Method for producing psicose 3-epimerase through high-density fermentation
An epimerase, high-density fermentation technology, applied in the direction of racemase/epimerase, microbial-based methods, isomerase, etc., can solve the problem of psicose 3-epimerase Problems such as low expression, low purity, and high cost have achieved a wide range of industrial application prospects, separation and purification savings, and the effect of reducing burdens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
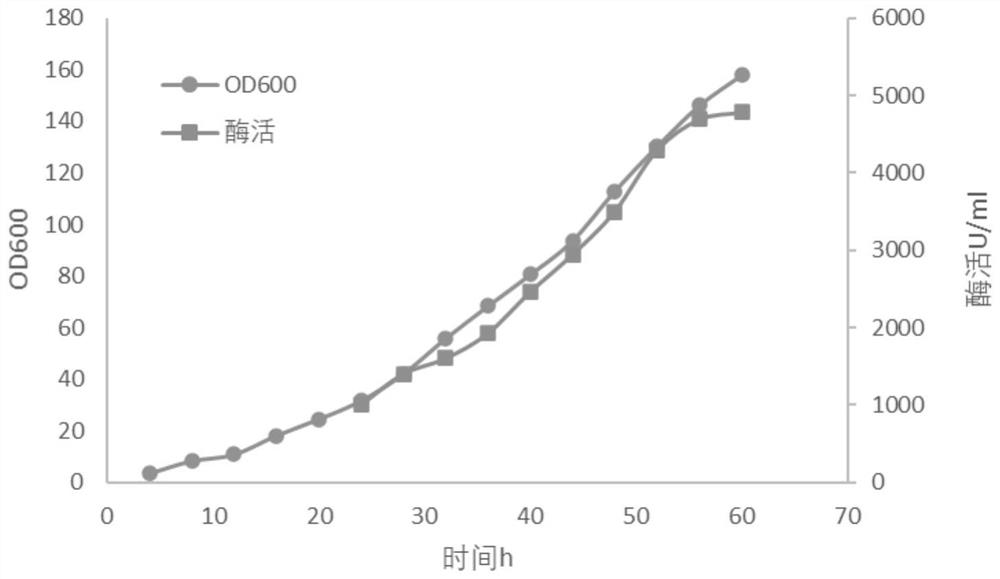
Embodiment 1
[0057] Embodiment 1 High-density fermentation (using peptone and yeast powder as nitrogen source in fermentation medium and feeding medium)
[0058] (1) Culture medium preparation
[0059] A. Activation medium: The composition of the activation medium is peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, sodium chloride 10g / L, after sterilizing at 121°C for 20min, add kanamycin to 50mg / L under sterile conditions.
[0060] B. Fermentation medium: The composition of the fermentation medium is peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 2.5g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 15g / L, manganese chloride tetrahydrate 0.1g / L, glucose 6g / L, sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
[0061] C. Feed medium: the composition of the feed medium is 15% by mass of glucose and 20% by mass of yeast powder, and it is sterilized at 121° C. for 20 minutes.
[0062] (2) Activation of bacteria
[0063] Activation of primary strains: Take 100 μL of the preserved bacterial solution of recombinant Bacillu...
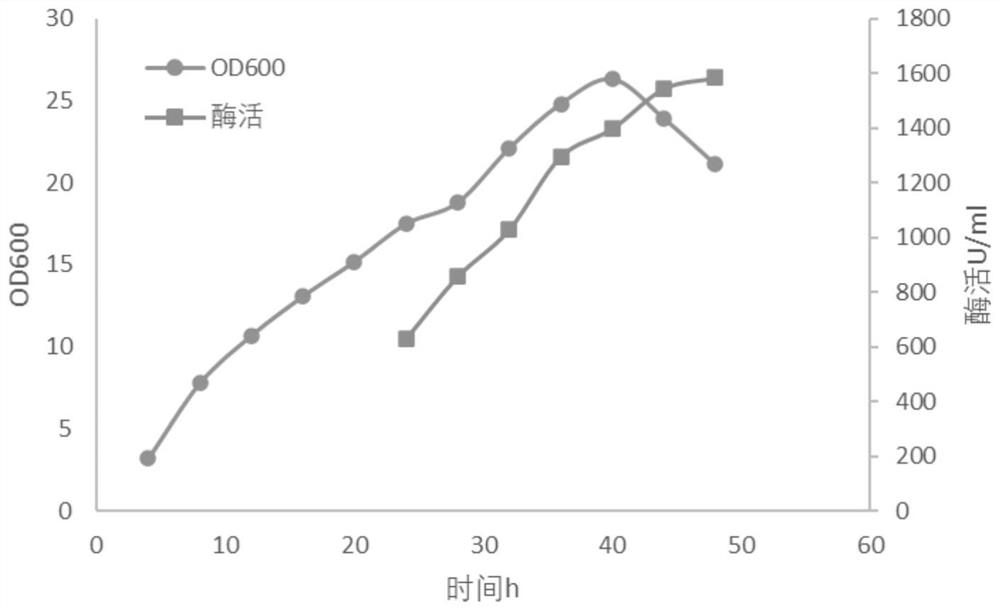
Embodiment 2
[0068] Embodiment 2 High-density fermentation (using peptone and yeast powder as nitrogen source in fermentation medium and feeding medium)
[0069] (1) Culture medium preparation
[0070] A. Activation medium: The composition of the activation medium is peptone 5g / L, yeast powder 1g / L, sodium chloride 8g / L, after sterilizing at 121°C for 20min, add kanamycin to 25mg / L under sterile conditions.
