Complex microbial inoculant and remediation of petroleum-chlorophenol combined pollution environment by using complex microbial inoculant
A compound bacterial agent and compound pollution technology, applied in water pollutants, bacteria, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of inability to degrade pollutants and weak degradation ability, and achieve obvious advantages in biodegradation and comprehensive functions. , easy to prepare
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1. Strain screening
[0030] Materials and methods
[0031] Soil samples: Dongying Dongxin Oil Production Plant has long been contaminated by oil.
[0032] Sludge sample: activated sludge in the secondary sedimentation tank of Qingdao Sewage Treatment Plant.
[0033] Inorganic salt medium: (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.0 g, K 2 HPO 4 1.0 g, KH 2 PO 4 1.0 g, anhydrous CaCl 2 0.01 g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g, NaNO 3 5.0 g, FeCl 3 Trace amount, distilled water 1000mL, adjust pH to 7.2~7.5, sterilize at 121℃ for 20min before use.
[0034] Petroleum hydrocarbon degrading bacteria screening medium: add a certain amount of petroleum on the basis of inorganic salt medium.
[0035] Chlorophenol-degrading bacteria screening medium: add a certain amount of chlorophenol on the basis of inorganic salt medium.
[0036] Screening of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Degrading Strain
[0037] Weigh 10g of petroleum-contaminated soil and add it to a sterilized Erlenmeyer flask containing 90mL...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2. Strain compounding
[0051] Materials and Methods
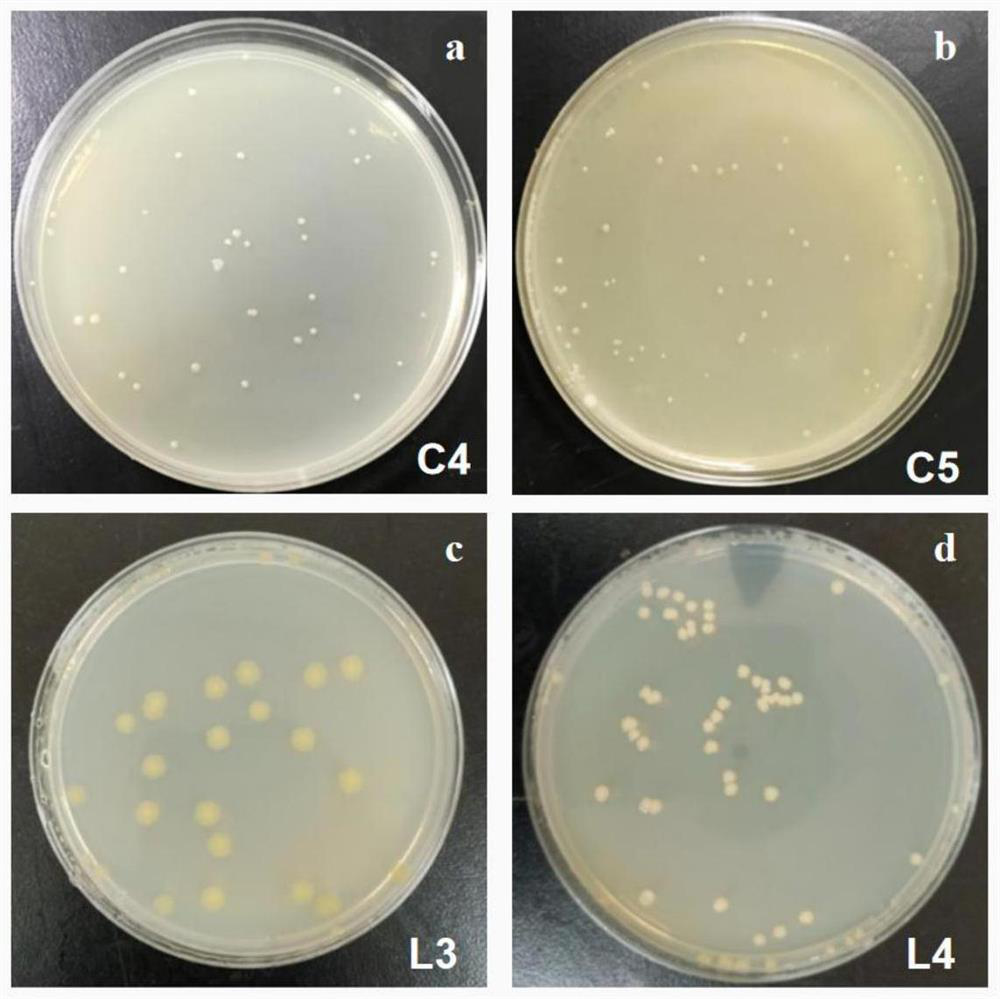
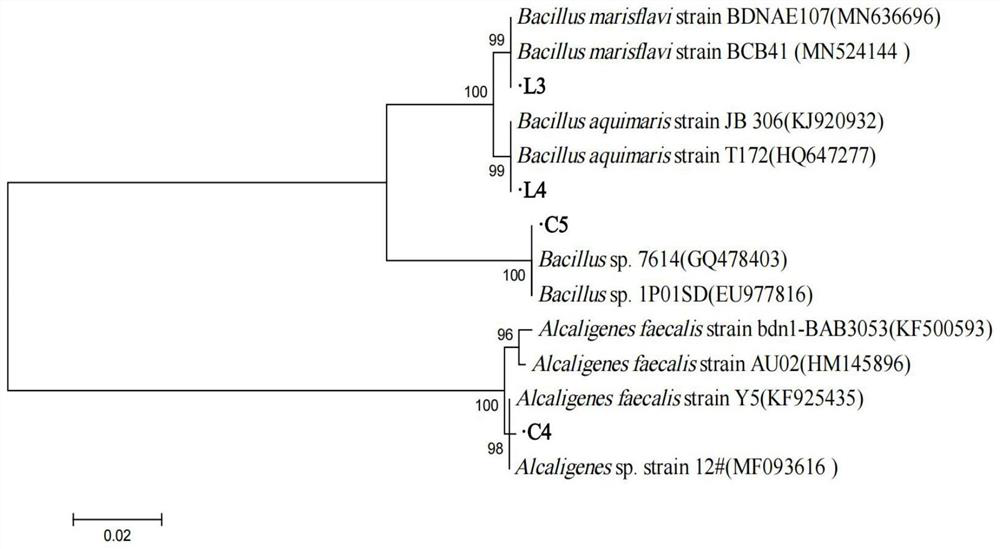
[0052] Strains: After screening, two petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria C4 and C5, and two chlorophenol-degrading bacteria L3 and L4 were obtained.
