Method for ultra-fast pretreatment of lignocellulose in biomass
A technology for pretreatment of biomass and lignocellulose, applied in fermentation and other directions, can solve the problems of ineffective lignin removal, poor pretreatment effect, and increased processing difficulty, and achieves low price, easy recycling, and step-by-step easy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] A method for ultra-fast pretreatment of lignocellulose in biomass, comprising steps:
[0031] 1. Wash a large piece of rice straw with a length of 2 cm twice with deionized water, and dry it to a constant weight at 60°C.
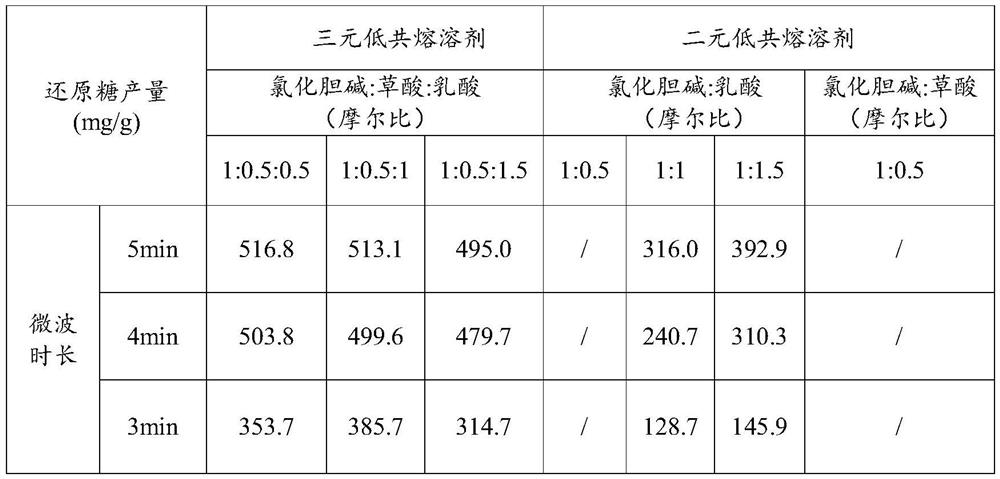
[0032] 2. Mix choline chloride, oxalic acid, and lactic acid in a molar ratio of 1:0.5:0.5, stir and mix at 60°C for 2 hours to obtain a transparent and uniform liquid, cool it to room temperature and store it for later use, and name the liquid three Elemental deep eutectic solvent.
[0033] 3. Take the rice straw obtained in step 1 and add it to the microwave digestion tank containing the ternary deep eutectic solvent obtained in step 2 according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1g:30mL, then place it in a microwave oven, treat it with microwaves at 680W for 4min, and take it out after filtration The solid filter residue is named as the filter residue to be treated.
[0034] 4. Wash the resulting filter residue to be treated with deionized water unt...
Embodiment 2
[0040] A method for ultra-fast pretreatment of lignocellulose in biomass, comprising steps:
[0041] 1. Wash a large piece of rice straw with a length of 2 cm twice with deionized water, and dry it to a constant weight at 60°C.
[0042] 2. Mix choline chloride, oxalic acid, and lactic acid in a molar ratio of 1:0.5:1, stir and mix at 60°C for 2 hours to obtain a transparent and uniform liquid, cool it to room temperature and store it for later use, and name the liquid three Elemental deep eutectic solvent.
[0043]3. Take the rice straw obtained in step 1 and add it to the microwave digestion tank containing the ternary deep eutectic solvent obtained in step 2 according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1g:30mL, then place it in a microwave oven, treat it with microwaves at 680W for 4min, filter and take The solid filter residue is named as the filter residue to be treated.
[0044] 4. Wash the resulting filter residue to be treated with deionized water until the pH is neutral...
Embodiment 3
[0047] A method for ultra-fast pretreatment of lignocellulose in biomass, comprising steps:
[0048] 1. Wash a large piece of rice straw with a length of 2 cm twice with deionized water, and dry it to a constant weight at 60°C.
[0049] 2. Mix choline chloride, oxalic acid, and lactic acid in a molar ratio of 1:0.5:1.5, stir and mix at 60°C for 2 hours to obtain a transparent and uniform liquid, cool it to room temperature and store it for later use, and name the liquid three Elemental deep eutectic solvent.
[0050] 3. Take the rice straw obtained in step 1 and add it to the microwave digestion tank containing the deep eutectic solvent obtained in step 2 according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1g:30mL, and then place it in a microwave oven, microwave at 680W for 4 minutes, and take the solid filter residue after filtration , and name the solid filter residue as the filter residue to be treated.
[0051] 4. Wash the resulting filter residue to be treated with deionized wat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com