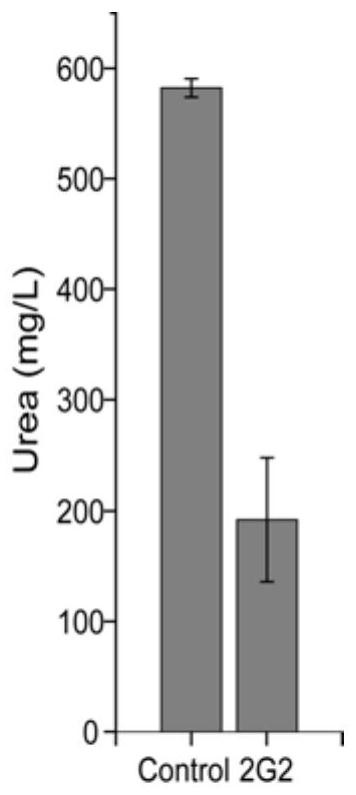
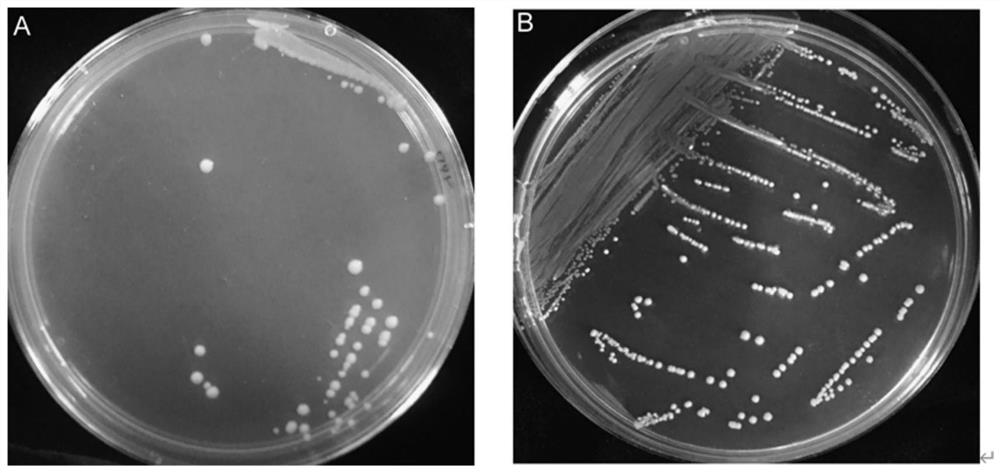
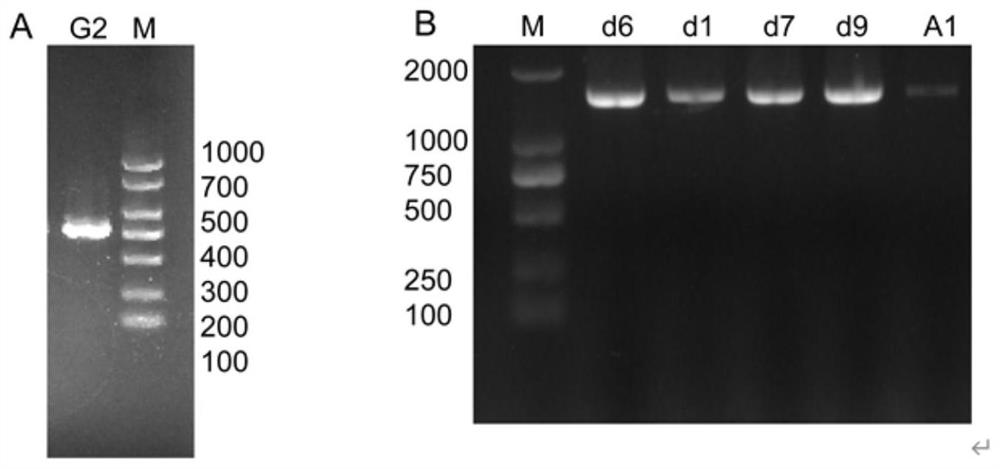
Strain for reducing accumulation of urea and ethyl carbamate in yellow wine and application of the strain
A technology for urea and wine brewing, which is applied in the preparation of wine, the preparation of alcoholic beverages, and methods based on microorganisms, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing the content of urea and urethane
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1: Screening and isolation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae G2
[0066] Pre-screening: Weigh 1g of yellow rice wine fermented mash sample into a sterile EP tube, mix thoroughly with 1mL of sterile saline, dilute to an appropriate multiple, take 100μL, and spread on YNB solid medium containing urea as the only nitrogen source , placed in a constant temperature incubator at 30°C and cultivated until a single colony grows on the plate, and picked by QPix420 biological screening system or manually.
[0067] Primary screening: Use the microbial screening system QPix420 or manual selection to transfer a single colony on the pre-screening plate to a 48-well plate containing the primary screening medium, and then culture it in an orifice shaker at 30°C and 220r / min After 48h, centrifuge the 48-well plate at 3500r / min for 5min, take 80μL of the supernatant in a 96PCR plate, add 20μL of diacetylmonoxime thiamine and 100μL of ferric ammonium phosphate solution, react at 100°C f...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Embodiment 2: the screening of producing urease and EC hydrolase bacterial strain lactic acid bacteria d6
[0071] Preliminary screening: Weigh 1g of rice wine fermented mash into a sterile EP tube, take 1mL of sterile saline and mix well, dilute to an appropriate multiple, take 100μL and apply it to the separation culture, and cultivate it in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for several days until a single colony grows. Use the QPix420 screening system to screen bacteria, pick a single colony into a 48-well plate with screening medium, and culture it anaerobically at 37°C for several hours. Since urease or EC hydrolase can react with the corresponding substrate to produce ammonia, the bromocresol purple changes from purple to yellow. According to the color reaction, select the target strain for primary screening.
[0072] Re-screening: select the target strain of primary screening and inoculate it in MRS medium for 72 hours, take the bacterial liquid in a refr...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Embodiment 3: Construction of phylogenetic tree
[0077] Use BLAST to compare the sequencing results of ITS2 (nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae G2 and lactic acid bacteria d616SrDNA (nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2) on NCBI. Based on the search results, MEGA 7.0 biological software was used to compare and analyze multiple sequences of test strains and related strains and construct a phylogenetic tree by Neighbor-Joining method. see results Figure 4A~B.
[0078] The results showed that the sequence homology between yeast G2 and ITS2 rRNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae was the highest, and the similarity reached 99%.
[0079] The 16S rRNA sequence homology between Lactobacillus d6 and Lactobacillus fermentum was the highest, with a similarity of 99%.
[0080] Using the molecular software MEGA7.0, 10 strains with high similarity to yeast G2 and lactic acid bacteria d6 were used for multiple sequence alignment analysis, and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com