Lactobacillus plantarum YL399 capable of producing high-activity tannase and application of lactobacillus plantarum YL399 in preparation of codonopsis pilosula fermented feed
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and fermented feed, applied to Lactobacillus plantarum YL399 and its application in the preparation of Codonopsis pilosula fermented feed, can solve the problem of low tannase activity and achieve the effect of expanding the source
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Isolation, identification and preservation of embodiment 1 Lactobacillus plantarum strain
[0033] 1. Isolation of Lactobacillus plantarum strains
[0034] Sample material: natural fermented corn silage.
[0035] After repeated streaking culture on the BCP medium plate, pick the single colony that produced the yellow circle and inoculate it on the solid MRS medium plate to continue the culture. Repeated streaking culture and purification on the solid MRS medium plate obtained multiple strains of pure culture strains.
[0036] Inoculate the purely cultured strains into liquid MRS medium for culture, then add 20% glycerol, and store in a -80°C refrigerator.
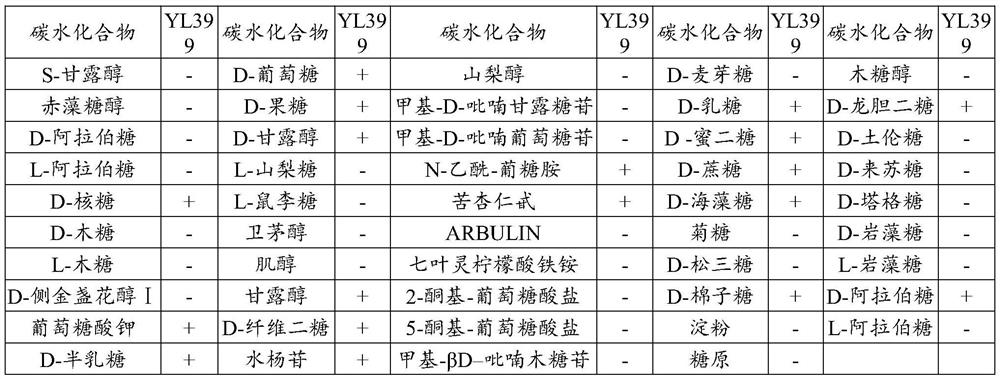
[0037] Several strains with positive Gram staining, negative catalase test, negative indole reaction, negative hydrogen sulfide production test, negative gelatin liquefaction test, negative hydrolyzed starch test and negative nitrate reduction test were screened out from purely cultured strains. strain. One of the...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The mensuration of the tannase activity produced by embodiment 2 plant lactobacillus (Lactobacillus plantarum) YL399
[0047] 1. Preparation of strain culture and cell-free medium
[0048] The Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) YL399 frozen strain was continuously passaged and activated in liquid MRS medium for 3 times, then inoculated in liquid MRS medium according to the inoculum size of 2%, and cultured statically at 37°C for 16h, 3000r / min , centrifuged at 4°C for 8 minutes, discarded the supernatant, and obtained bacterial precipitates; the obtained bacterial precipitates were ultrasonically disrupted to lyse the cell wall: add an equal volume of sterile normal saline, add lysozyme to a concentration of 1 mg / ml, and bathe in constant temperature water at 37°C for 30 minutes, ice Sonicate the bacterial cells in the bath (800w, 2s, 2s, 40°C, 15min), centrifuge at 4000r / min, 4°C for 10min to collect the supernatant, which is the cell-free extract contai...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 Application of plant Lactobacillus (Lactobacillus plantarum) YL399 producing high-activity tannase of the present invention in the preparation of Codonopsis pilosula fermented feed
[0053] 1. Preparation of Lactobacillus plantarum YL399 freeze-dried starter
[0054] The frozen Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) YL399 strain was continuously passaged and activated in liquid MRS medium for 3 times, then inoculated into liquid MRS medium at an inoculum size of 2%, cultured at 37°C for 16 h, and centrifuged (3000 ~6000rpm / min, 10min, 4°C) to obtain bacterial cell precipitation, add lyoprotectant (40g / L glucose, 5g / L sodium ascorbate, 80g / L fructooligosaccharide and 30g / L trehalose), freeze-dry, Pack the Lactobacillus plantarum YL399 freeze-dried starter and store it at 4°C. The number of live bacteria of the obtained Lactobacillus plantarum YL399 freeze-dried starter is >100 billion / g.
[0055] 2. Preparation of Codonopsis pilosula fermented feed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com