A hole-transporting host material and its preparation method and its application in the preparation of organic electroluminescent devices
A technology for electroluminescent devices and host materials, which is applied in the manufacture of electro-solid devices, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state devices, etc. Efficiency attenuation and other problems, to achieve the effect of good hole transport capacity, reduce instability factors, and improve stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
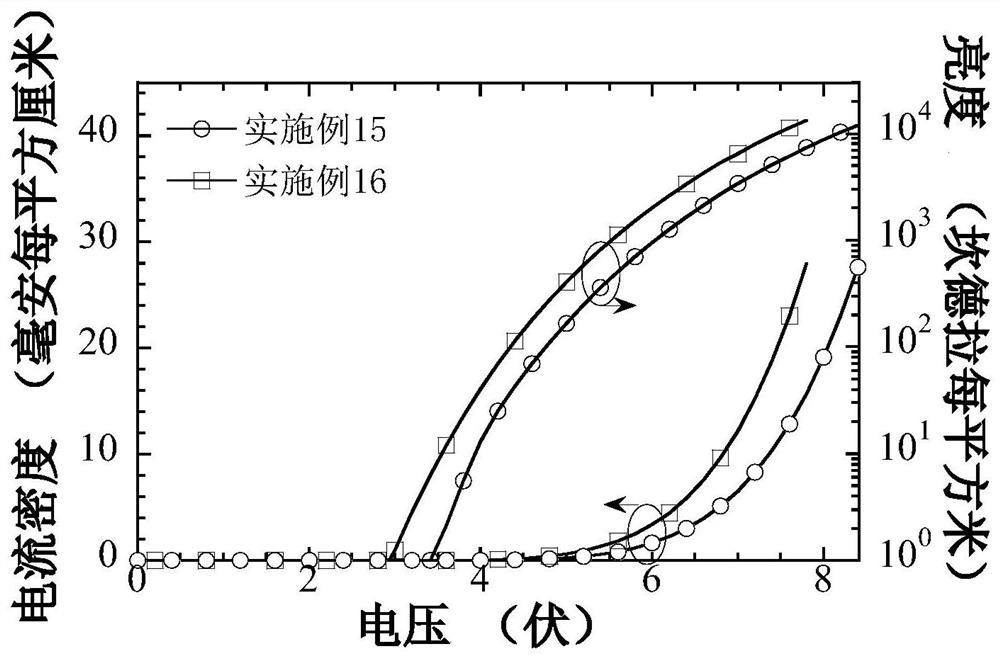
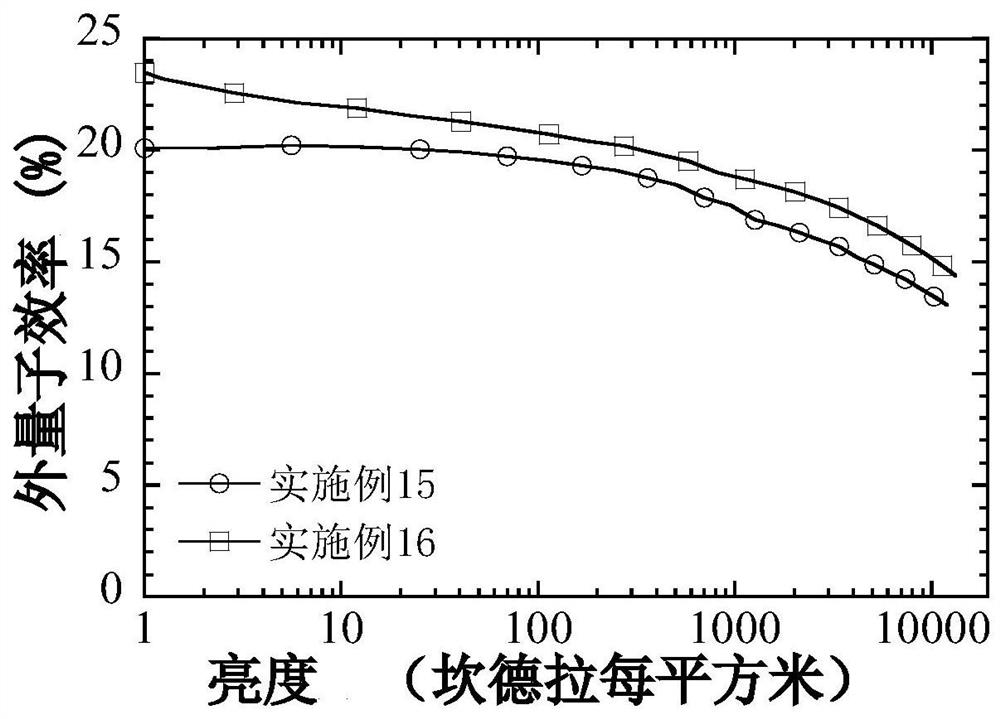
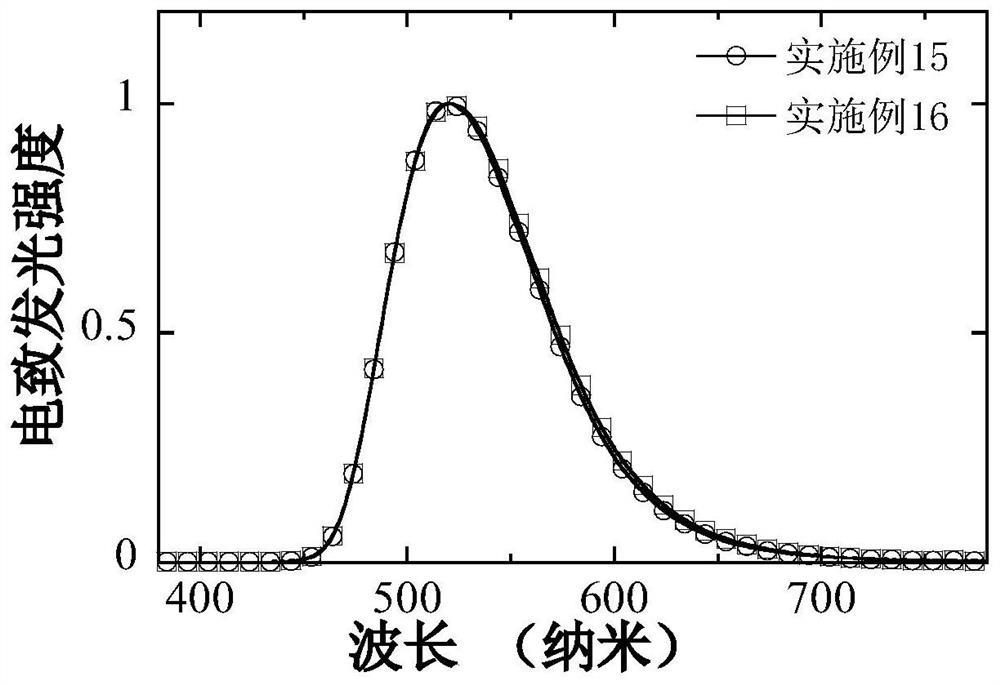
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] A hole-transporting host material H 1 The preparation includes the following preparation steps:
[0050] Intermediate M 4 The reaction formula is as follows:
[0051]
[0052] The specific reaction steps are as follows:
[0053] Intermediate M 1 Synthesis: in a 250mL there-necked flask of nitrogen atmosphere, 10g (59.8mmol) carbazole, 16.93g (71.77mmol) o-dibromobenzene, 3g (0.016mmol) cuprous oxide, 41.32g (299mmol) potassium carbonate, 2.16 g (11.96 mmol) 1,10-phenanthroline was mixed well and dissolved in 100 ml of dimethylformamide solution. The system was heated to 155°C and the reaction was stirred for 24 hours. After the reaction was completed, after the system was cooled to room temperature, it was diluted with about 250 ml of dichloromethane solution, and then the salts in the system were removed by suction filtration under reduced pressure. The organic solvent obtained by suction filtration was evaporated under reduced pressure to remove excess solven...
Embodiment 2
[0062] A hole-transporting host material H 2 The preparation includes the following preparation steps:
