Novel efficient preparation process of 2, 3, 5, 6-tetrafluorobenzyl alcohol
A technology for the preparation of tetrafluorobenzyl alcohol, which is applied in the field of preparation of new high-efficiency 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzyl alcohol, can solve the problems of easy explosion and fire, and achieve the goal of reducing pollution and strong cost advantages Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
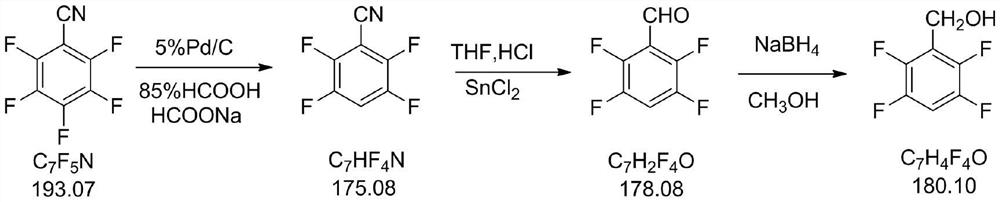
[0029] 2000 g of 85% formic acid and 100 g of pentafluorobenzonitrile (0.518 mol) were added to a 3 L reaction kettle. Start stirring and add 539 g of sodium formate dihydrate. Heated to 50-60°C and added 6.3g of 5% Pd / C (dry basis); heated to 70-80°C and reacted for 5 hours. The end of the reaction was when the remaining starting material was less than 1.0%. Cool to 20-30°C and filter. The filtrate was pumped and concentrated under reduced pressure. Concentrate to dryness, add 500 g of water to the kettle and stir. The aqueous phase was extracted twice with 400 g of dichloromethane. Dichloromethane was recovered from the organic phase at atmospheric pressure, and 78.9 g of 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzonitrile was obtained by distillation under reduced pressure, with a yield of 87% and a purity of 99.4%.
Embodiment 2
[0031] 2000 g of 85% formic acid and 100 g of pentafluorobenzonitrile (0.518 mol) were added to a 3 L reaction kettle. Start stirring and add 539 g of sodium formate dihydrate. Heat to 50-60°C and add 3.2g of 10% Pd / C (dry basis); raise the temperature to 70-80°C and react for 6 hours. The end of the reaction was when the remaining starting material was less than 1.0%. Cool to 20-30°C and filter. The filtrate was pumped and concentrated under reduced pressure. Concentrate to dryness, add 500 g of water to the kettle, and stir. The aqueous phase was extracted twice with 400 g of dichloromethane. Dichloromethane was recovered from the organic phase at atmospheric pressure, and 77.1 g of 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzonitrile was obtained by distillation under reduced pressure, with a yield of 85% and a purity of 99.0%.
Embodiment 3
[0033]250 g of 2-methyltetrahydrofuran was added to the drying reaction kettle, and stirring was started. The ice water is cooled to 0-10°C and dry hydrogen chloride gas is introduced into it. Use wet pH test paper to test the bottle mouth, and stop the introduction of hydrogen chloride when the pH test paper turns red quickly. After adding 81.2 g of stannous dichloride (0.428 mol), it was stirred for 1 hour. 50 g of 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzonitrile (0.2856 mol) was added in portions, and the reaction was incubated for 5 hours. The end of the reaction was when the remaining starting material was less than 1.0%. Add water to hydrolyze. The organic phase is washed with water. The 2-methyltetrahydrofuran was recovered from the organic phase under normal pressure, and then distilled under reduced pressure to obtain 48.2 g of 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzaldehyde, with a purity of 98.3% and a yield of 94.7%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com