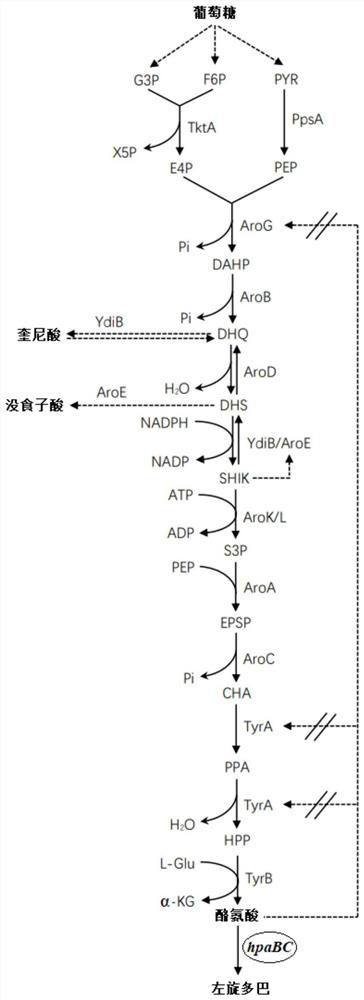
Method for producing levodopa through microbial fermentation and application
A microbial fermentation and levodopa technology, which is applied in the fields of food, feed and medicine, can solve the problems of residual raw materials and large amount of starting raw materials, and achieve the effect of increasing production yield and glucose metabolic flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] This example describes the acquisition of the E. coli 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid 3-monooxygenase B gene.
[0049] According to the NCBI Reference Sequence published by Pubmed: NC_012971.2: Escherichia coliBL21 (DE3) wild-type 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid 3-monooxygenase B (the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3, and the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 shows) the nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO: 4 design primers.
[0050] Forward primer (T7hpaB-F) SEQ ID NO: 5:
[0051] 5'-GGGAATTCCATATGAAACCAGAAGATTTCCGC-3',
[0052] Reverse primer (T7hpaB-R) SEQ ID NO: 6:
[0053] 5'-CGGAATTCATTATTTCAGCAGCTTTATCCAGCAT-3'; Among them, the parts in italics are the enzyme cutting sites NdeI and EcoRI respectively. The PCR reaction was carried out in 50 μl total system, and the reaction conditions were: denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes; denaturation at 94°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 58°C for 1 minute, extension at 72°C for 2 minutes, a total of 30 cycles; extensi...
Embodiment 2
[0055] This example describes the construction of a wild-type 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid 3-monooxygenase B gene expression vector.
[0056] The PCR product in Example 1 was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis, and the target fragment was recovered according to the instructions of the gel recovery kit. Take 100 μl of the PCR product and digest it with restriction endonucleases NdeI and EcoRI, and then connect it to the hpaC / pET-24a vector digested with NdeI and EcoRI (hpaC is 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid 3-monooxygenase C, previously inserted into the pET-24a vector), the ligation product mixture was transformed into Escherichia coli Top10, 20 clones were picked, and PCR identification was performed with primers T7hpaB-F and T7hpaB-R. The positive clones identified by PCR were selected for sequence determination, and the vectors with correct sequencing were saved and named: pET-hpaBC.
Embodiment 3
[0058] This example describes error-prone PCR amplification of the E. coli 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid 3-monooxygenase B gene.
[0059] Utilizing the property that Taq DNA polymerase does not have 3'-5' proofreading function, under the concentration of high magnesium ion concentration (8mmol / L) and different concentration of dNTP (wherein the concentration of dATP and dGTP is 1.5mmol / L, the concentration of dTTP and dCTP 3.0mmol / L) to control the frequency of random mutations, introduce random mutations into the target gene, and construct a mutation library. Template concentration A 260 The value is 1000ng / mL, the enzyme concentration is 5U / μL, and the primer concentration is 100μM.
[0060] Error-prone PCR reaction system (50μl): 5μl of 10×PCR reaction buffer, 5μl of dNTP (2.5nM), MgCl 2 5 μl, forward primer (T7hpaB-F) 1 μl, reverse primer (T7hpaB-R) 1 μl, DNA template (PCR product of Example 1) 1 μl, Taq DNA polymerase 0.5 μl, ddH 2 O 31.5 μl.
[0061]PCR program: pre-den...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com