a predetermined threshold.)
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
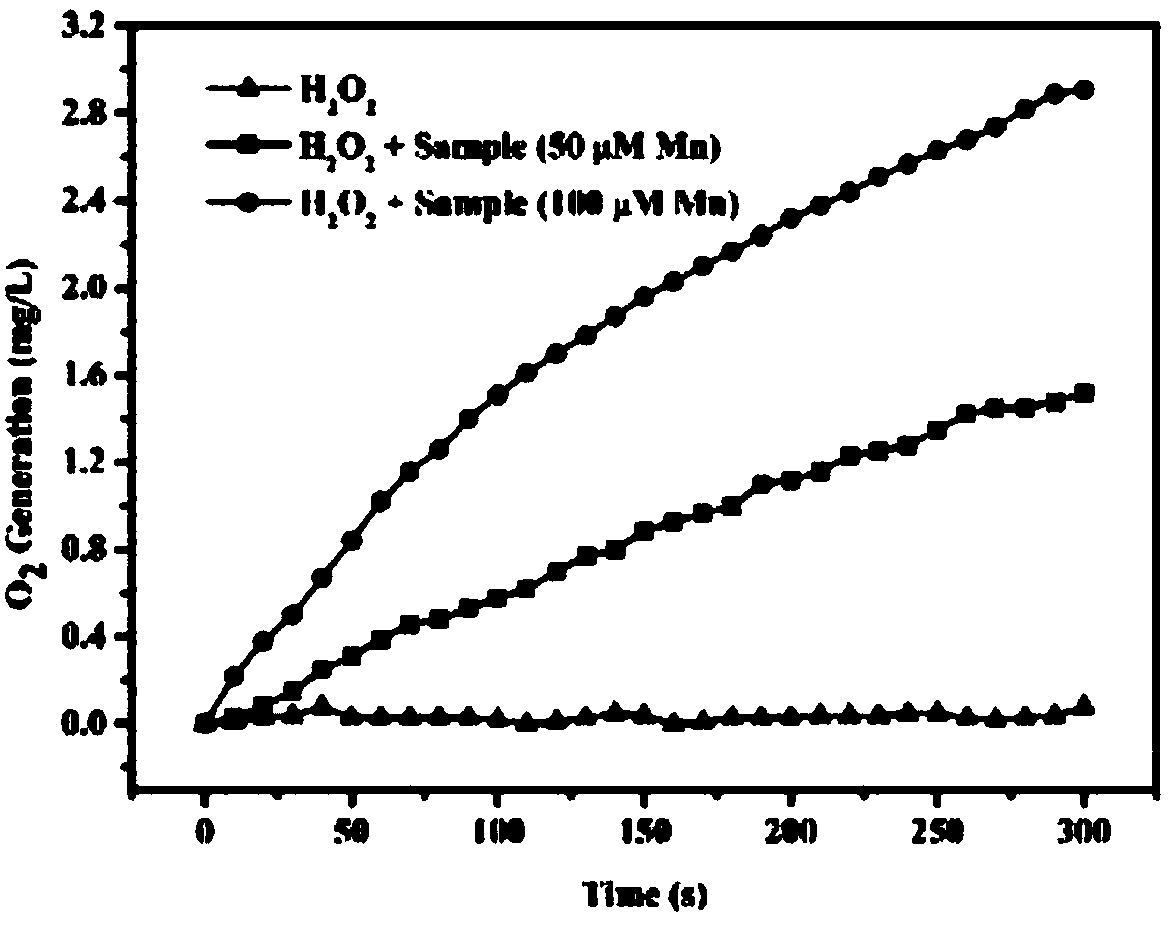
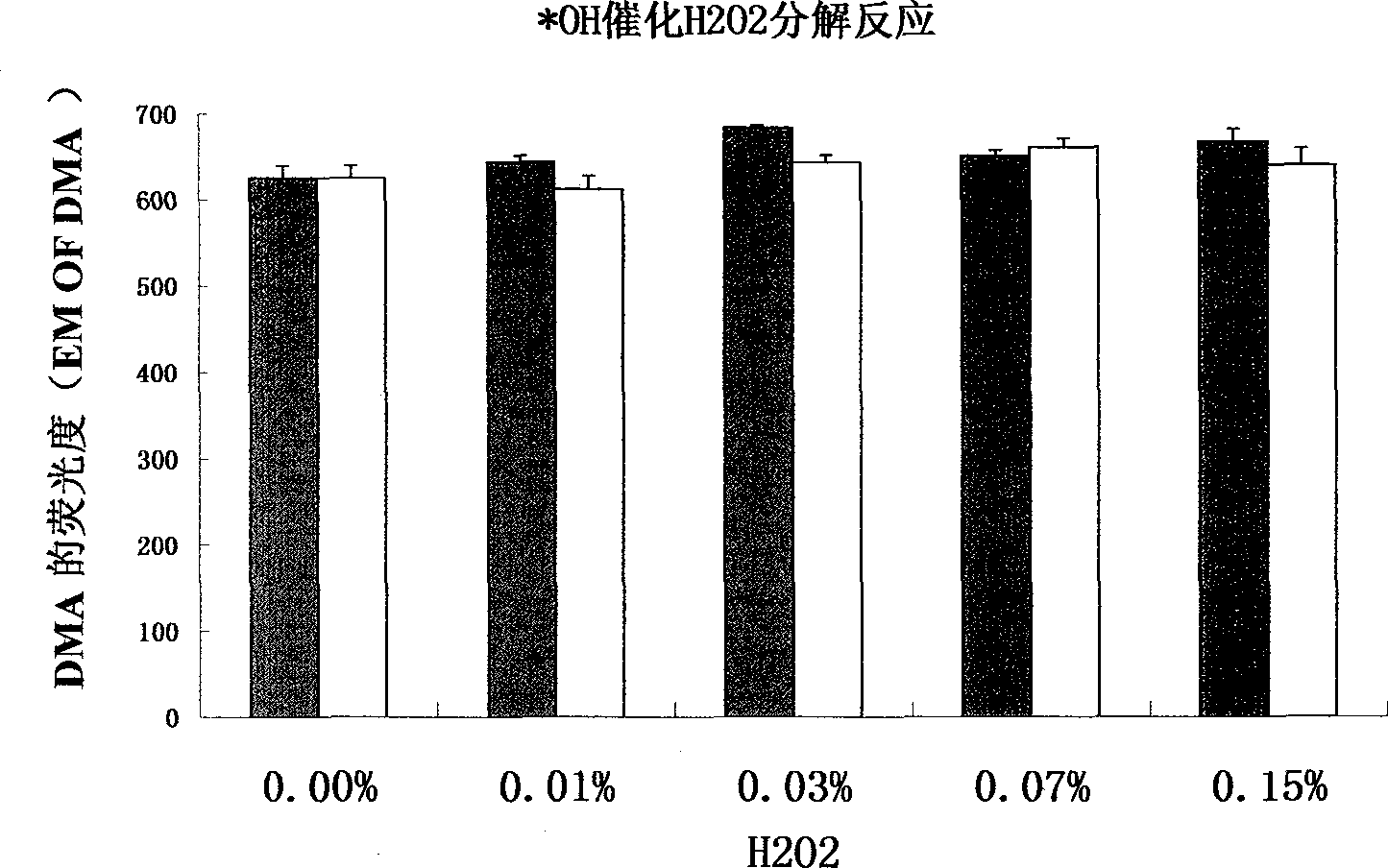
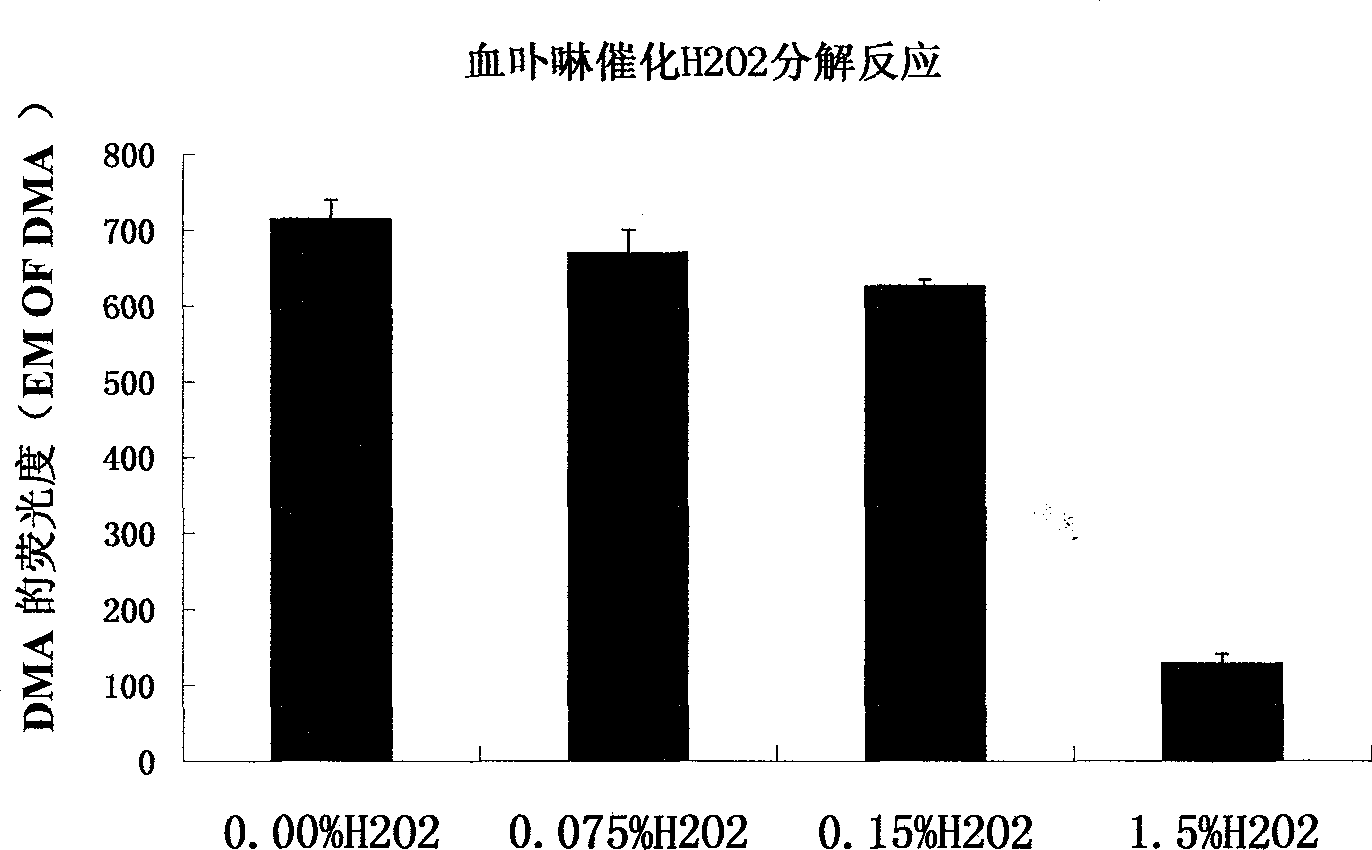
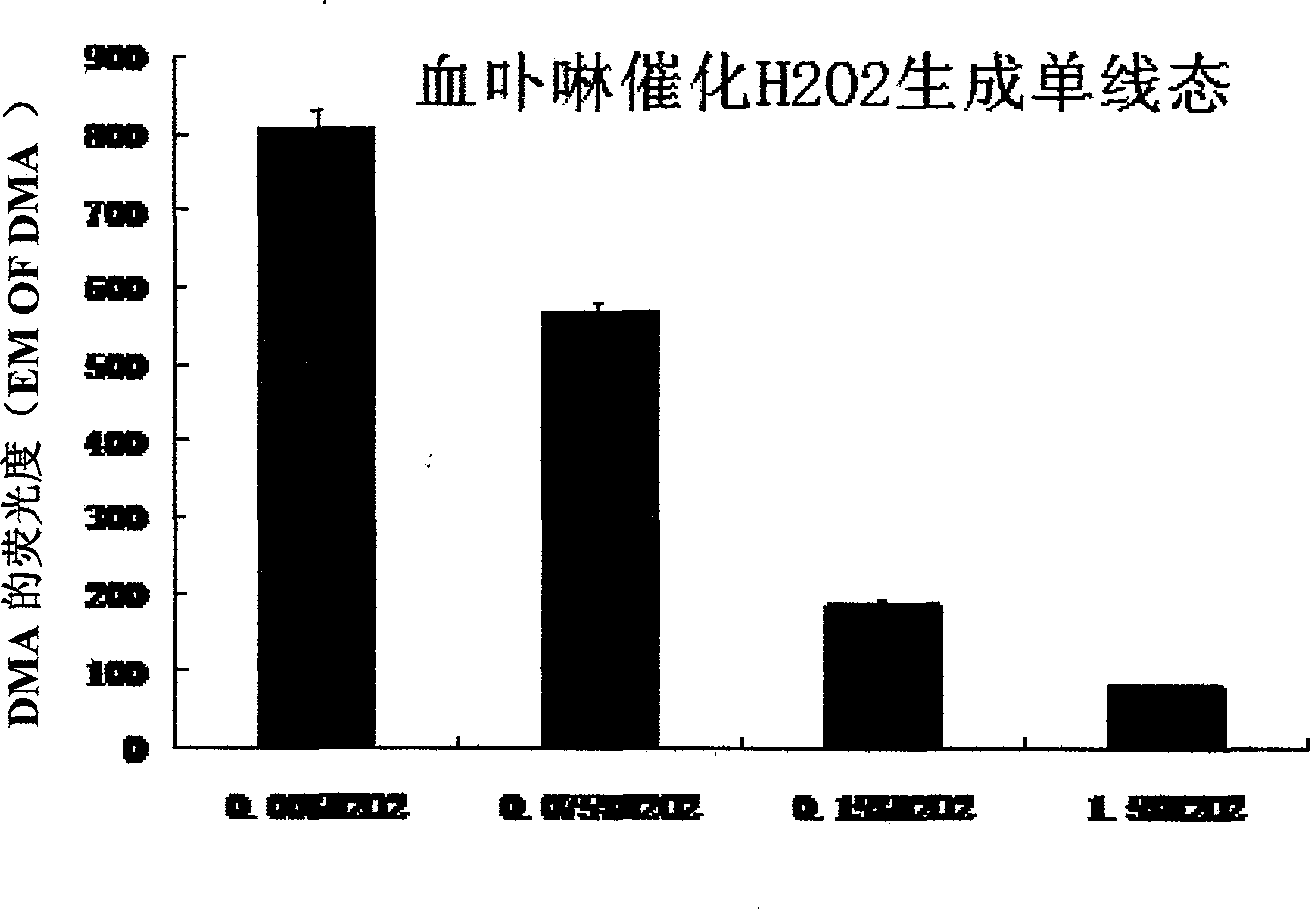
Serial drug capable of catalyzing decomposition of hydrogen dioxide by phytochromes
In the invention, phytochromes are activated in focuses such as tumors, vascular patches and skin diseases, in a fixed-point and fixed-quantity way by a specific means through the utilization of the specific affinity action of the phytochromes on the focuses, the decomposition reaction of H2O2 is catalyzed by the phytochromes to generate <1>O2, and the apoptosis or the necrosis of pathological cells is caused, thereby achieving the purpose of treating the diseases. A corresponding serial novel drug is screened, developed and used for CDT (Chemodynamic Therapy) or RCDT (Radiochemodynamic Therapy). The invention relates to the serial novel drug which is used for CDT and RCDT. The serial novel drug can catalyze the chemical reaction of decomposing the H2O2 to generate the <1>O2, does not have obvious side effect on the normal tissues and organs of a human body, and meanwhile, has the capability of affiliating the focuses. The phytochromes are used as a