Environment-tolerant aeromonas hydrophila bacteriophage ZPAH34 and application
A technology of Aeromonas hydrophila and bacteriophage, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of harm, economic loss of breeding, high incidence of disease, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the survival rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Phage isolation, purification and titer determination
[0035] The source water sample of Aeromonas hydrophila phage ZPAH34 in the present invention was collected in Nanhu, Hongshan District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province. Filter with a μm filter to remove host bacteria and other impurities, and store the obtained phage stock solution at 4°C.
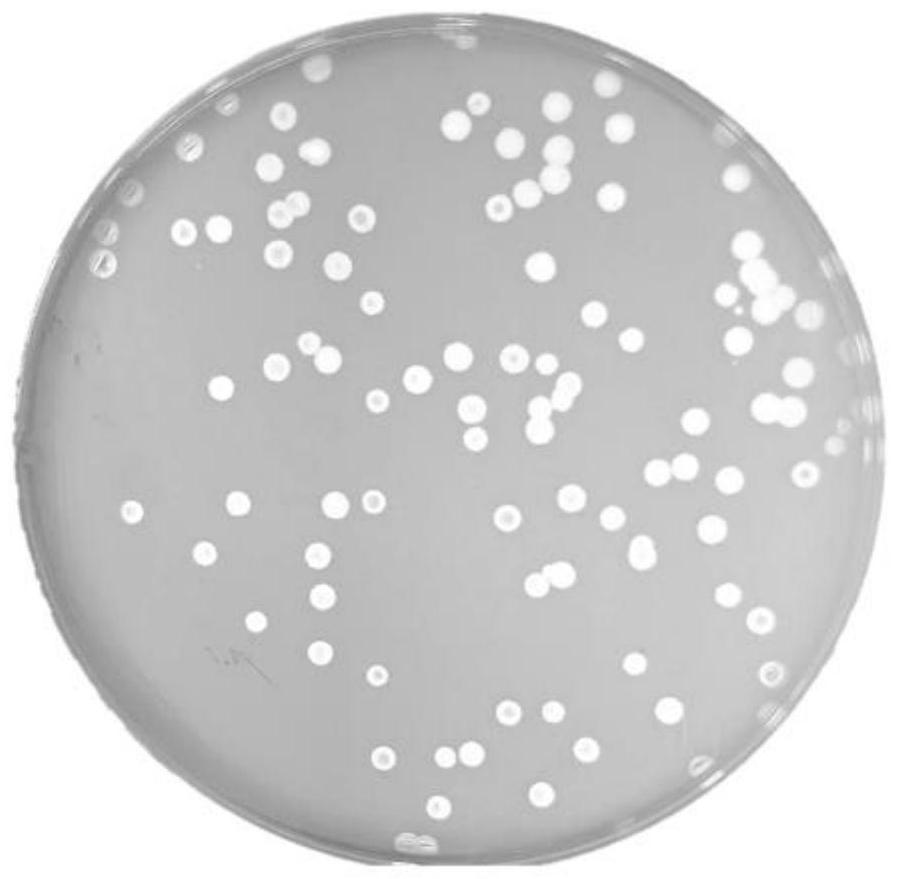
[0036] (1) Phage isolation and purification: prepare a plate of LA solid medium, dilute the phage stock solution by 10-fold gradient, and finally dilute to 10 -6 . Take 100 μL of the diluted phage solution and 100 μL of the host bacterial solution in a 5 mL centrifuge tube by the double-layer plate method, then add 3.8 mL of 0.7% LB semi-solid medium and quickly turn it up and down to mix well, pour it on a solid plate, and at 28 Incubate at ℃ for 12h. Obtain clear and transparent plaques on the double-layer plate, pick a single plaque and add it to 10 mL of LB liquid medium, and add 100 μL of Aeromonas hydrophila bacterial solut...
