Near-infrared responsive hyaluronic acid hydrogel for articular cartilage repair and its preparation method
A technology of hyaluronic acid and articular cartilage, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems of poor light penetration ability, high degree of cell damage, and limited application, and achieve the effects of reducing friction coefficient, deep tissue penetration, and improving lubrication Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
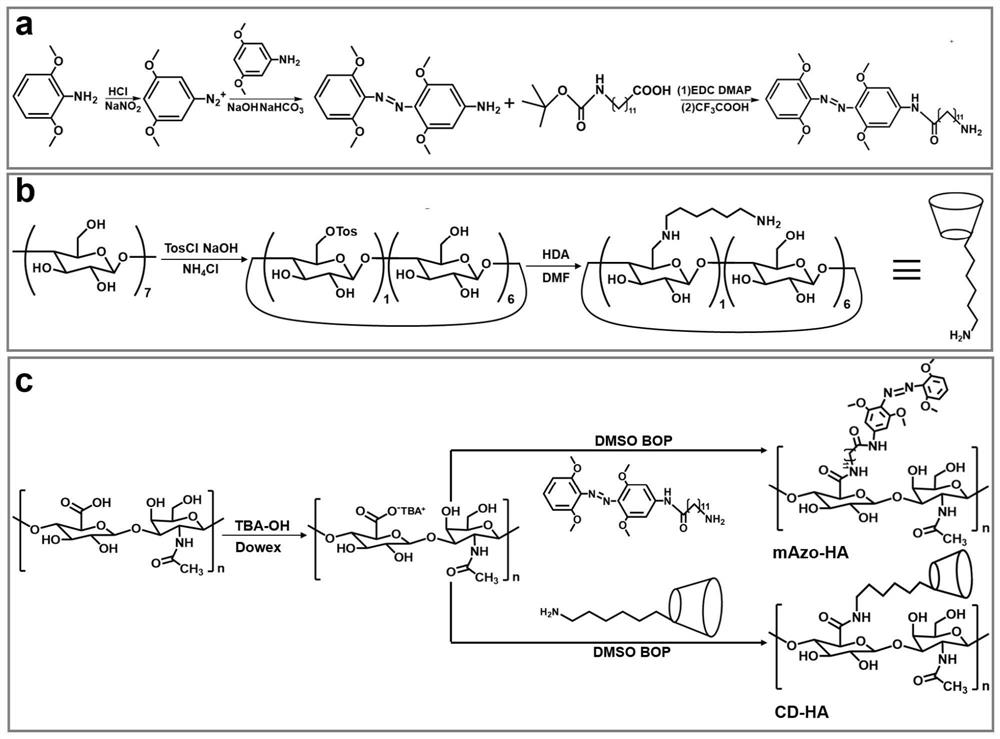
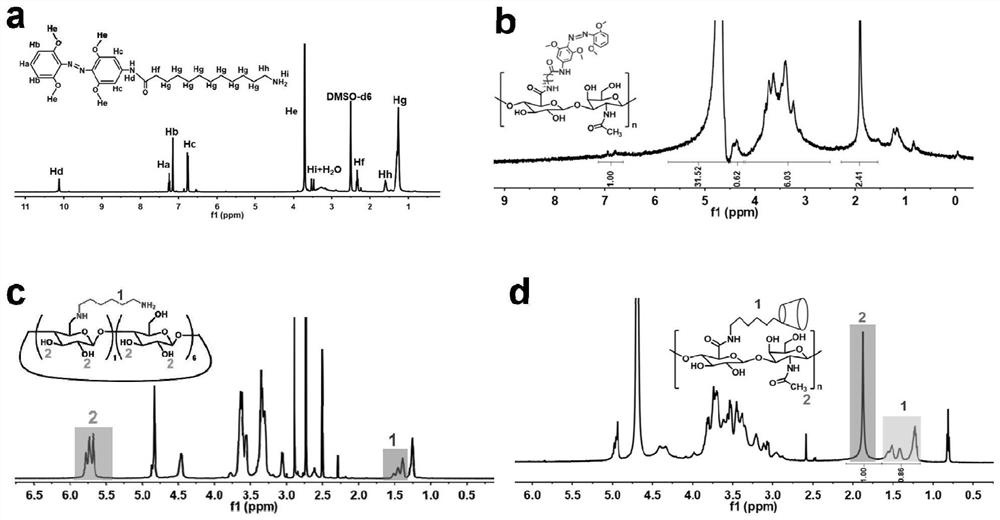
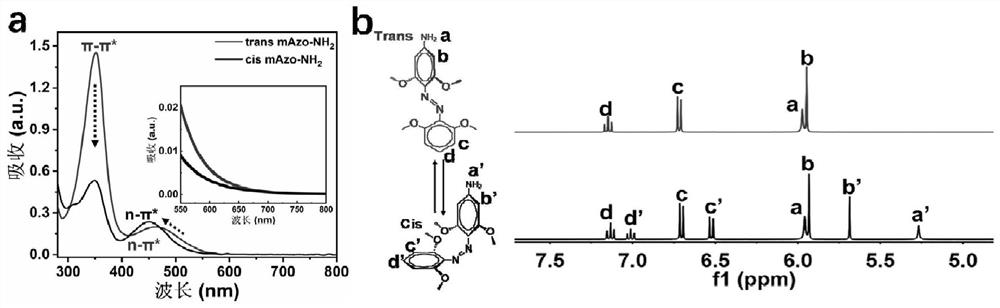
[0079] The preparation method steps of the near-infrared responsive hyaluronic acid hydrogel for articular cartilage repair provided in this example are as follows:
[0080] (1) Preparation of hyaluronic acid (mAzo-HA) modified by azobenzene derivatives
[0081] (11) Preparation of tetra-o-methoxy substituted azobenzene (mAzo)
[0082] Dissolve 1g of granular 2,6-dimethoxyaniline in a mixed solution of 1.2mL of water and 1.5mL of 37wt% hydrochloric acid. After cooling to 2°C, slowly add 4mL of NaNO with a concentration of 1.8mol / L 2 solution and stirred for 20 minutes. At 2°C, slowly add the above mixed solution to the suspension formed by 1 g of 3,5-dimethoxyaniline and 40 mL of water, then add a 2 mol / L sodium bicarbonate solution to adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 8, and stir Overnight (about 12h). Use dichloromethane to extract the reacted solution, separate the liquid from the organic layer with a separatory funnel, concentrate the organic solution by rotary ...
Embodiment 2
[0099] The preparation method steps of the near-infrared responsive hyaluronic acid hydrogel for articular cartilage repair provided in this example are as follows:
[0100] (1) Preparation of hyaluronic acid (mAzo-HA) modified by azobenzene derivatives