catalyst, and the acting mechanism, the usage, the therapeutic effect and the like of the phytochromes are completely different from those of traditional photo-dynamic therapy. Oxygen and visual light are not needed, and a completely independent novel drug series can be formed.
Owner:WUXI ZHAOZHEN RADIATION TECH
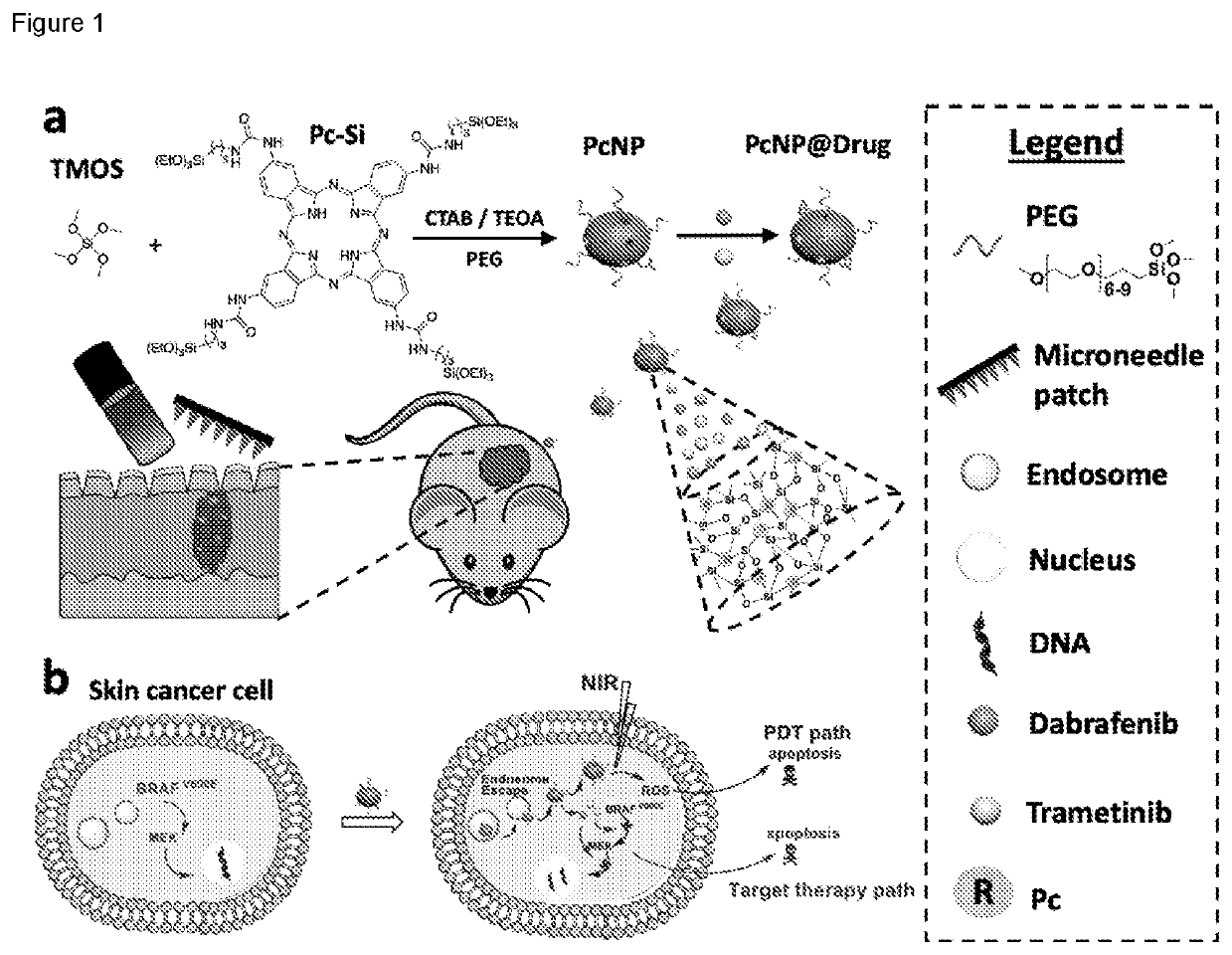
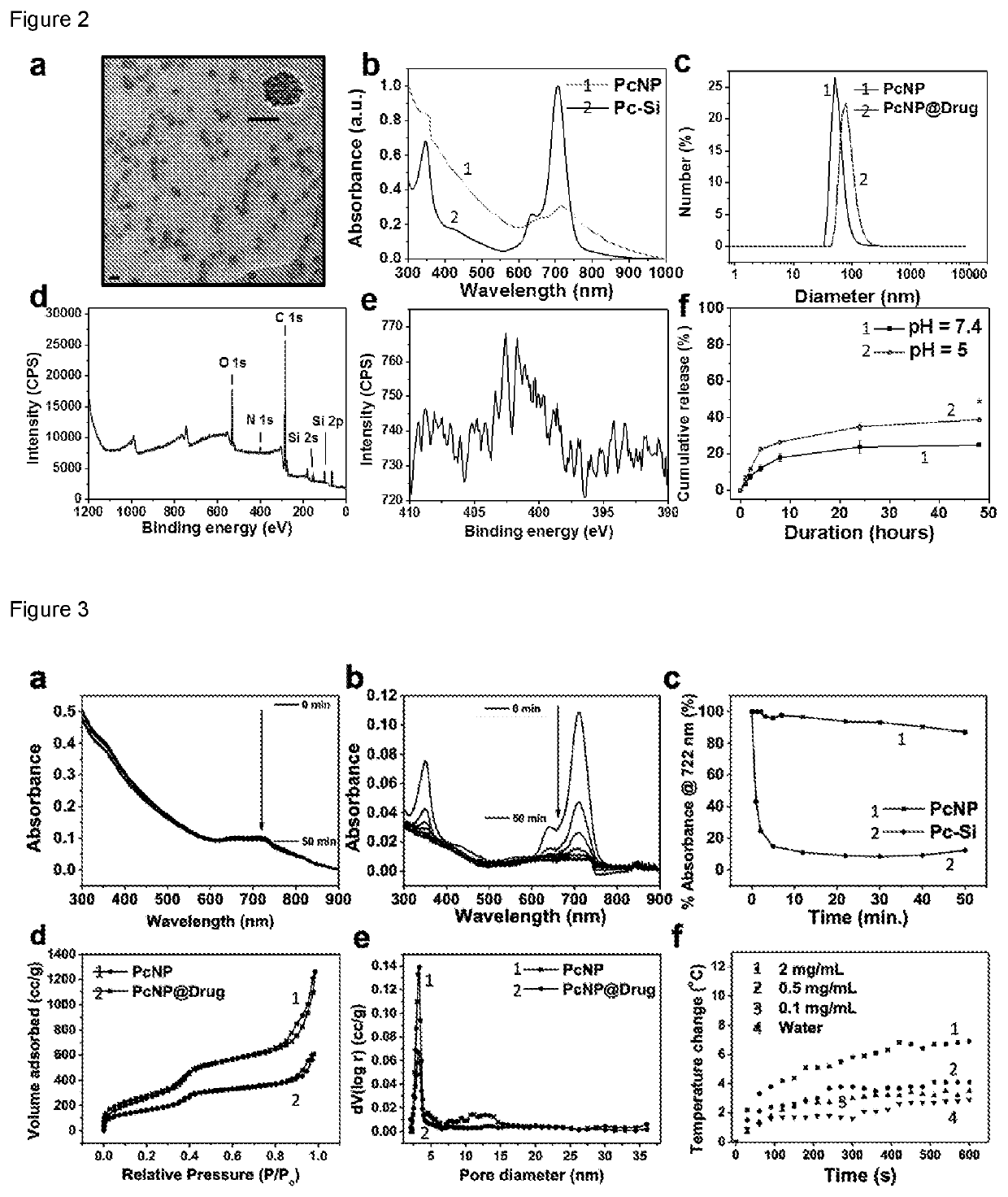
Photodynamically active organosilica nanoparticles and medical uses thereof
The present application provides an organosilica nanoparticle comprising: (a) a photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy covalently incorporated therein; and (b) optionally, at least one agent encapsulated therein, as well as a pharmaceutical composition comprising said organosilica nanoparticle. Also provided herein are said organosilica nanoparticle or pharmaceutical composition for use as a medicament or in the treatment of a disease, disorder, or condition. More specifically, provided is a method for treating a disease, disorder, or condition in a subject using said aid organosilica nanoparticle or pharmaceutical composition.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Application method of aggregation-induced emission-based photosensitizer in cell imaging and photodynamic therapy