[0053] culture medium
[0054] Beef extract liquid medium, petroleum-chlorophenol inorganic salt medium
[0055] Assay method: prepare petroleum-chlorophenol inorganic salt medium (the concentration of chlorophenol in the medium is 50mg / L; the content of petroleum is 2g / L), sterilized for later use;
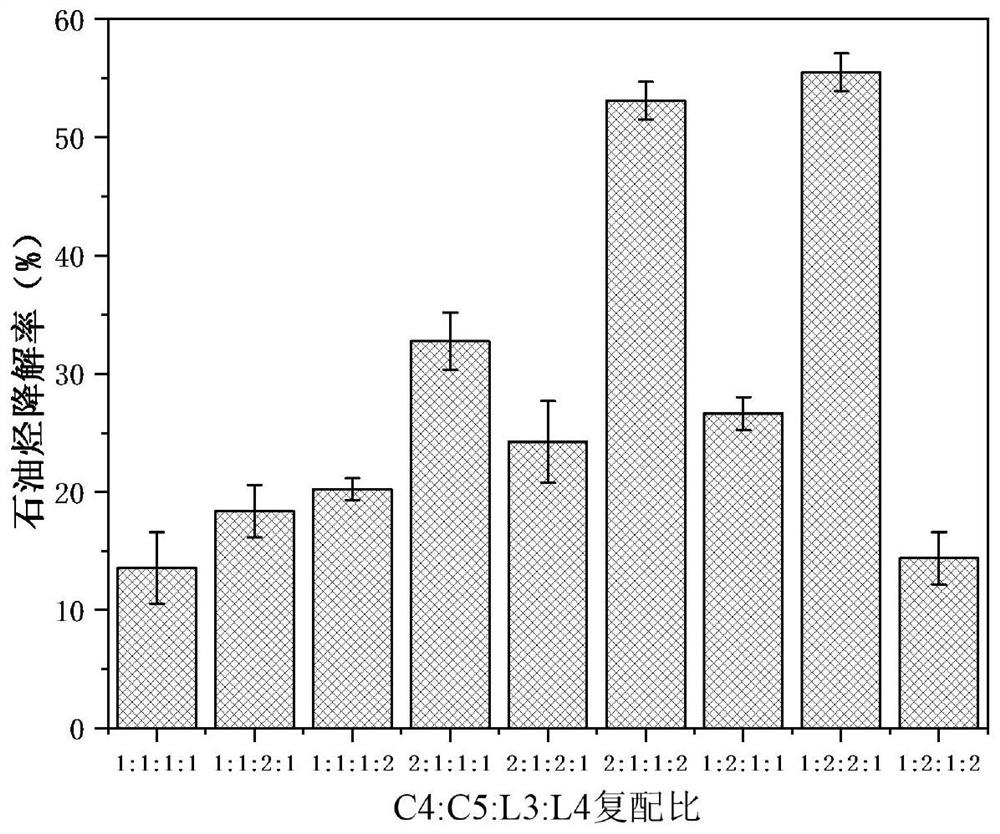
[0056] Two petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria Alcaligenes faecails Y5 C4 and Bacillus sp.7614 C5; two chlorophenol-degrading bacteria Bacillus marisflavi strain BCB4-1 L3, Bacillus sp. aquimaris T 172) L4, according to the inoculation amount of compound bacteria is 10%, the bacterial liquid is added in the inorganic salt liquid medium with chlorophenol concentration of 50mg / L, oil concentration of 2g / L, pH=7.5, and different V C4 :V C5 :V L3 :V ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3. Remediation of petroleum-chlorophenol compound polluted environment by compound bacterial agent
[0065] Experimental setup:
[0066] The petroleum inorganic salt medium was prepared, and after sterilization, an appropriate amount of chlorophenol compound was added for use.
[0067] The mixed fermentation broth of 10% (V:V) compound bacteria was added to the prepared medium containing petroleum-chlorophenol inorganic salt.
[0068] The inorganic salt medium without the inoculated strain was used as the blank control group.
[0069] All treatments were incubated at 35°C for 7 days at 160 r / min.
[0070] The organic phase of the cultured medium was extracted with n-hexane, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, the operation was repeated three times, and concentrated to 2 mL with a nitrogen blower, and relevant assays were carried out.
[0071] The infrared analysis of the remaining oil was determined by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com