[0101] (11) Preparation of tetra-o-methoxy substituted azobenzene (mAzo)
[0102] Dissolve 1g of granular 2,6-dimethoxyaniline in a mixed solution of 1.2mL of water and 1.5mL of 37wt% hydrochloric acid. After cooling to 3°C, slowly add 4mL of NaNO with a concentration of 1.8mol / L 2 solution and stirred for 20 minutes. At 3°C, slowly add the above mixed solution to the suspension formed by 1 g of 3,5-dimethoxyaniline and 40 mL of water, then add a 2 mol / L sodium bicarbonate solution to adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 8.5, and stir Overnight (about 12h). Use dichloromethane to extract the reacted solution, separate the liquid from the organic layer with a separatory funnel, concentrate the organic solution by rotar...
Embodiment 3
[0119] The preparation method steps of the near-infrared responsive hyaluronic acid hydrogel for articular cartilage repair provided in this example are as follows:
[0120] (1) Preparation of hyaluronic acid (mAzo-HA) modified by azobenzene derivatives
[0121] (11) Preparation of tetra-o-methoxy substituted azobenzene (mAzo)
[0122] Dissolve 1g of granular 2,6-dimethoxyaniline in a mixed solution of 1.2mL of water and 1.5mL of 37wt% hydrochloric acid. After cooling to 4°C, slowly add 4mL of NaNO with a concentration of 1.8mol / L 2 solution and stirred for 20 minutes. At 4°C, slowly add the above mixed solution to the suspension formed by 1 g of 3,5-dimethoxyaniline and 40 mL of water, then add a 2 mol / L sodium bicarbonate solution to adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 8.5, and stir Overnight (about 12h). Use dichloromethane to extract the reacted solution, separate the liquid from the organic layer with a separatory funnel, concentrate the organic solution by rotar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com