Embodiment 2
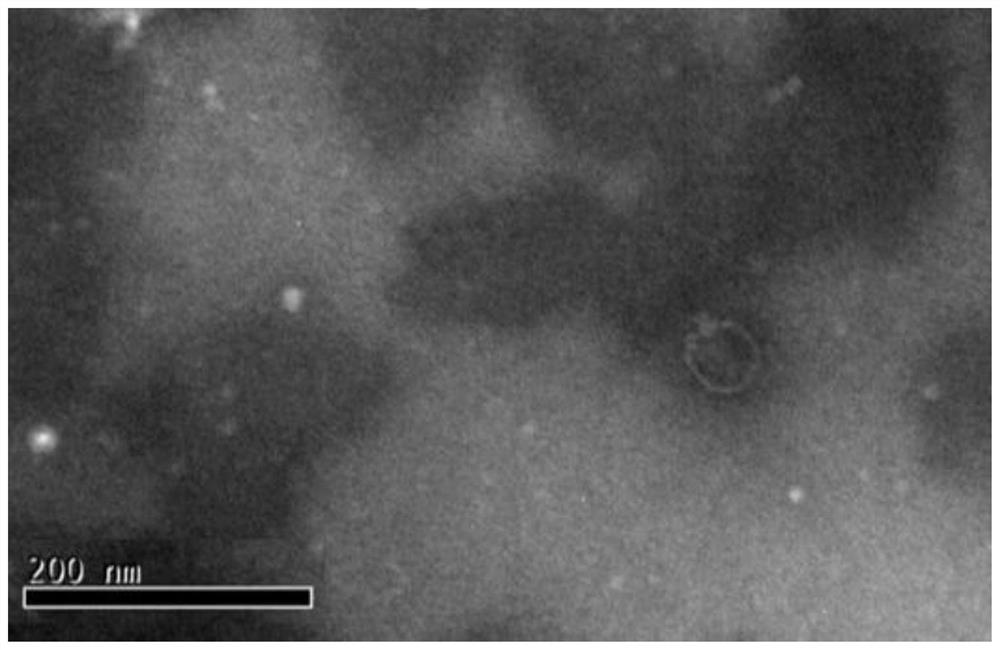
[0040] Electron microscope observation of bacteriophage ZPAH34
[0041] First, expand the phage culture, prepare a 250 mL conical flask, add 100 mL LB liquid medium and 200 μL host bacterial liquid, and culture at 28 °C for 3 h on a shaker, and inoculate the upper agar containing plaque on the double-layer plate with aseptic inoculation. The rings were picked up in a conical flask and incubated at 28°C on a shaker for another 4h. After the incubation, the cells were centrifuged at 10,000 r / min for 10 min, and the supernatant was aspirated and filtered with a 0.22 μm filter. The filtrate was ultracentrifuged at 30,000 r / min for 2 h in a vacuum environment, the supernatant was discarded, 500 μL of ammonium acetate solution was added, the spin column was repeatedly and gently pipetted, and the solution was transferred to a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube to obtain a titer ≥ 10 10 Phage enrichment in PFU / mL. Prepare the copper mesh, wash it several times with sterile water, then immerse...
Embodiment 3
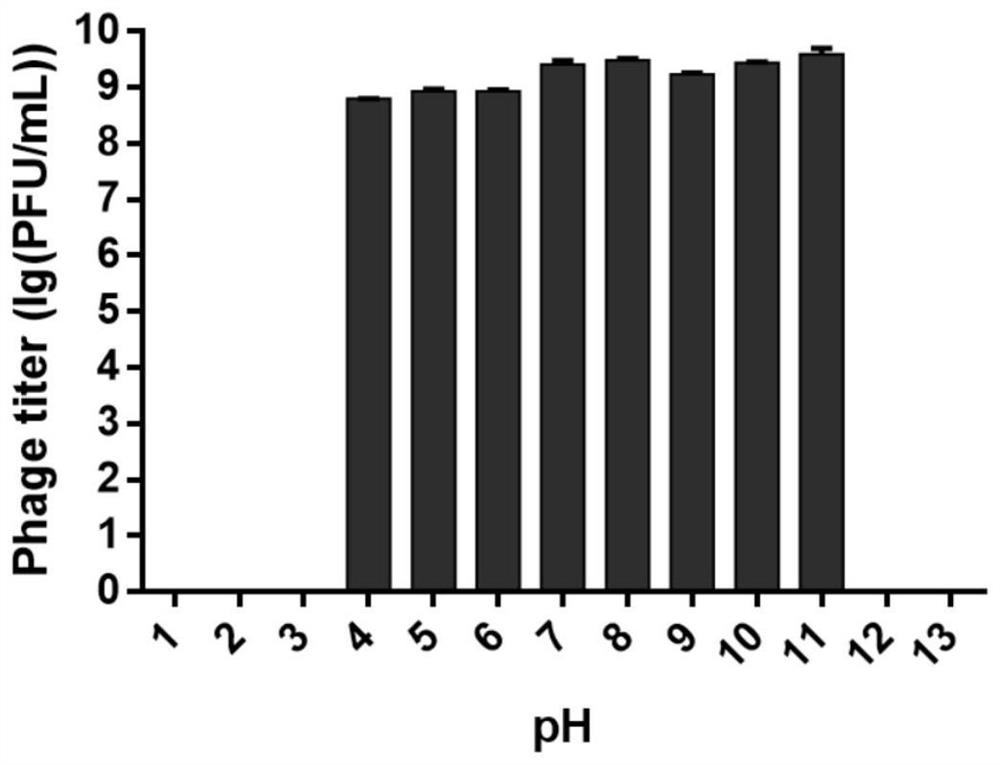
[0042] Example 3: Determination of optimal multiplicity of infection for phage ZPAH34
[0043] The host bacteria Aeromonas hydrophila ZYAH75 (NZ_CP016990) was cultured overnight, and the OD was adjusted. 600 At about 0.8, the concentration of bacterial liquid is 10 8 CFU / mL, the bacterial solution was diluted tenfold to 10 5 CFU / mL. Add 100 μL of different dilutions of phage solution (10 8 -10 2 PFU / mL) and 100 μL of host bacteria in 800 μL of LB medium. Vortex to mix, and the mixture was incubated at 28°C with shaking for 4h. After culturing, centrifuge at 4°C and 8000 r / min for 10 min, take the supernatant, dilute different concentration gradients ten-fold, and measure the phage titer by double-layer agar plate method. The ratio when the phage titer is the highest is the best multiplicity of infection of the phage. The results are shown in Table 1, showing that when MOI=0.001, the titer of phage ZPAH34 is the maximum value of 4×10 8 PFU / mL, so the optimal multiplici...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com