ActiveCN112920117APrevent leakageSolving Aggregate Fluorescence QuenchingOrganic chemistryPhotodynamic therapyNanostructureFluorochrome Dye
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical materials, and discloses an application of a photosensitizer based on aggregation-induced emission in cell imaging and photodynamic therapy. The applicaiton is characterized in that an aggregation-induced emission compound is covalently or non-covalently introduced into a polydiacetylene supramolecular system, and is spontaneously assembled and polymerized under the hydrophilic and hydrophobic action among molecules to obtain nanoparticles. According to the invention, AIE micromolecules are covalently / non-covalently introduced into a polydiacetylene supramolecular system by utilizing the excellent performance of diacetylene in the aspect of self-assembly, and the aggregation-induced emission supramolecular polymer is spontaneously assembled under the hydrophilic and hydrophobic action among molecules. The problem of aggregation fluorescence quenching is solved, and good water solubility is achieved. In addition, polymerization of diacetylene enables the aggregate structure to be rigidified, and leakage of the fluorescent dye can be prevented, so that a novel nanostructure with a clear structure is developed. The invention discusses the application of the supramolecular luminescent nano material in cell imaging and photodynamic therapy for the first time, and realizes integration of diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
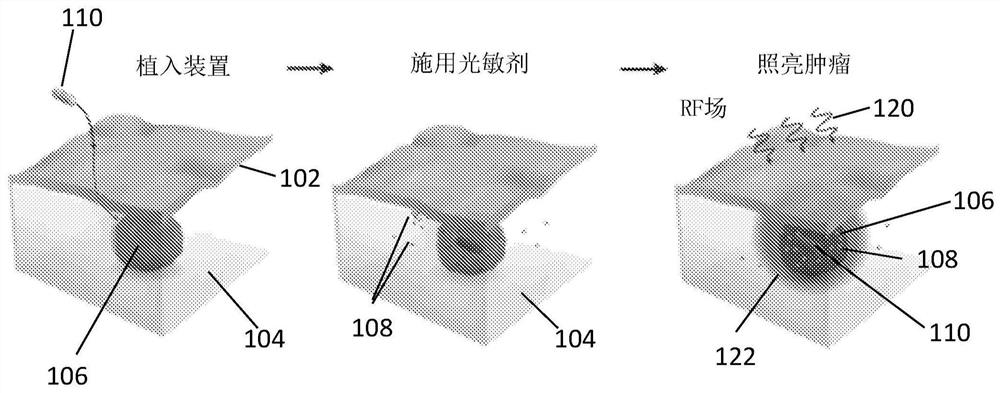
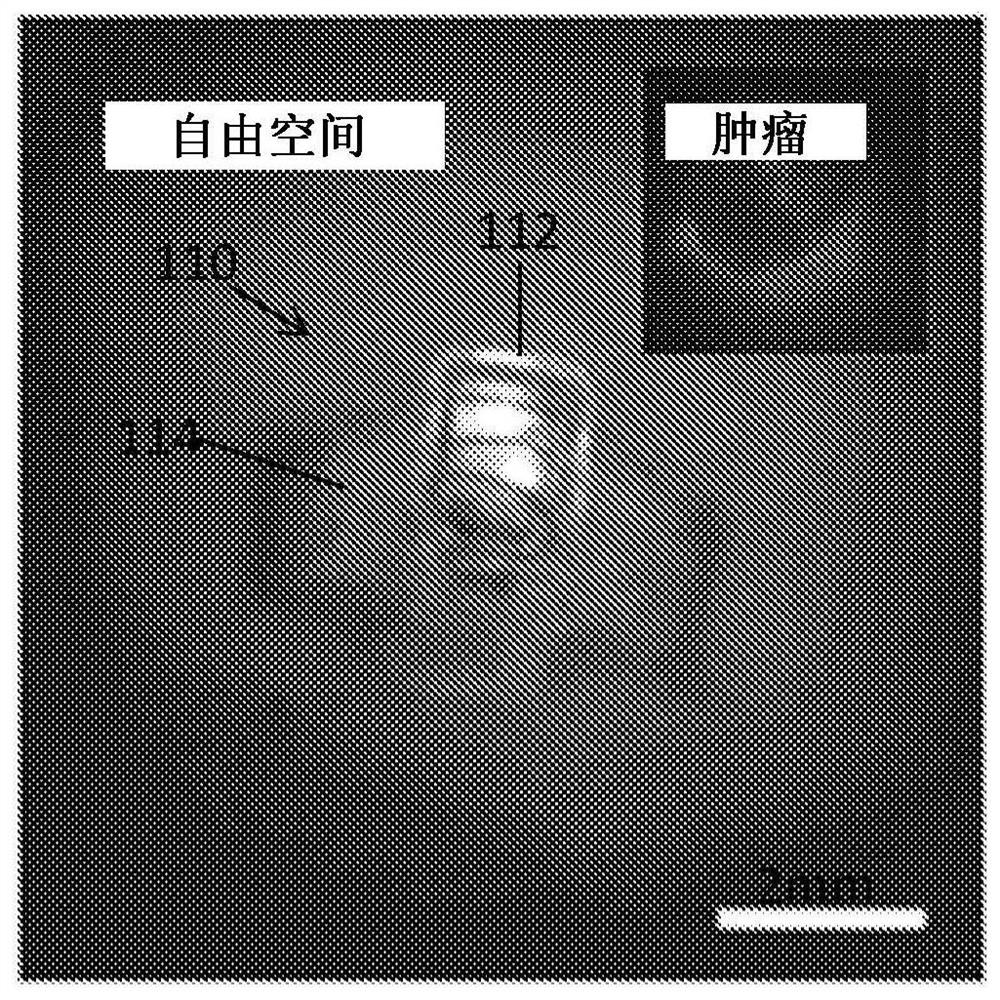
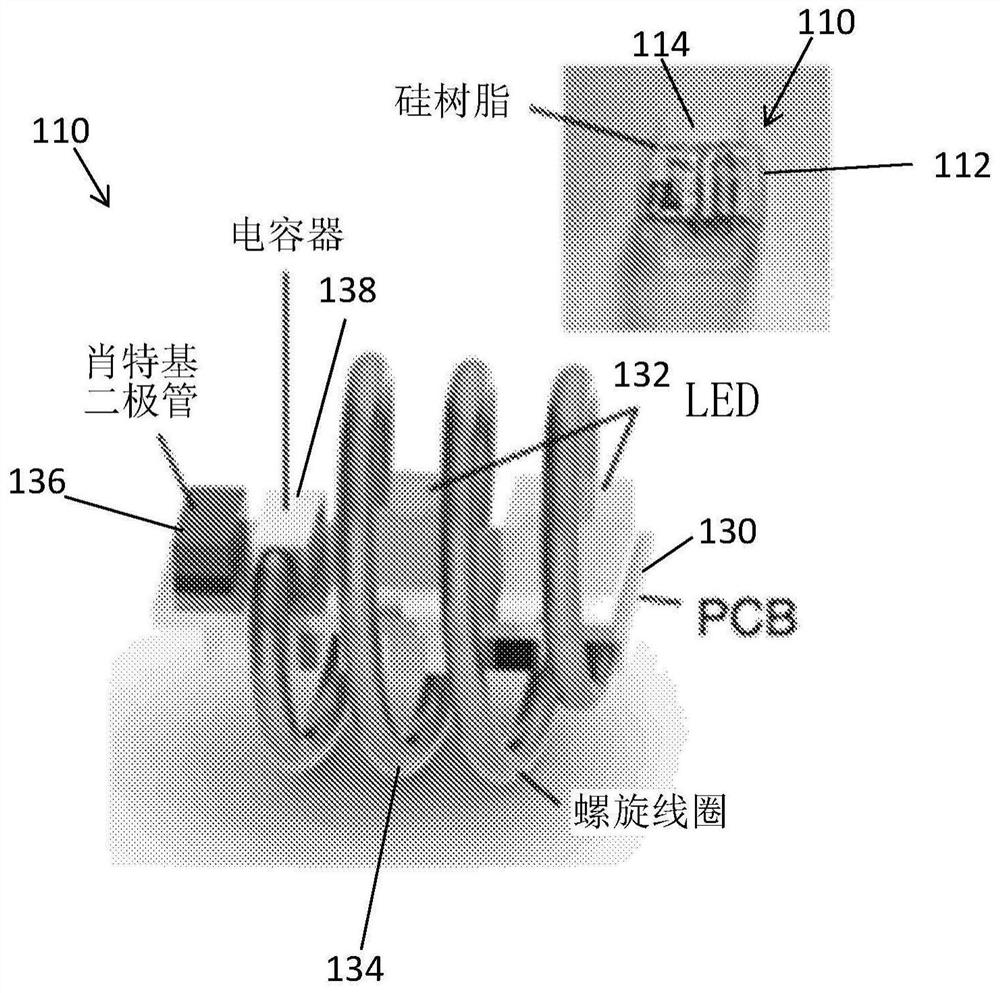
Photodynamic therapy devices, systems and methods
Wirelessly powered photodynamic therapy devices are disclosed and systems and methods using such devices are also disclosed. In an embodiment, a photodynamic therapy system comprises: an implantable illumination device comprising a light source configured to emit light having a spectrum which overlaps with an absorption peak of an absorption target and a receiver antenna coupled to the light source and configured to extract power from a radiofrequency power signal incident on the implantable illumination device; and a transmitter comprising an antenna, a powering module configured to generatea drive signal which causes the antenna to generate the radiofrequency power signal, and a dosimetry module coupled to the antenna and configured to detect a radiofrequency signal backscattered from the implantable illumination device and determine an indication of the power extracted by the implantable illumination device from the radiofrequency signal backscattered from the implantable illumination device.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