[0063] Hole-transporting host material H 2 The synthetic reaction formula is as follows:
[0064]
[0065] The specific reaction steps are as follows:
[0066] with the hole-transporting host material H 1 compared to the synthesis reaction, the difference is that the intermediate M 3 Replaced with an equivalent amount of 2-(4-bromophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-phenanthro[9,10-d]imidazole, other raw materials and steps are the same as the hole transport host material H 1 synthesis reaction. Finally, the hole-transporting host material H is obtained. 2 , the yield is 65%. H 2 Molecular formula: C 58 H 35 N 3 ; Molecular weight: m / z: 773.28; Elemental analysis results are: C, 90.01; H, 4.56; N, 5.43. .
Embodiment 3
[0068] A hole-transporting host material H 3 The preparation includes the following preparation steps:
[0069] Intermediate M 6 The reaction formula is as follows:
[0070]
[0071] The specific reaction steps are as follows:
[0072] Intermediate M 5 Synthesis of: in a 250mL there-necked flask under nitrogen atmosphere, 6.6g of 2-(methylthio)phenylboronic acid (38.9mmol), 10.0g of 5-chloro-3-iodopyridine-2-2-amine (38.9g mmol), 16.3 g of potassium borate (117 mmol) were fully dissolved in 180 mL of tetrahydrofuran and 60 mL of distilled water blend solution and stirred uniformly. Under full nitrogen protection, 1.26 g (1.17 mmol) of tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium was added to the system, and the mixture was heated under reflux for 24 hours. The system was then cooled to room temperature and extracted with ethyl acetate and distilled water. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and evaporated in vacuo to give crude product which was pur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com