Method for treating polyformaldehyde production wastewater
A technology for the production of wastewater and treatment methods, which is applied in natural water treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., and can solve the problems of large oxidants, hazardous waste of catalysts, and high treatment costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
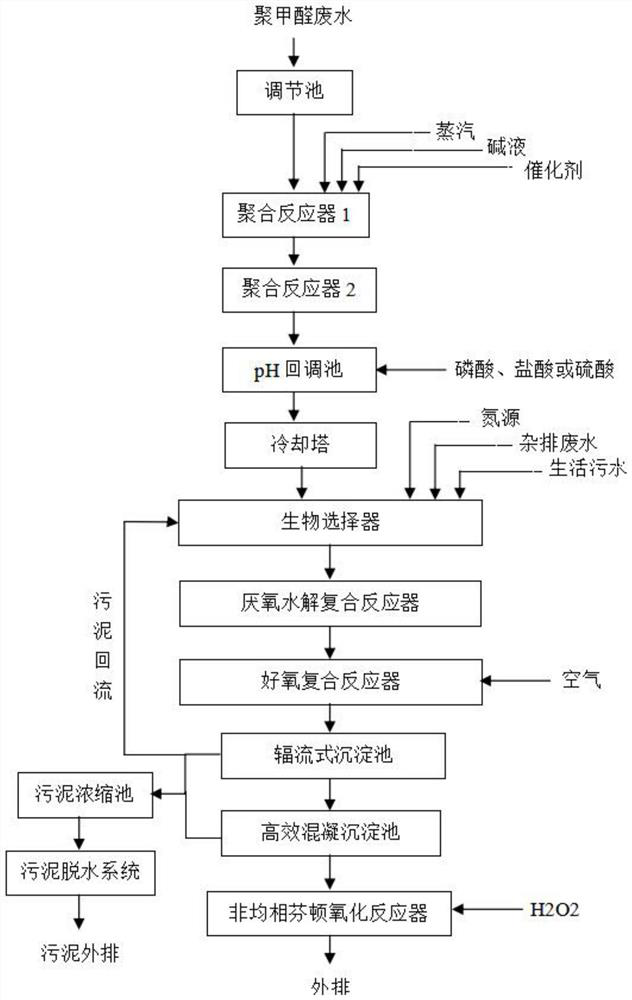
[0056] See the process flow figure 1 .
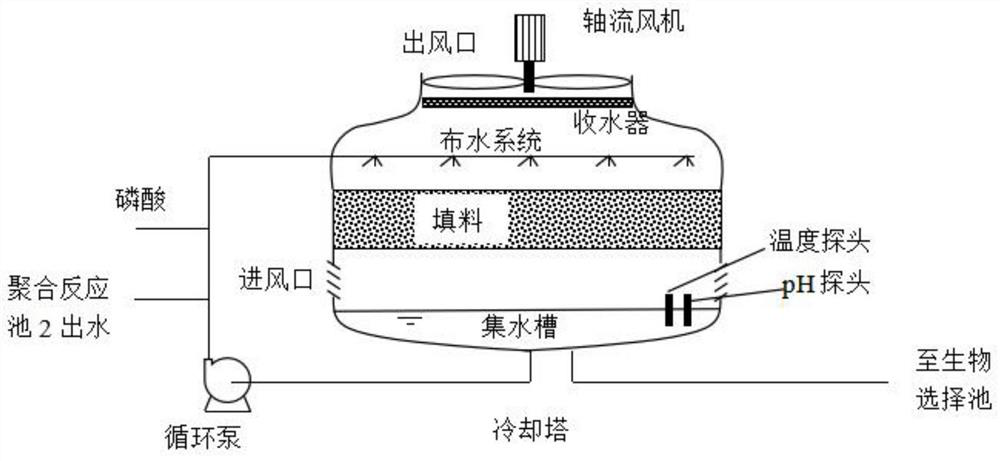
[0057] figure 2 Schematic diagram of the cooling system coupled with pH adjustment and temperature control.
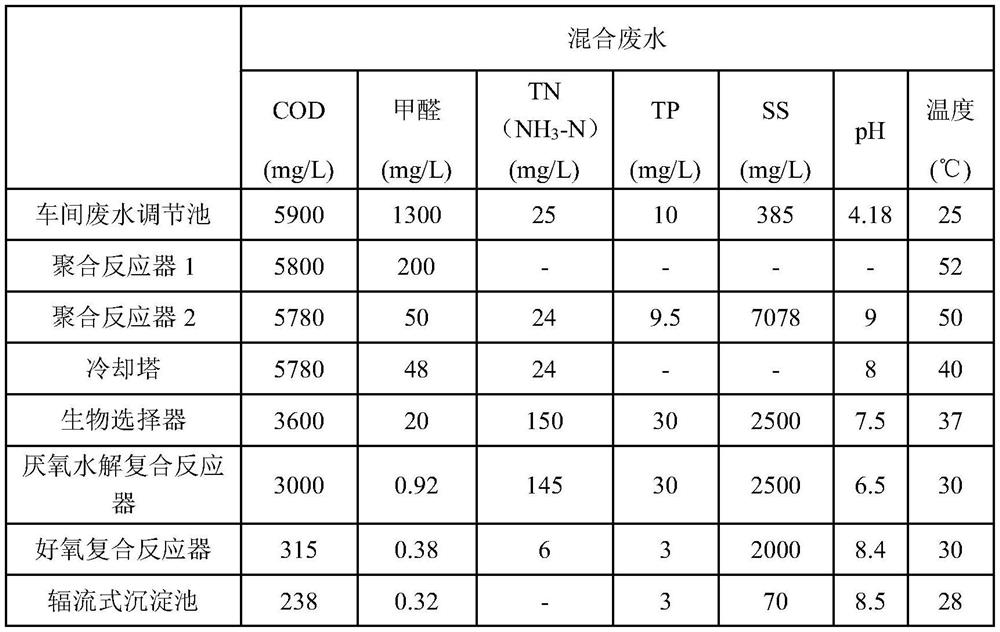
[0058] Take the polyoxymethylene wastewater from the workshop (including the sewage in the production plant and the sewage in the polymerization area, a total of 55m 3 / h), the concentration of each index is: COD concentration is 5900mg / L, TP concentration is 10mg / L, SS concentration is 385mg / L, TN (NH 3 -N) concentration is 25mg / L, formaldehyde concentration is 1300mg / L, pH is 4.18, temperature is 25°C.
[0059] 1. The polyoxymethylene wastewater enters the adjustment tank (in wastewater treatment, adjustment refers to homogenization. Since the concentration of the influent water generally changes with time, by staying in the adjustment tank for a period of time, the water quality in the adjustment tank can be homogenized, and the change is not so drastic. (through the adjustment tank, the amount of water is also regulated...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com