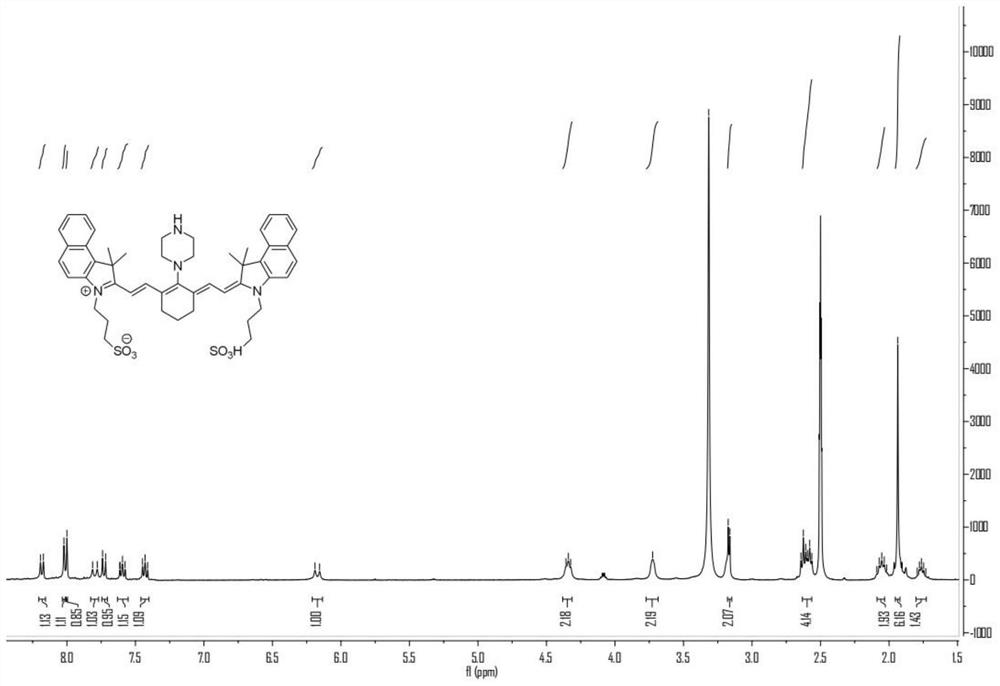
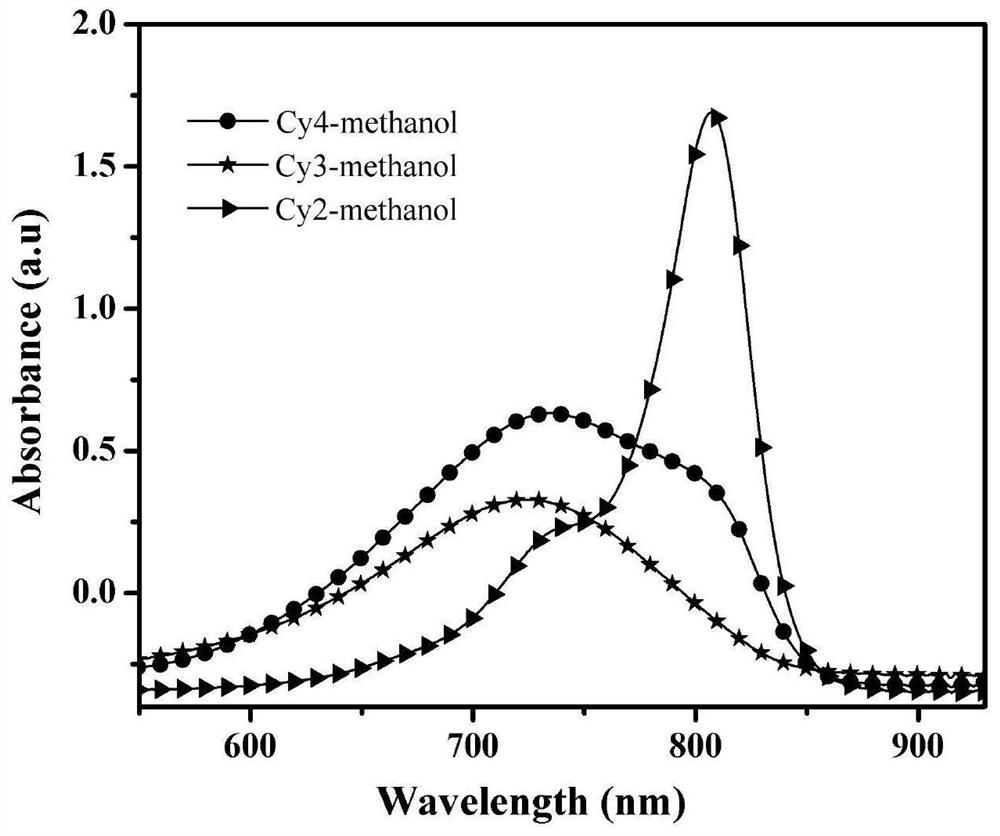
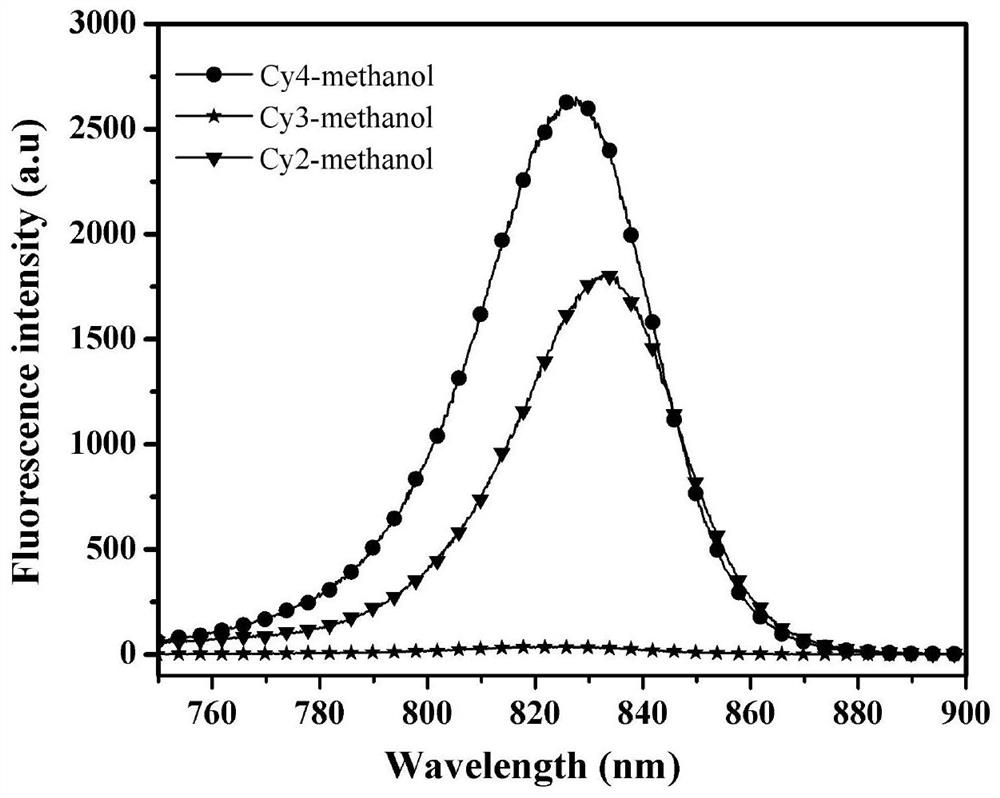
Heptamethine indocyanine dye as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113462187AStrong near-infrared absorptionGood light stabilityMethine/polymethine dyesPhotodynamic therapyPhoto stabilityFluorescence
The invention provides a heptamethine indocyanine dye as well as a preparation method and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of fine chemical engineering. The heptamethine indocyanine dye provided by the invention has a structure as shown in a formula 1, has strong near-infrared absorption in a near-infrared region, and has good light stability and photo-thermal conversion efficiency, and the photo-thermal conversion rate and photo-thermal stability of the heptamethine indocyanine dye are obviously improved compared with indocyanine green. Meanwhile, the heptamethine indocyanine dye provided by the invention has a good fluorescence property. The heptamethine indocyanine dye disclosed by the invention belongs to small organic molecules, has low