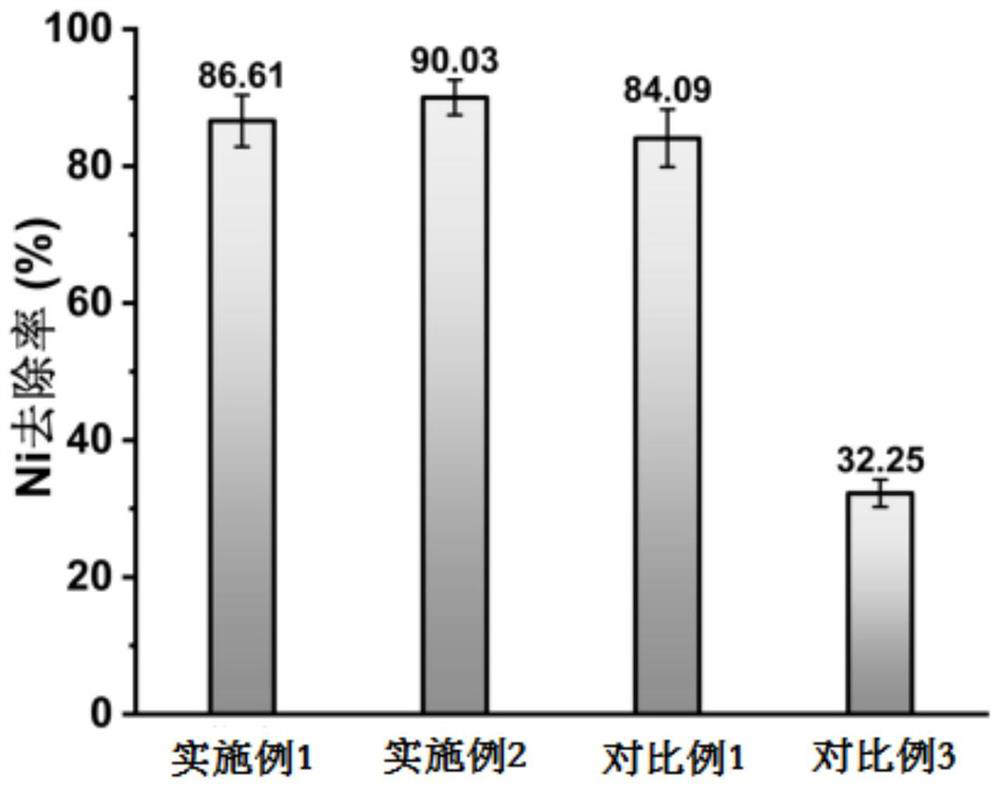
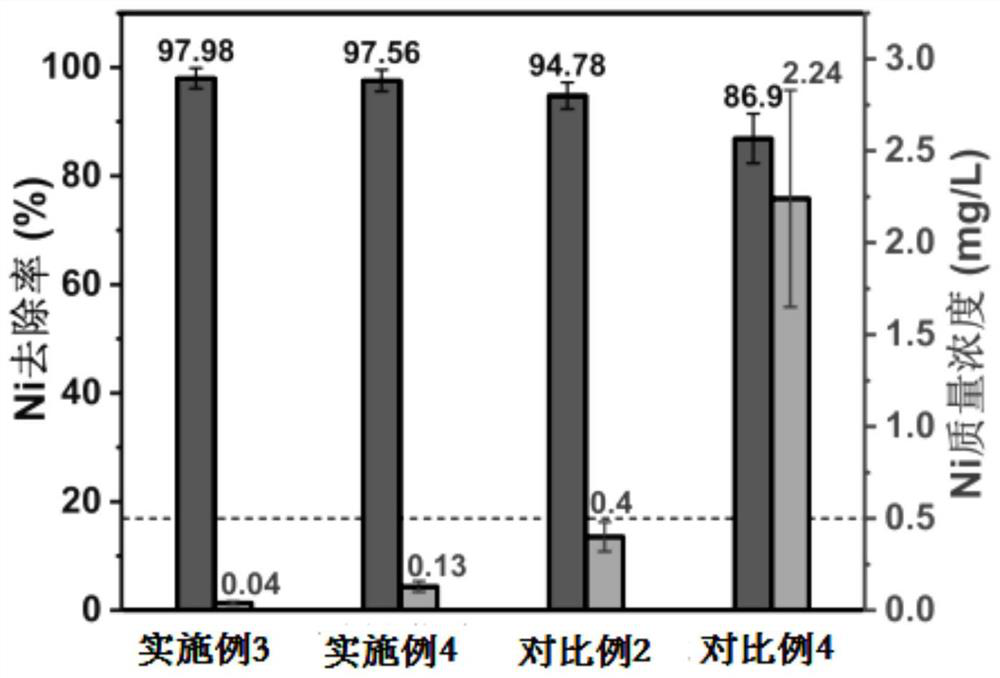
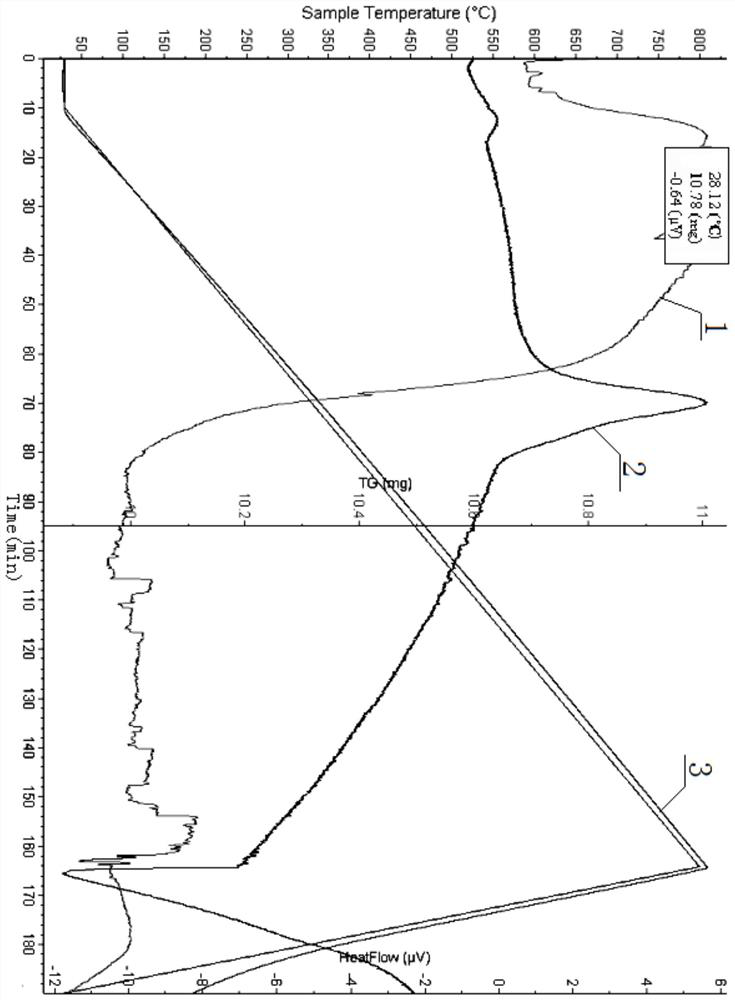
Method for biomineralization treatment of chemical nickel plating wastewater
A technology of electroless nickel plating and biomineralization, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, methods based on microorganisms, sustainable biological treatment, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective recovery of sedimentation products, rational use of unfavorable resources, etc., and achieve high removal The effect of high rate, fast removal rate and high removal efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A method for biomineralization treatment of chemical nickel plating wastewater, the following steps are followed in turn:
[0029] 1. In a sterile environment, firstly inoculate Bacillus Pasteurella into LB solid medium supplemented with urea by streaking on a plate, and culture at 37°C for 36 hours to obtain plate colonies, and then pick out the surrounding color that turns dark red. A single colony was inoculated into 3ml of LB liquid medium supplemented with urea, incubated at 30°C and 220rpm for 24h on a shaker, then the bacterial liquid was inoculated into LB liquid medium at a volume ratio of 1:100, and again at 30°C Shaker was incubated for 24h to obtain a bacterial liquid with an OD value of 3.2, wherein the formula of the LB solid medium added with urea was: sodium chloride 10g / L, tryptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, urea 10g / L, agar 20g / L, phenol red 0.05g / L, the formula of the LB liquid medium added with urea is: sodium chloride 10g / L, tryptone 10g / L, yeast pow...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0033] In step 2, before adding the bacterial solution to the mixed solution of urea and nickel chloride, resuspend it, specifically:
[0034] The bacterial solution was first centrifuged at 4°C and the precipitate was taken, then washed once with sterile physiological saline and twice with sterile water, and finally added sterile water to resuspend, so that the volume of bacterial solution before and after resuspension was the same , wherein the OD value of the resuspended bacterial solution was 3.0.
Embodiment 3
[0036] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0037] In step 2, the present embodiment replaces the mixed solution of urea and nickel chloride in embodiment 1 with the mixed solution of urea and electroless nickel plating wastewater, and the concentration of urea in the mixed solution is set with embodiment 1, and the concentration of nickel ion is 28.93mg / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com