[0071] B. Fermentation medium: The composition of the fermentation medium is peptone 5g / L, yeast powder 1g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.5g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 5g / L, manganese chloride tetrahydrate 0.02g / L, glucose 2g / L, sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
[0072] C. Feed medium: the composition of the feed medium is 10% by mass of glucose and 10% by mass of yeast powder, and it is sterilized at 121° C. for 20 minutes.
[0073] (2) Activation of bacteria
[0074] Activation of primary strains: Take 50 μL of the preserved bacterial liquid of recombinant Bacillus subt...
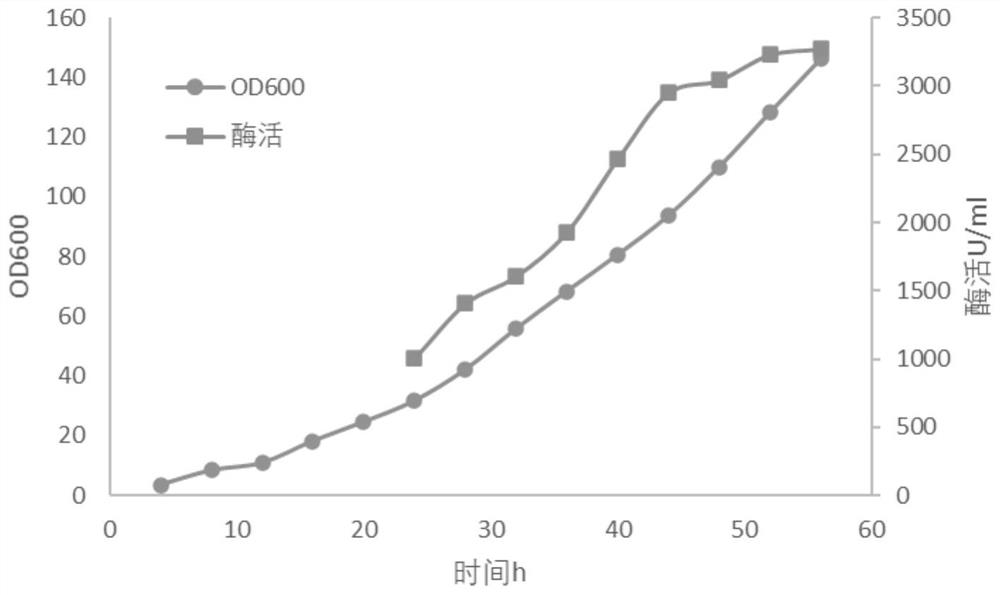
Embodiment 3
[0079] Embodiment 3 High-density fermentation (using peptone and yeast powder as nitrogen source in fermentation medium and feeding medium)
[0080] (1) Culture medium preparation
[0081]A. Activation medium: The composition of the activation medium is peptone 15g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, sodium chloride 10g / L, after sterilizing at 121°C for 20min, add kanamycin to 50mg / L under sterile conditions.
[0082] B. Fermentation medium: The composition of the fermentation medium is peptone 15g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 5g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 20g / L, manganese chloride tetrahydrate 0.2g / L, glucose 10g / L, sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
[0083] C. Feed medium: the composition of the feed medium is 30% by mass of glucose and 30% by mass of yeast powder, and it is sterilized at 121° C. for 20 minutes.
[0084] (2) Activation of bacteria
[0085] Activation of primary strains: Take 500 μL of the preserved bacterial solution of recombinant Bacillus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com