cytotoxicity and multiple chemical sites, and is easy to further design and synthesize functional molecules; and has good biocompatibility, is easy to remove in a living body, has a clear biodegradation pathway, and can be applied to the fields of biomarkers, optical imaging, photo-thermal imaging, photo-acoustic imaging, photodynamic therapy and photo-thermal therapy.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
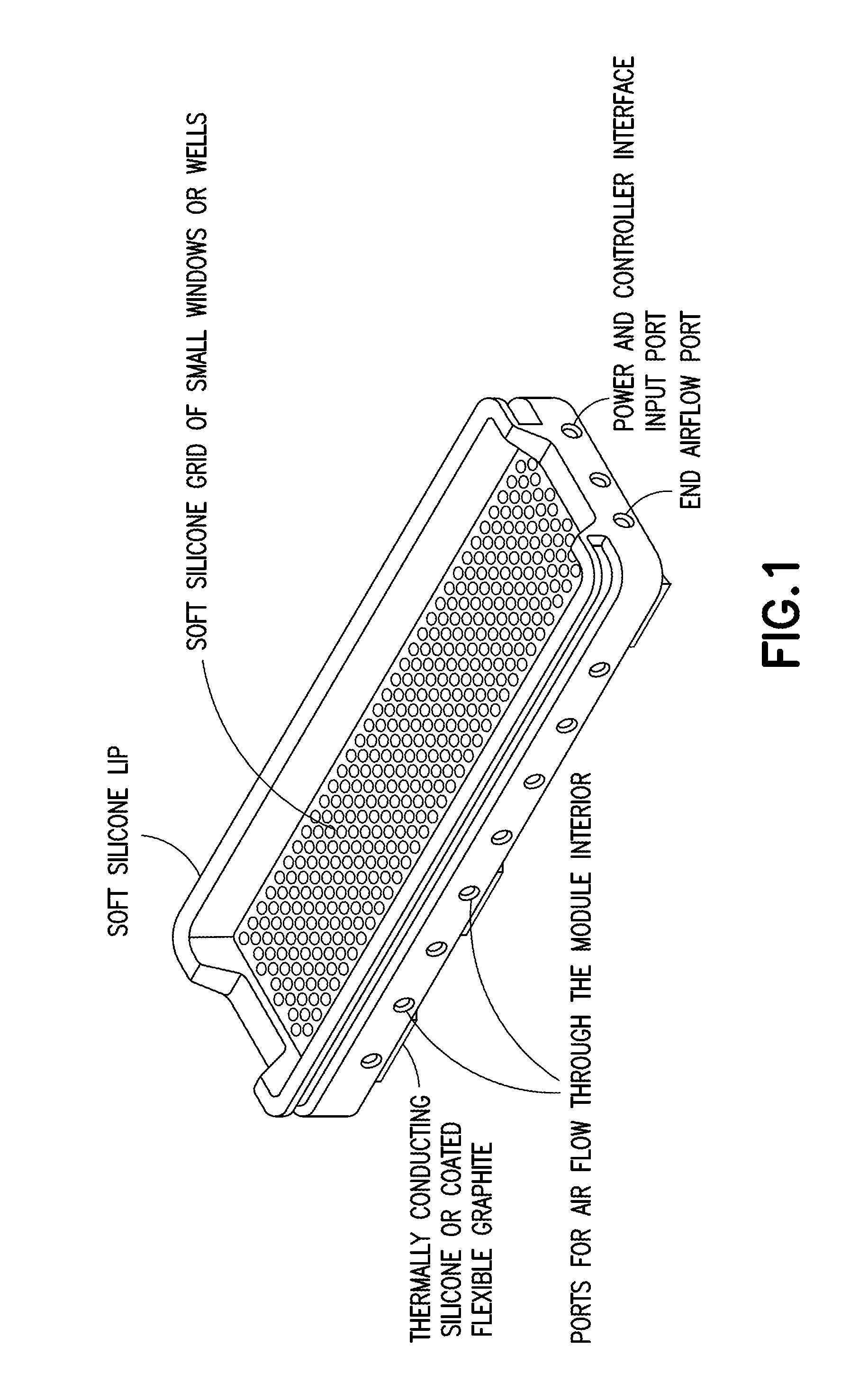
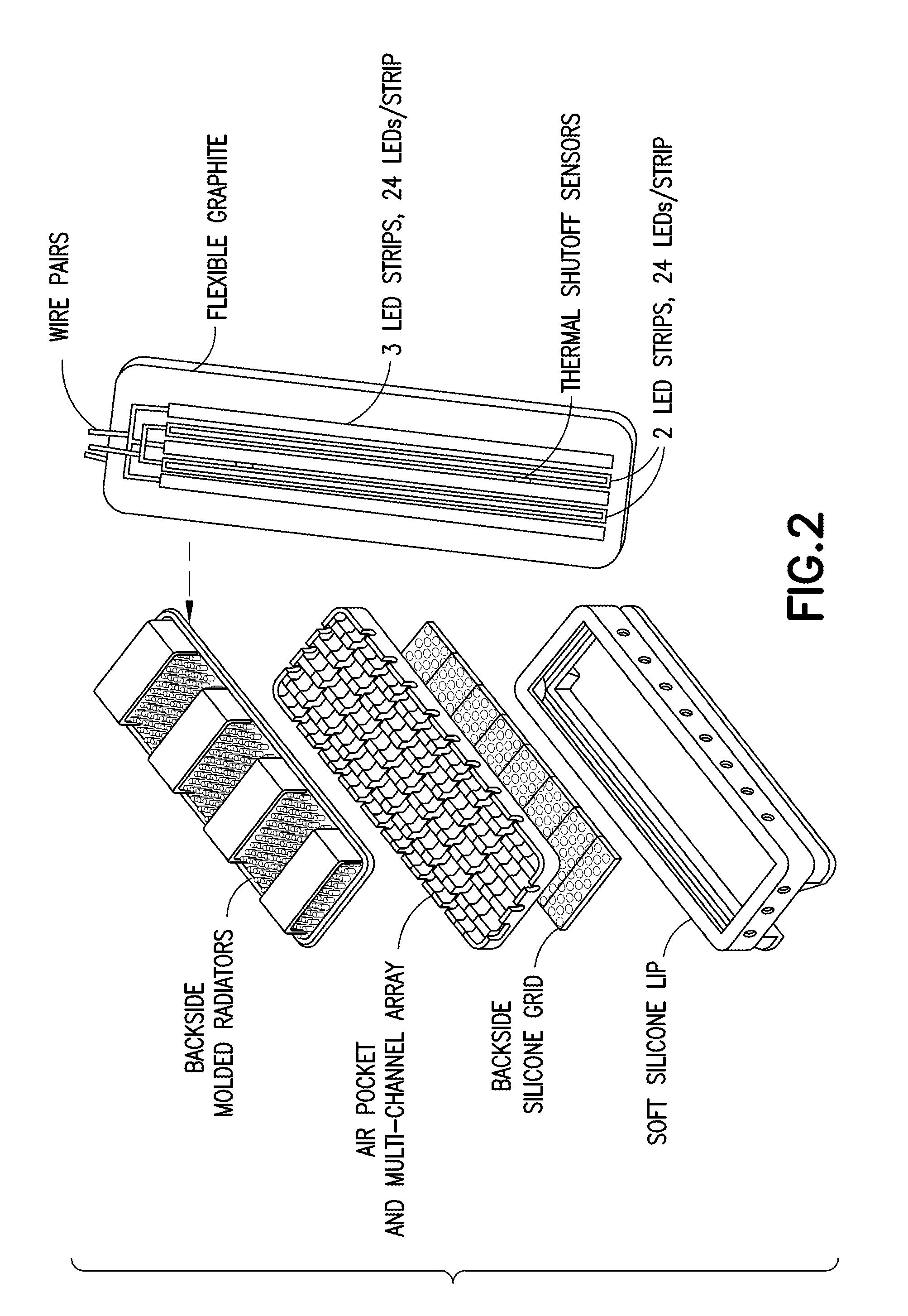
Illuminator for photodynamic therapy
InactiveUS20070249716A1Improved irradiance uniformityUniform strengthBiocideOrganic active ingredientsFluorescenceEngineering
An apparatus and method for photodynamic therapy or photodynamic diagnosis using an illuminator comprising a plurality of light sources generally conforming to a contoured surface and irradiating the contoured surface with substantially uniform intensity visible light. The light sources may comprise generally U-shaped fluorescent tubes that are driven by electronic ballasts. Adjustment of the ballast voltage controls the output power of the tubes. The tubes are supported by a sheet-metal or plastic housing and are covered by a polycarbonate shield which directs cooling airflow within the unit and prevents glass-patient