Method for extracting folium cortex eucommiae polysaccharide by utilizing microbial fermentation method
A microbial fermentation method and the technology of Eucommia leaves, applied in the field of microbial fermentation technology in the extraction of polysaccharides from Eucommia leaves, can solve the problems of increasing production costs and limiting industrial applications, and achieve the promotion of dissociation, easy dissolution, and improved extraction yield Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Isolation and screening of fermentation strains
[0021] The microbial strains fermenting Eucommia leaves were isolated and screened according to the following steps:
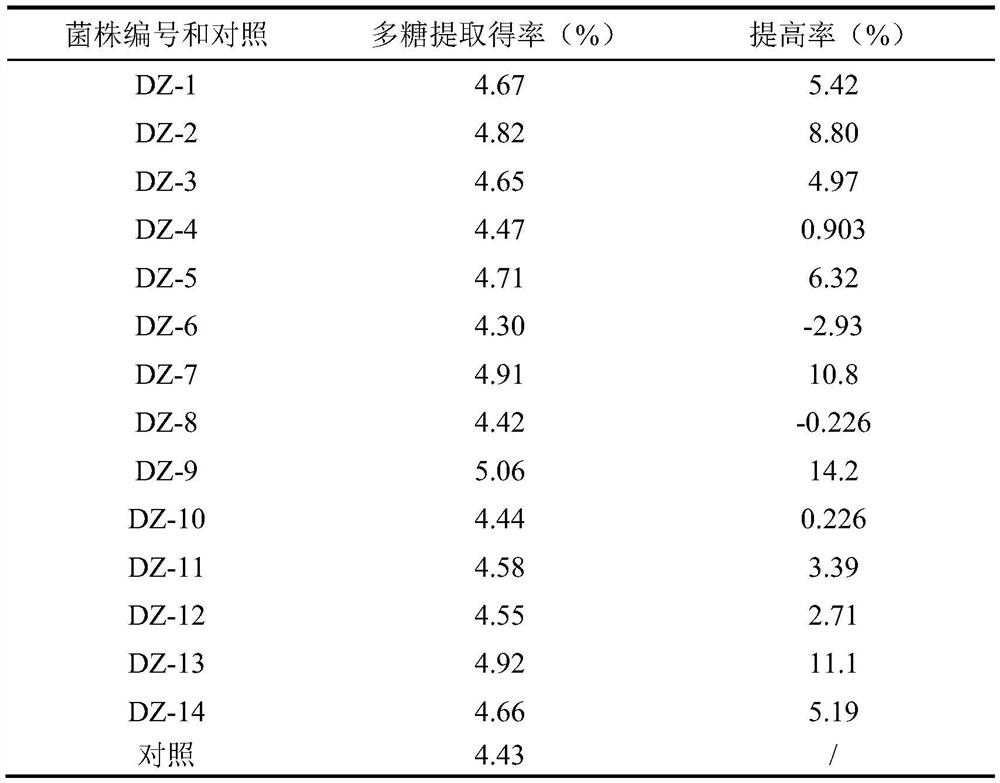
[0022] (1) About 5 g of eucommia leaf powder was added to a 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask, and then 5 mL of sterile saline was added to moisten it, and incubated at a constant temperature of 28°C for 4 days. The enriched cultures covered with mold were diluted 1×10 with sterile saline -6 , 1×10 -7 , 1×10 -8 After doubling, draw 0.1mL of the diluted solution and spread it on the potato dextrose agar plate medium (PDA), culture at a constant temperature of 28°C for 2 days, pick mold colonies with different colors and shapes and transfer them to fresh PDA plate medium, and place them at 28°C. After culturing at constant temperature at ℃ for 3 days, 14 purely cultured strains were obtained, and the numbers of each strain are shown in Table 1.
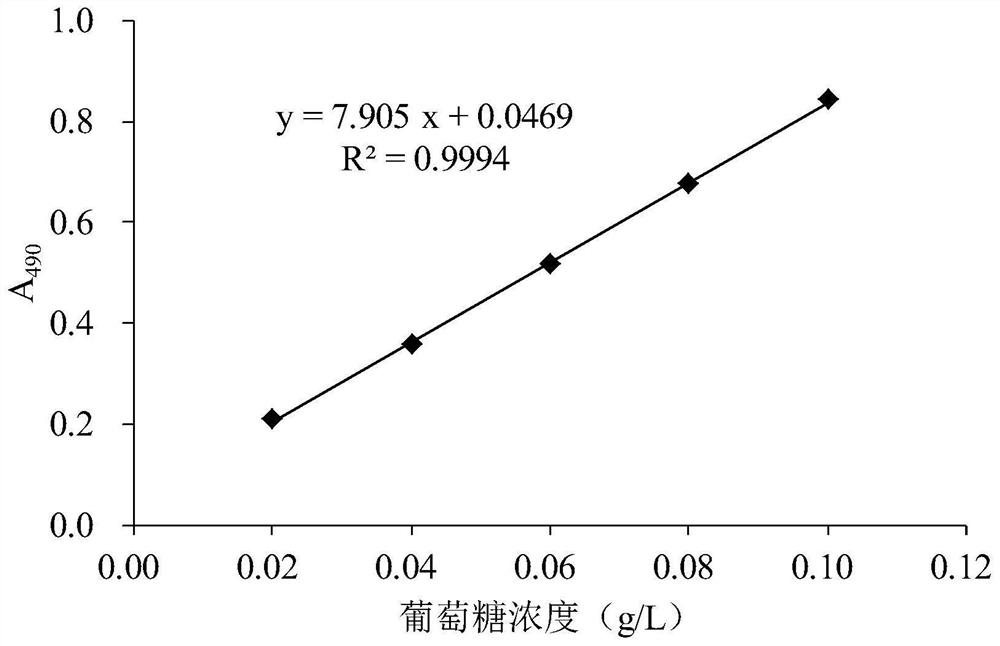
[0023] (2) Add 5 mL of sterile saline to the fresh plat...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: the mutagenesis selection of fermentation strain DZ-9
[0035] Carry out mutagenesis breeding on strain DZ-9, and screen strains with excellent fermentation performance, the specific method is as follows:
[0036] (1) Preparation of spore liquid: After the bacterial strain DZ-9 was activated and cultured on PDA plate medium for 2 days, 5 mL of sterile normal saline was added, stirred with an inoculation loop to suspend the spores, and then transferred to a triangular flask containing 45 mL of sterile normal saline Medium (with 20–30 glass beads added), shake at room temperature for 20 minutes. The spore suspension was filtered to remove mycelium (triangular funnel pad with 2 layers of lens-cleaning paper), counted the spores in the suspension with a hemocytometer under a microscope, and diluted it with sterile saline to adjust the number of spores to 1× 10 8 individual / mL.