contact in the event of tube breakage. An aluminum reflector located behind the tubes increases both the output irradiance and the uniformity of the output distribution. The spacing of the U-shaped tubes is varied to increase the output at the edges of the illuminator to make the output more uniform. Also, different portions of the tubes are cooled at different amounts, to improve uniformity. A light sensor monitors output from the U-shaped tubes to provide a signal for adjusting the output from the tubes.
Owner:DUSA PHARMA INC
All-solid-state Raman frequency multiplication dark red laser and laser generation method
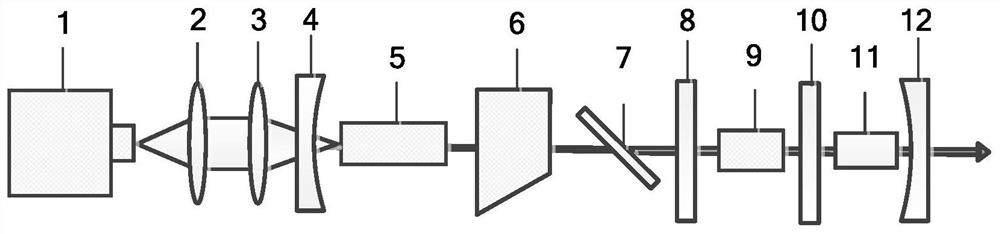
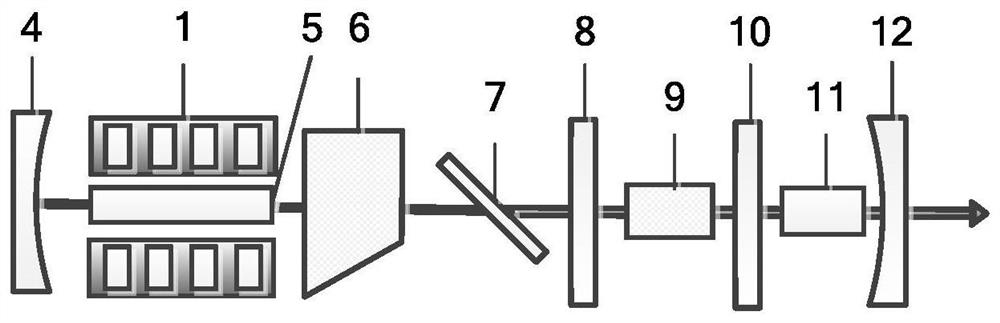
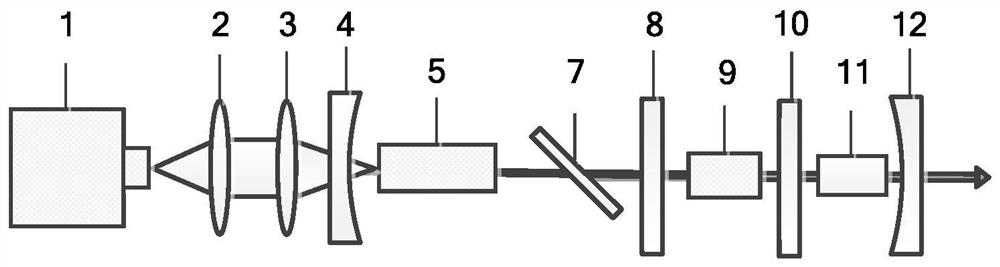
PendingCN111725698AHigh beam qualityEfficient Nonlinear Frequency Transformation MethodActive medium materialNonlinear optical crystalFluorescence
The invention discloses an all-solid-state Raman frequency multiplication dark red laser and a laser generation method. The laser includes a pumping unit, an input endoscope (4), a laser crystal (5),a polarizing film (7), a first insertion lens (8), a Raman crystal (9), a second insertion lens (10), a nonlinear optical crystal (11) and an output endoscope (12), the input endoscope (4) and the output endoscope (12) form a fundamental frequency light resonant cavity, and the first insertion lens (8) and the output endoscope (12) form a Raman light resonant cavity; the dark red laser has the advantages of being high in output power, good in light beam quality, simple in structure, stable in performance, low in cost and the like, and has important application in the fields of laser display, biophotonics, fluorescence imaging, photodynamic therapy and the like.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Photodynamically active organosilica nanoparticles and medical uses thereof
The present application provides an organosilica nanoparticle comprising: (a) a photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy covalently incorporated therein; and (b) optionally, at least one agent encapsulated therein, as well as a pharmaceutical composition comprising said organosilica nanoparticle. Also provided herein are said organosilica nanoparticle or pharmaceutical composition for use as a medicament or in the treatment of a disease, disorder, or condition. More specifically, provided is a method for treating a disease, disorder, or condition in a subject using said aid organosilica nanoparticle or pharmaceutical composition.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com