[0037] (2) Mutagenesis: under red light illumination, take 2.0mL of the above s...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Classification and Identification of Bacterial Strain DZ-9-67
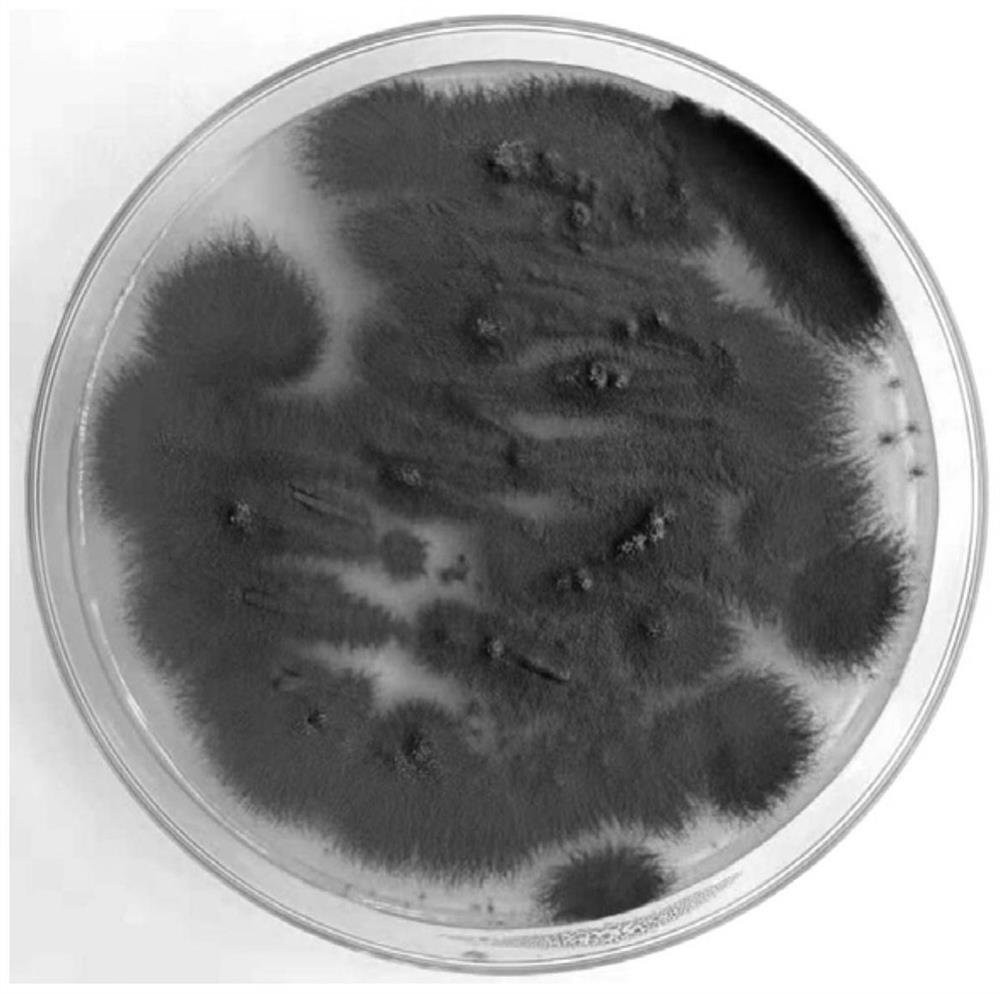
[0040] Strain DZ-9-67 was inoculated on PDA plate medium and cultured at 28°C for 3 days. The colonies were grayish white and short fluffy at the beginning, and then gradually turned green to olive green. Sporulation. The top of the aerial hyphae produces conidiophores, with 1–4 branches at the top of the stalk, and the terminal cells of each branch divide into clusters of conidia, forming a typical brush-shaped conidia spike; the conidia are spherical or Nearly spherical, 2.5–3.0 μm in diameter, green. See the photos of the colony of Penicillium papaya DZ-9-67 cultured on PDA plate medium at 28°C for 3 days figure 1 .
[0041] The strain DZ-9-67 was handed over to Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. and the rDNA nucleotide sequence of its ribosomal ITS region was measured as SEQ ID NO.1, which is listed in NCBI (National Center for BiotechnologyInformation, https : / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com